IT infrastructure assessment is a systematic approach to evaluating the current state of an organization’s technology environment, identifying areas for improvement, and planning for future needs. This article delves into the methodologies and significance of IT infrastructure assessment, drawing insights from Davids Achonu’s comprehensive study.
By exploring the practical applications and outcomes of these assessments, we aim to provide a robust framework for enterprises seeking to enhance their IT infrastructure’s performance and reliability.
Importance of IT Infrastructure Assessment
The assessment of IT infrastructure is not merely a technical exercise; it is a strategic imperative for large enterprises. The complex and dynamic nature of today’s business environment presents numerous challenges that necessitate a thorough evaluation of IT systems and resources. Enterprises must contend with fierce competition, the constant demand for innovative services, and the need to manage vast amounts of data efficiently. An effective IT infrastructure assessment addresses these challenges by providing a clear picture of the current state of IT assets, identifying potential risks, and uncovering opportunities for optimization.
One of the primary benefits of IT infrastructure assessment is its role in enhancing the return on investment (ROI) from IT resources. By systematically examining the performance and utilization of hardware, software, networks, and other critical components, organizations can pinpoint inefficiencies and implement targeted improvements. This process not only boosts operational efficiency but also supports business stability by ensuring that IT systems are robust, scalable, and aligned with organizational goals.
Furthermore, IT infrastructure assessments are essential for informed decision-making. They provide a data-driven foundation for strategic planning, helping businesses to prioritize investments, mitigate risks, and adapt to emerging technologies. The insights gained from these assessments enable IT leaders to make evidence-based decisions that drive innovation and support the enterprise’s long-term vision.
Methodologies and Approach
Conducting an effective IT infrastructure assessment requires a structured methodology that ensures a comprehensive evaluation of all IT components. The process involves several critical steps that together provide a clear and actionable understanding of the current IT environment.
Generic IT Infrastructure Assessment Process
The generic assessment process begins with identifying the IT components that need evaluation. This includes hardware such as servers and desktops, software applications, network infrastructure, and other critical systems.
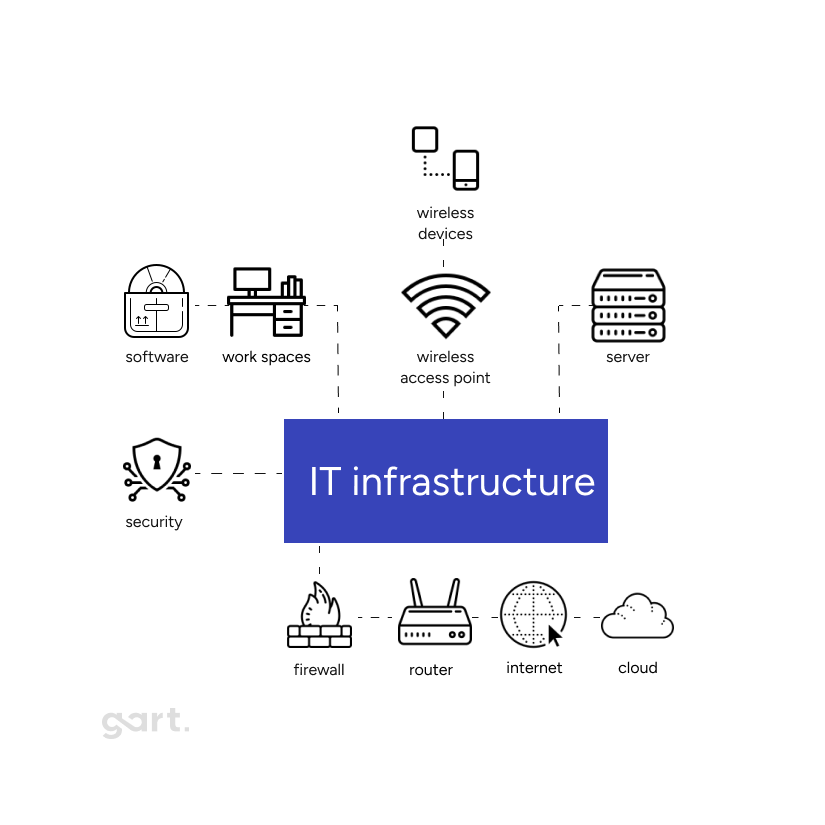
The steps involved in this process are:
- Identifying IT Components: Determine which components of the IT infrastructure will be assessed. This typically includes servers, desktops, networks, and applications.
- Data Collection: Gather comprehensive data on the identified components. This can involve automated tools and manual collection methods to ensure all relevant information is captured.
- Developing an Inventory Report: Compile the collected data into a detailed inventory report. This report serves as a foundational document for the assessment.
- Data Validation: Validate the accuracy of the collected data by consulting with IT stakeholders and verifying against existing records.
- Final Assessment Report: Generate a final report that summarizes the findings of the assessment, highlights key areas for improvement, and provides recommendations for optimization.
The practical application of these methodologies can vary depending on the specific needs and goals of the organization. Two common approaches are:
Centralized Assessment
This approach involves conducting the assessment from a central location, focusing on a holistic view of the entire IT infrastructure. It is beneficial for organizations with a unified IT management structure.
Benefits:
- Consistency: Ensures uniformity in data collection and assessment methodologies, leading to consistent results.
- Efficiency: Streamlines the assessment process by leveraging centralized resources and expertise.
- Simplified Management: Easier to manage and coordinate the assessment activities from a single point of control.
Drawbacks:
- Limited Local Insight: May miss out on specific local nuances or issues that could be critical for a thorough assessment.
- Scalability Issues: Can become less efficient for very large organizations with multiple locations, as central teams might struggle to cover all areas effectively.
Distributive Assessment
In contrast, a distributive approach involves assessing IT components at various locations or departments. This method is suitable for large enterprises with decentralized IT operations, allowing for a more granular evaluation.
Benefits:
- Local Expertise: Local teams have better knowledge of their specific environments, leading to more accurate and relevant assessments.
- Scalability: Easier to scale across large organizations with multiple locations, as each local team handles their own assessment.
- Flexibility: Can adapt to local conditions and requirements more effectively.
Drawbacks:
- Inconsistency: Potential for variations in assessment methodologies and results across different locations.
- Coordination Challenges: Requires effective coordination and communication between local teams to ensure overall coherence.
- Resource Intensive: May require more resources and personnel to manage assessments at multiple locations.
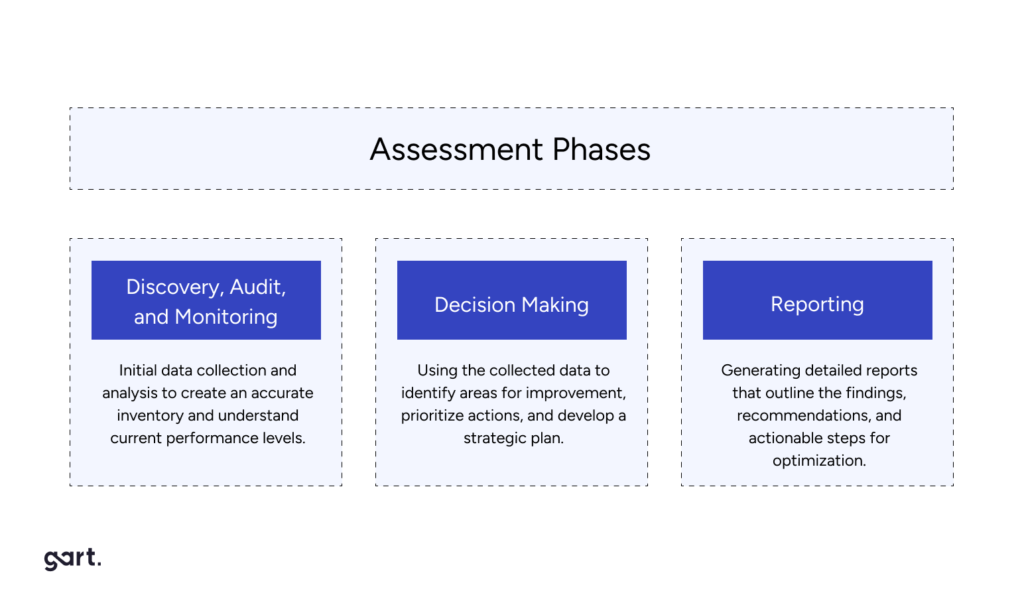
Assessment Phases
The assessment process typically follows three main phases:
Discovery, Audit, and Monitoring: Initial data collection and analysis to create an accurate inventory and understand current performance levels.
Decision Making: Using the collected data to identify areas for improvement, prioritize actions, and develop a strategic plan.
Reporting: Generating detailed reports that outline the findings, recommendations, and actionable steps for optimization.
Phase 1: Discovery, Audit, and Monitoring
Discovery: Identify all IT assets, including hardware, software, networks, and other critical components. This involves creating a comprehensive inventory of the IT environment.
Audit: Conduct a thorough audit to verify the existence and status of the identified assets. This step ensures the accuracy of the inventory.
Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring of the IT environment to gather performance data and identify any issues or anomalies. This helps in understanding the current state and performance of the infrastructure.
Phase 2: Decision Making
Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify patterns, inefficiencies, and areas that need improvement.
Prioritization: Prioritize the issues and opportunities based on their impact on the business and the feasibility of addressing them.
Strategic Planning: Develop a strategic plan for optimizing the IT infrastructure, including short-term and long-term goals, resource allocation, and timelines.
Phase 3: Reporting
Comprehensive Reports: Generate detailed reports that summarize the findings of the assessment. These reports should include inventories, performance metrics, identified issues, and recommendations.
Stakeholder Communication: Present the reports to key stakeholders, ensuring they understand the findings and the proposed actions. This step is crucial for securing buy-in and support for the optimization initiatives.
Actionable Recommendations: Provide clear, actionable recommendations for addressing the identified issues and optimizing the IT infrastructure. These recommendations should be practical and aligned with the organization’s strategic goals.
Assessment Tools and Techniques
A thorough IT infrastructure assessment relies heavily on the use of specialized tools that can automate data collection, provide detailed insights, and support informed decision-making.
Microsoft Assessment and Planning (MAP) Toolkit
The Microsoft Assessment and Planning (MAP) Toolkit is a powerful, agentless inventory, assessment, and reporting tool that helps organizations streamline their IT infrastructure assessment processes. The MAP Toolkit provides a comprehensive platform for collecting data on hardware and software assets, analyzing performance metrics, and generating detailed reports. Here are some key features and benefits of using the MAP Toolkit:
- Agentless Inventory: The MAP Toolkit does not require any software installation on the devices being assessed. It performs an agentless inventory, which means it can gather data without interfering with the normal operations of the IT environment.
- Comprehensive Data Collection: The toolkit collects data on a wide range of IT assets, including servers, desktops, network devices, and installed software. This data is crucial for creating an accurate inventory and understanding the current state of the IT infrastructure.
- Performance Metrics Analysis: In addition to inventory data, the MAP Toolkit also gathers performance metrics. This includes information on CPU, memory, disk usage, and network performance. Analyzing these metrics helps identify bottlenecks and areas where improvements are needed.
- Capacity Planning: The MAP Toolkit supports capacity planning by providing insights into current resource utilization and future growth needs. This helps organizations plan for hardware upgrades, software deployments, and other IT initiatives.
- Cloud Readiness: The tool includes features for assessing cloud readiness, helping organizations evaluate their existing infrastructure’s suitability for migration to cloud services. It provides recommendations for moving workloads to the cloud, enhancing flexibility and scalability.
- Detailed Reporting: The MAP Toolkit generates comprehensive reports that summarize the findings of the assessment. These reports include detailed inventories, performance analysis, and actionable recommendations, which are essential for informed decision-making.
Assessment Outcomes
The outcomes of an IT infrastructure assessment typically include:
Detailed Inventory: A comprehensive inventory of all IT assets, including hardware, software, and network components.
Performance Insights: Detailed performance metrics that highlight the current state and utilization of IT resources.
Identified Issues: A list of identified issues and inefficiencies within the IT infrastructure.
Optimization Opportunities: Opportunities for optimization and improvement, including potential cost savings, performance enhancements, and risk mitigations.
Strategic Recommendations: Strategic recommendations for addressing the identified issues and optimizing the IT infrastructure.
Migration Strategy
After the assessment, the next steps often involve developing and implementing a migration or optimization strategy. This strategy typically includes:
- Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines the steps, timelines, and resources required for moving IT components to a new or optimized environment.
- Implement the migration in phases to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition. This may involve migrating critical components first, followed by less critical ones.
- Thoroughly test the migrated components to ensure they function correctly and meet performance expectations in the new environment.
- Deploy the migrated components into the production environment, ensuring minimal downtime and disruption to business operations.
- Continuously monitor and optimize the migrated environment to ensure it meets the organization’s performance and efficiency goals.
- Document the new environment and provide training to IT staff to ensure they are equipped to manage and maintain the optimized infrastructure.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively assess, migrate, and optimize their IT infrastructure, ensuring it is robust, efficient, and aligned with their strategic goals.
Common IT Infrastructure Challenges
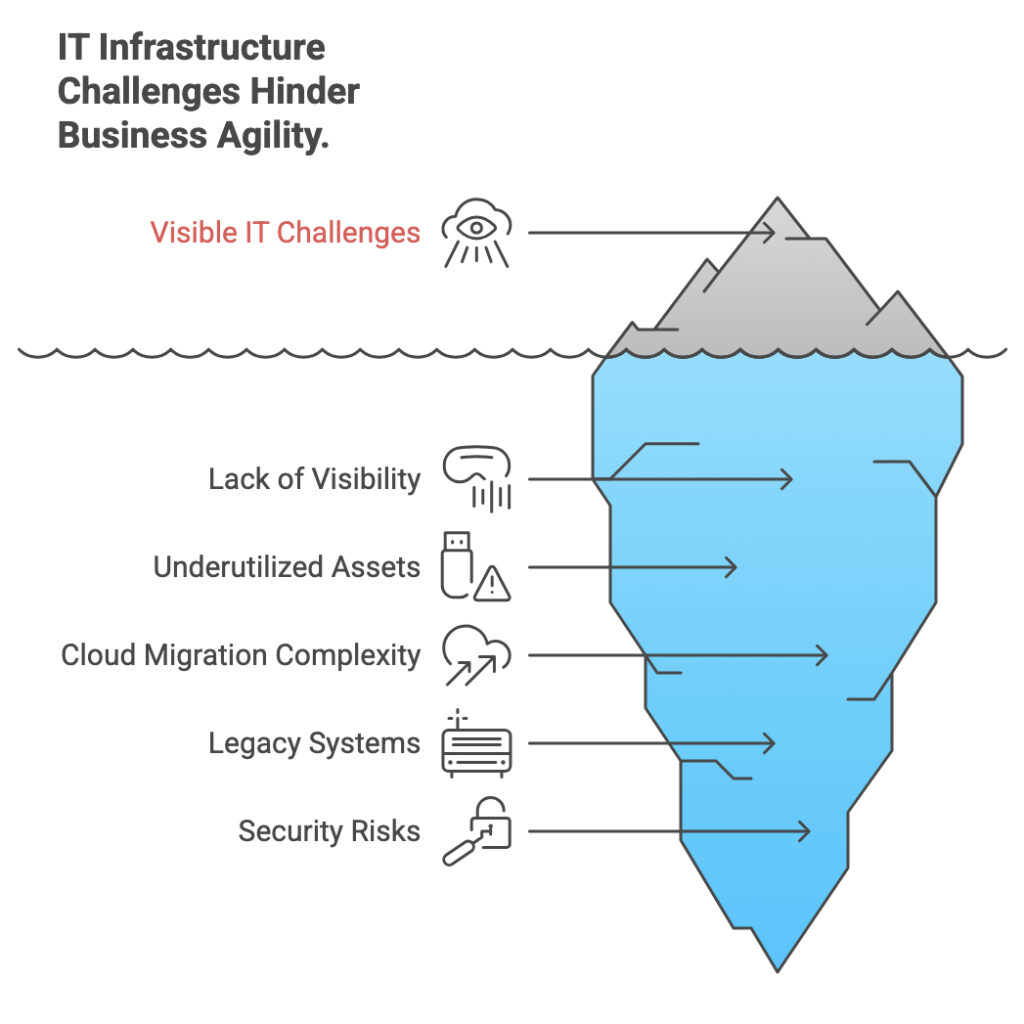
Enterprises often face a variety of persistent challenges when managing their IT infrastructure, which can impede business agility and innovation.
One of the most frequent issues is the lack of visibility into the complete IT environment, making it difficult to conduct a thorough IT infrastructure audit or IT system health check. Without a clear and accurate inventory, organizations struggle with infrastructure gap analysis, resulting in underutilized assets, redundant resources, and hidden vulnerabilities.
Another major challenge lies in cloud migration readiness. Many enterprises underestimate the complexity of migrating workloads to the cloud, overlooking dependencies, compliance requirements, and integration hurdles. This can lead to prolonged migration timelines and unexpected costs.
Additionally, legacy systems and fragmented infrastructure create operational silos that hinder enterprise infrastructure optimization efforts and prevent seamless interoperability between on-premises and cloud environments.
Security risks and compliance gaps further complicate the picture, especially for large organizations subject to strict regulations. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive enterprise infrastructure audit combined with continuous monitoring and proactive IT infrastructure assessment to identify bottlenecks and plan for enterprise IT optimization.
Implementing regular cloud infrastructure reviews helps enterprises stay aligned with evolving technology landscapes, optimize IT infrastructure costs, and enhance overall performance and resilience.
Difference Between IT Infrastructure Assessment and IT Infrastructure Audit
IT infrastructure assessment and IT infrastructure audit are both crucial processes for managing and optimizing an organization’s IT resources. However, they differ in their objectives, scope, methodologies, and outcomes. Understanding these differences can help organizations determine which process is more appropriate for their specific needs.
IT Infrastructure Assessment:
Purpose: To evaluate the overall performance, efficiency, and capacity of the IT infrastructure.
Scope: Broad, covering various aspects such as hardware, software, network, and processes.
Outcome: Recommendations for improvements, optimizations, and future growth planning.
Frequency: Periodic or as needed, based on business needs.
IT Infrastructure Audit:
Purpose: To ensure compliance with internal policies and external regulations, and to identify security vulnerabilities.
Scope: Specific, focusing on compliance, security, and adherence to standards.
Outcome: Audit report highlighting compliance status, security issues, and areas for improvement.
Frequency: Regular intervals, often mandated by regulatory requirements.

In summary
IT infrastructure assessment is a vital practice for large enterprises aiming to thrive in a competitive market. It ensures that IT resources are optimized, risks are managed, and the organization is well-prepared to meet future demands. By leveraging proven methodologies and tools, such as those outlined in David Achonu’s research, businesses can achieve a higher level of IT maturity and operational excellence.
Book your IT Infrastructure Audit now.
See how we can help to overcome your challenges








