What is Digital Transformation in Healthcare?
Imagine walking into a hospital where your medical records are instantly accessible on a secure digital platform, doctors consult you virtually from anywhere, and AI systems analyze your blood tests to predict diseases before symptoms appear. That’s digital transformation in healthcare.
In simple terms, it refers to leveraging technology to revolutionize how healthcare is delivered, managed, and experienced. It involves integrating digital solutions like electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, AI diagnostics, IoT-connected devices, and robotic surgeries to improve patient care, operational efficiency, and medical outcomes.
Why is it Gaining Momentum Globally?
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated healthcare digitization, but the momentum continues due to:
Rising Patient Expectations:Today’s patients demand convenience, accessibility, and personalized care, just like their experiences with Amazon or Netflix.
Technological Advancements:AI, IoT, and big data analytics have matured, making them viable for large-scale healthcare applications.
Cost Pressures and Resource Constraints:Hospitals face financial constraints and staff shortages. Digital transformation optimizes workflows, reducing costs while improving quality.
Regulatory Push:Governments and health bodies globally are mandating secure digital health records, telemedicine, and interoperability standards to improve national healthcare systems.
A Statista report projects the global digital healthcare market to reach $504.4 billion by 2025, underscoring how essential digital transformation has become for competitive and efficient healthcare delivery.
88% of healthcare technology leaders prioritize improving the patient experience in their investments (according to a Deloitte survey)
This shift underscores the necessity for healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and administrative staff, to stay abreast of ongoing digital advancements.
Key Drivers of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Emerging Technologies Shaping Healthcare
Technological innovations are the backbone of healthcare’s digital transformation. Here’s how the main technologies are driving change:
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by:
Automating administrative tasks like record-keeping and billing
Enhancing predictive diagnostics by analyzing medical images for early disease detection
Personalizing treatment plans based on patient history, genetics, and lifestyle
Enabling AI-powered chatbots to handle appointment scheduling, symptom checks, and medication reminders, reducing the burden on human staff
For example, AI diagnostic platforms like Google DeepMind Health detect eye diseases with the same accuracy as ophthalmologists, enabling earlier intervention and better outcomes.
IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT-connected health devices include:
Wearables: Smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor heart rate, oxygen saturation, and sleep cycles, alerting users to anomalies.
Remote Patient Monitoring Devices: Track vitals for chronic patients, reducing hospital visits while enabling proactive care.
Connected Hospital Equipment: Optimize operations by tracking equipment usage, availability, and maintenance schedules.
This improves real-time patient monitoring, operational efficiency, and resource utilization, making healthcare delivery smarter and more responsive.
Robotics
Robotics in healthcare enables:
Minimally invasive surgeries: Robotic surgical systems like da Vinci Surgical System enhance precision, reducing recovery time and hospital stays.
Remote surgeries: Surgeons operate robotic instruments from distant locations, expanding access to specialized care globally.
3D Printing
3D printing is transforming:
Prosthetics: Creating customized, affordable prosthetics quickly for amputees.
Implants and Organs: Producing tailor-made implants and researching bioprinted organs for transplantation.
These emerging technologies are not just futuristic concepts – they are real-world solutions enhancing healthcare daily.
Changing Patient Expectations and Demographics
Today’s patients are digital natives, especially younger demographics who expect:
Online appointment booking
Access to digital medical records
Telehealth consultations
Personalized health recommendations
With over 5.3 billion internet users globally, healthcare providers must adapt to digital-first expectations to remain competitive and patient-centric, as the demand for digital healthcare services is rising.
Updated Regulations Driving Adoption
Governments worldwide are introducing regulations to support digital transformation:
HIPAA (US): Mandates data privacy and security for protected health information (PHI).
GDPR (EU): Enforces strict data protection rules for personal data, including health records.
ISO/IEC 27799: Provides guidelines for information security management in healthcare.
Compliance with these standards is not optional. Healthcare providers must adopt digital solutions with built-in security and privacy measures to avoid legal repercussions and build patient trust.
Gart guides you through every step of the compliance process, providing the expertise, tools, and support you need. Contact Us.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
1. Reduced Costs - automating administrative tasks and other processes allows healthcare providers to save time and money while enhancing patient care. Through digital transformation, workflows are streamlined, and operational efficiency is increased, which helps reduce overhead costs.
2. Optimized Workflow - digital transformation has enabled healthcare providers to optimize their workflows. Automating tasks like patient information management and appointment scheduling allows medical staff to focus more on delivering effective patient care. Additionally, digital tools such as AI-powered chatbots can handle simple patient interactions, reducing the burden on physicians.
3. Enhanced Patient Interaction - digital transformation has empowered healthcare providers to interact with patients more effectively. Innovative technologies enable health professionals to easily access patient records, aiding in better diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, digital solutions like telemedicine allow doctors to offer timely medical advice even when they are not physically present at the hospital or clinic.
4. Improved Administration - digitizing processes makes managing administrative tasks more efficient for healthcare organizations. Automation of activities like scheduling appointments, filing insurance claims, and maintaining accurate financial records reduces manual errors while improving accuracy and speed.
Challenges to Healthcare Digital Transformation
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Healthcare deals with highly sensitive patient data. Digital systems, if not secured, can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, risking:
Data breaches exposing personal health information
Compliance violations leading to hefty fines
Loss of patient trust and reputational damage
Implementing robust cybersecurity frameworks, encryption, and continuous monitoring is non-negotiable for digital health systems.
Resistance to Change within Organizations
Healthcare has traditionally been conservative in adopting new technologies. Reasons for resistance include:
Fear of disrupting established workflows
Lack of digital literacy among staff
Concerns about technology reliability during critical care situations
Change management, leadership support, and comprehensive staff training are essential to overcome this barrier.
Interoperability and Legacy System Integration
Most healthcare organizations run on legacy systems that do not integrate easily with modern digital applications. Challenges include:
Data silos are hindering unified patient views
Incompatibility with new software or cloud platforms
High costs and risks are associated with migrating from outdated systems
Adopting interoperability standards like HL7 FHIR and working with experienced technology partners can mitigate these challenges.
Skills Gaps and Staff Shortages
Digital transformation requires staff to be digitally proficient. However, many healthcare professionals:
Lack of training in new digital tools and platforms
Feel overwhelmed by technological complexity, which affects adoption rates
Continuous upskilling programs and user-friendly solutions can bridge the skills gap and enhance digital confidence among healthcare staff.
Successful Cases of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
1. Infrastructure Optimization and Data Management in Healthcare
Challenge
A health tech company came with outdated infrastructure that hindered efficient data management and slowed down critical operations. The existing system was not scalable and faced frequent downtimes, affecting the overall patient care experience.
Solution
Gart Solutions implemented a comprehensive infrastructure optimization strategy, including:
Modernizing legacy systems to enhance speed and scalability
Integrating cloud solutions for seamless, secure data management
Ensuring HIPAA compliance for patient data security
Enabling dynamic scaling to meet demand spikes efficiently
Impact
Faster data access, reduced downtimes, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced patient experiences.
Learn details from the Case Study.
2. CI/CD Pipelines and Infrastructure for E-Health Platform
Challenge
An e-health platform aimed to accelerate their development process and improve the reliability of their applications. However, they faced significant challenges with manual deployments, which were time-consuming and error-prone, leading to inconsistent performance and delayed updates.
Solution
Gart Solutions designed and implemented automated CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines tailored to the platform’s unique architecture.
Key implementation steps included:
Automated Build and Testing Pipelines:Code commits automatically triggered builds, testing suites, and static code analysis to catch bugs early.
Infrastructure Optimization:Upgraded and containerized infrastructure to support CI/CD operations efficiently with Kubernetes orchestration for scalability.
Deployment Automation:Introduced automated deployment scripts for seamless rollout of features across production and staging environments without downtime.
Monitoring and Rollback Strategies:Integrated real-time monitoring tools with automated rollback protocols to ensure rapid issue remediation in case of deployment failures.
Impact
Reduced deployment times from days to hours
Significantly minimized human errors, enhancing application stability
Improved development velocity, allowing frequent feature releases
Increased user satisfaction due to faster bug fixes and feature updates
This case demonstrates that CI/CD pipelines aren’t just DevOps best practices – they are strategic enablers of digital agility in healthcare platforms, ensuring compliance, security, and innovation at scale.
Struggling with digital transformation for your healthcare project? Get expert guidance and IT Consultancy for your project free of charge. “Quick wins” – guaranteed. Contact Us.
How Digital Transformation Enhances Patient Experience
Telehealth and Remote Consultations
Imagine consulting your doctor while sipping coffee at home, with prescriptions emailed within minutes. That’s the new healthcare reality.
Telehealth is among the most impactful transformations in healthcare, enabling:
Remote Consultations: Patients consult doctors without visiting clinics, saving time, reducing exposure to infections, and increasing accessibility for remote populations.
Mental Health Services: Telepsychiatry platforms provide discreet, accessible therapy sessions, crucial in an era of rising mental health challenges.
Chronic Disease Management: Regular remote check-ins for diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic conditions enable proactive care, preventing complications and hospital admissions.
During the pandemic, telehealth usage surged by over 154% compared to pre-pandemic levels (CDC data) and continues to grow as patients demand convenience and digital-first care experiences.
Personalized Medicine and AI Diagnostics
Digital transformation enables hyper-personalized treatments tailored to individual patient profiles by leveraging:
AI Diagnostics:AI algorithms analyze radiology images, blood tests, and genetic data to detect diseases earlier than traditional methods. For example, IBM Watson Health analyzes patient records to recommend tailored treatment options for oncologists.
Genomic Medicine:Advances in data processing allow healthcare providers to customize medications and treatments based on patient genetics, enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Predictive Analytics:Big data analytics predict patient risks, enabling early interventions for conditions like sepsis, cardiac events, or diabetic complications.
Patients no longer experience generic treatment plans but benefit from precision medicine designed for their unique biological and lifestyle factors, resulting in improved outcomes and satisfaction.
Conclusion
Healthcare organizations understand that digital transformation is crucial for enhancing healthcare services and strengthening patient relationships. Beyond technology investments, this transformation necessitates a shift in organizational culture and employee engagement, requiring enterprise-wide involvement.
Leading health organizations are adopting six key strategies to advance digitally:
Establish digital leadership and governance aligned with business strategies.
Cultivate a digital culture supported by leadership at all organizational levels.
Develop next-generation talent with a focus on workforce quality and quantity.
Integrate cybersecurity at all stages for robust risk management.
Emphasize flexibility and scalability to adapt to evolving technologies.
Implement measurable, accountable KPIs to track the success of digital initiatives.
Successfully navigating digital transformation in healthcare requires expertise and a business-first approach of IT Consulting.
Gart Solutions can guide healthcare providers through the process of Digital Transformation, accelerating the adoption of digital healthcare technologies and improvement of patient outcomes.
Contact Gart today to learn more about how we can help you solve the challenges of digital transformation in healthcare.

As climate change, resource depletion, and environmental issues loom large, businesses are turning to technology as a powerful ally in achieving their sustainability goals. This isn't just about saving the planet (although that's pretty important), it's also about creating a more efficient and resilient future for all.
Data is the new oil, and when it comes to sustainability, it's a game-changer. Technology empowers businesses to collect and analyze vast amounts of data, allowing them to make informed decisions about their environmental impact. By automating processes, streamlining operations, and enabling data-driven decision-making, businesses can minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and optimize resource utilization.
Digital technologies, such as cloud computing, remote collaboration tools, and virtual platforms, have the potential to reduce the need for physical infrastructure and travel, thereby minimizing the associated environmental impacts.
One of the primary challenges is striking a balance between sustainability goals and profitability. Many businesses struggle to reconcile the perceived trade-off between environmental considerations and short-term financial gains. Implementing sustainable practices often requires upfront investments in new technologies, infrastructure, or processes, which can be costly and may not yield immediate returns. Convincing stakeholders and shareholders of the long-term benefits and value of sustainability can be a complex task.
The Environmental Impact of IT Infrastructure
One of the primary concerns regarding IT infrastructure is energy consumption. Data centers, which house servers, storage systems, and networking equipment, are energy-intensive facilities. They require substantial amounts of electricity to power and cool the hardware, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and straining energy grids. According to estimates, data centers account for approximately 1% of global electricity consumption, and this figure is expected to rise as data volumes and computing demands continue to grow.
Furthermore, the manufacturing process of IT equipment, such as servers, computers, and other hardware components, involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, which can have detrimental effects on the environment. The mining of rare earth metals and other minerals used in electronic components can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and the depletion of natural resources.
E-waste, or electronic waste, is another pressing issue related to IT infrastructure. As technological devices become obsolete or reach the end of their lifecycle, they often end up in landfills or informal recycling facilities, posing risks to human health and the environment. E-waste can contain hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into soil and water sources, causing pollution and potential harm to ecosystems.
By addressing the environmental impact of IT infrastructure, businesses can not only reduce their carbon footprint and resource consumption but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Striking a balance between technological innovation and environmental stewardship is crucial for achieving long-term sustainability goals.
DevOps and Sustainability
DevOps practices play a pivotal role in optimizing resources and reducing waste, making them a powerful ally in the pursuit of sustainability. By seamlessly integrating development and operations processes, DevOps enables organizations to achieve greater efficiency, agility, and environmental responsibility.
At the core of DevOps is the principle of automation and continuous improvement. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes, DevOps eliminates manual efforts, reduces human errors, and minimizes resource wastage. This efficiency translates into lower energy consumption, decreased hardware utilization, and a reduced carbon footprint.
CI/CD for Improved Eco-Efficiency
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) are essential DevOps practices that contribute to sustainability. CI/CD enables organizations to rapidly and frequently deliver software updates and improvements, ensuring that applications run optimally and efficiently. This approach minimizes the need for resource-intensive deployments and reduces the overall environmental impact of software development and operations.
Moreover, CI/CD facilitates the early detection and resolution of issues, preventing potential inefficiencies and resource wastage. By integrating automated testing and quality assurance processes, organizations can identify and address performance bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and other issues that could lead to increased energy consumption or resource utilization.
Monitoring and Analytics for Identifying and Eliminating Inefficiencies
DevOps emphasizes the importance of monitoring and analytics as a means to gain insights into system performance, resource utilization, and potential areas for improvement. By leveraging advanced monitoring tools and techniques, organizations can gather real-time data on energy consumption, hardware utilization, and application performance.
This data can then be analyzed to identify inefficiencies, such as underutilized resources, redundant processes, or areas where optimization is required. Armed with these insights, organizations can take proactive measures to streamline operations, adjust resource allocation, and implement energy-saving strategies, ultimately reducing their environmental footprint.
For a deeper dive into how monitoring and analytics can drive efficiency and sustainability, explore this case study of a software development company that optimized its workload orchestration using continuous monitoring.
Our case study: Implementation of Nomad Cluster for Massively Parallel Computing
Cloud Computing and Sustainability
Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative technology that not only enhances efficiency and agility but also holds significant potential for promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact. By leveraging the power of cloud services, organizations can achieve remarkable energy and resource savings, while simultaneously minimizing their carbon footprint.
Energy and Resource Savings through Cloud Services
One of the primary advantages of cloud computing in terms of sustainability is the efficient utilization of shared resources. Cloud service providers operate large-scale data centers that are designed for optimal resource allocation and energy efficiency. By consolidating workloads and leveraging economies of scale, cloud providers can maximize resource utilization, reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste.
Additionally, cloud providers invest heavily in implementing cutting-edge technologies and best practices for energy efficiency, such as advanced cooling systems, renewable energy sources, and efficient hardware. These efforts result in significant energy savings, translating into a lower carbon footprint for organizations that leverage cloud services.
Flexible Cloud Models for Cost Optimization for Sustainable Operations
Cloud computing offers flexible deployment models, including public, private, and hybrid clouds, allowing organizations to tailor their cloud strategies to meet their specific needs and optimize costs. By embracing the pay-as-you-go model of public clouds or implementing private clouds for sensitive workloads, businesses can dynamically scale their resource consumption, avoiding over-provisioning and minimizing unnecessary energy expenditure.
Cloud providers offer a diverse range of compute and storage resources with varying payment options and tiers, catering to different use cases and requirements. For instance, Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances with multiple pricing models, including Dedicated, On-Demand, Spot, and Reserved instances. Choosing the most suitable instance type for a specific workload can lead to significant cost savings.
Dedicated instances, while the most expensive option, are ideal for handling sensitive workloads where security and compliance are of paramount importance. These instances run on hardware dedicated solely to a single customer, ensuring heightened isolation and control.
On-demand instances, on the other hand, are billed on an hourly basis and are well-suited for applications with short-term, irregular workloads that cannot be interrupted. They are particularly useful during testing, development, and prototyping phases, offering flexibility and scalability on-demand.
For long-running workloads, Reserved instances offer substantial discounts, up to 72% compared to on-demand pricing. By investing in Reserved instances, businesses can secure capacity reservations and gain confidence in their ability to launch the required number of instances when needed.
Spot instances present a cost-effective alternative for workloads that do not require high availability. These instances leverage spare computing capacity, enabling businesses to benefit from discounts of up to 90% compared to on-demand pricing.
Our case study: Cutting Costs by 81%: Azure Spot VMs Drive Cost Efficiency for Jewelry AI Vision
Additionally, DevOps teams employ various cloud cost optimization practices to further reduce operational expenses and environmental impact. These include:
- Identifying and deleting underutilized instances
- Moving infrequently accessed storage to more cost-effective tiers
- Exploring alternative regions or availability zones with lower pricing
- Leveraging available discounts and pricing models
- Implementing spend monitoring and alert systems to track and control costs proactively
By adopting a strategic approach to resource utilization and cost optimization, businesses can not only achieve sustainable operations but also unlock significant cost savings. This proactive mindset aligns with the principles of environmental stewardship, enabling organizations to thrive while minimizing their ecological footprint.
Read more: Sustainable Solutions with AWS
Reduced Physical Infrastructure and Associated Emissions
Moving to the cloud isn't just about convenience and scalability – it's a game-changer for the environment. Here's why:
Bye-bye Bulky Servers
Cloud computing lets you ditch the on-site server farm. No more rows of whirring machines taking up space and guzzling energy. Cloud providers handle that, often in facilities optimized for efficiency. This translates to less energy used, fewer emissions produced, and a lighter physical footprint for your business.
Commuting? Not Today
Cloud-based tools enable remote work, which means fewer cars on the road spewing out emissions. Not only does this benefit the environment, but it also promotes a more flexible and potentially happier workforce.
Cloud computing offers a win-win for businesses and the planet. By sharing resources, utilizing energy-saving data centers, and adopting flexible deployment models, cloud computing empowers organizations to significantly reduce their environmental impact without sacrificing efficiency or agility. Think of it as a powerful tool for building a more sustainable future, one virtual server at a time.
Effective Infrastructure Management and Sustainability
Effective infrastructure management plays a crucial role in achieving sustainability goals within an organization. By implementing strategies that optimize resource utilization, reduce energy consumption, and promote environmentally-friendly practices, businesses can significantly diminish their environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency.
Virtualization and Consolidation Strategies for Reducing Hardware Needs
Virtualization technology has revolutionized the way organizations manage their IT infrastructure.
By ditching the extra servers, you're using less energy to power and cool them. Think of it like turning off all the lights in empty rooms – virtualization ensures you're only using the resources you truly need. This translates to significant energy savings and a smaller carbon footprint.
Fewer servers mean less hardware to manufacture and eventually dispose of. This reduces the environmental impact associated with both the production process and electronic waste (e-waste). Virtualization helps you be a more responsible citizen of the digital world.
Our case study: IoT Device Management Using Kubernetes
Optimizing with Third-Party Services
In the pursuit of sustainability and resource efficiency, businesses must explore innovative strategies that can streamline operations while reducing their environmental footprint. One such approach involves leveraging third-party services to optimize costs and minimize operational overhead. Cloud computing providers, such as Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud, offer a vast array of services that can significantly enhance the development process and reduce resource consumption.
A prime example is Amazon's Relational Database Service (RDS), a fully managed database solution that boasts advanced features like multi-regional setup, automated backups, monitoring, scalability, resilience, and reliability. Building and maintaining such a service in-house would not only be resource-intensive but also costly, both in terms of financial investment and environmental impact.
However, striking the right balance between leveraging third-party services and maintaining control over critical components is crucial. When crafting an infrastructure plan, DevOps teams meticulously analyze project requirements and assess the availability of relevant third-party services. Based on this analysis, recommendations are provided on when it's more efficient to utilize a managed service, and when it's more cost-effective and suitable to build and manage the service internally.
For ongoing projects, DevOps teams conduct comprehensive audits of existing infrastructure resources and services. If opportunities for cost optimization are identified, they propose adjustments or suggest integrating new services, taking into account the associated integration costs with the current setup. This proactive approach ensures that businesses continuously explore avenues for reducing their environmental footprint while maintaining operational efficiency.
One notable success story involves a client whose services were running on EC2 instances via the Elastic Container Service (ECS). After analyzing their usage patterns, peak periods, and management overhead, the DevOps team recommended transitioning to AWS Fargate, a serverless solution that eliminates the need for managing underlying server infrastructure. Fargate not only offered a more streamlined setup process but also facilitated significant cost savings for the client.
By judiciously adopting third-party services, businesses can reduce operational overhead, optimize resource utilization, and ultimately minimize their environmental impact. This approach aligns with the principles of sustainability, enabling organizations to achieve their goals while contributing to a greener future.
Our case study: Deployment of a Node.js and React App to AWS with ECS
Green Code and DevOps Go Hand-in-Hand
At the heart of this sustainable approach lies green code, the practice of developing and deploying software with a focus on minimizing its environmental impact. Green code prioritizes efficient algorithms, optimized data structures, and resource-conscious coding practices.
At its core, Green Code is about designing and implementing software solutions that consume fewer computational resources, such as CPU cycles, memory, and energy. By optimizing code for efficiency, developers can reduce the energy consumption and carbon footprint associated with running applications on servers, desktops, and mobile devices.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
DevOps promotes continuous monitoring of applications, providing valuable insights into resource utilization. These insights can be used to identify areas for code optimization, ensuring applications run efficiently and consume less energy.
Infrastructure Automation:
Automating infrastructure provisioning and management through tools like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) helps eliminate unnecessary resources and idle servers. Think of it like switching off the lights in an empty room – automation ensures resources are only used when needed.
Containerization
Containerization technologies like Docker package applications with all their dependencies, allowing them to run efficiently on any system. This reduces the need for multiple servers and lowers overall energy consumption.
Cloud-Native Development
By leveraging cloud platforms, developers can benefit from pre-built, scalable infrastructure with high energy efficiency. Cloud providers are constantly optimizing their data centers for sustainability, so you don't have to shoulder the burden alone.
DevOps practices not only streamline development and deployment processes, but also create a culture of resource awareness and optimization. This, combined with green code principles, paves the way for building applications that are not just powerful, but also environmentally responsible.
How Businesses Are Using DevOps, Cloud, and Green Code to Thrive
Case Study 1: Transforming a Local Landfill Solution into a Global Platform
ReSource International, an Icelandic environmental solutions company, developed elandfill.io, a digital platform for monitoring and managing landfill operations. However, scaling the platform globally posed challenges in managing various components, including geospatial data processing, real-time data analysis, and module integration.
Gart Solutions implemented the RMF, a suite of tools and approaches designed to facilitate the deployment of powerful digital solutions for landfill management globally.
Case Study 3: The #1 Music Promotion Services Cuts Costs with Sustainable AWS Solutions
The #1 Music Promotion Services, a company helping independent artists, faced rising AWS infrastructure costs due to rapid growth. A multi-faceted approach focused on optimization and cost-saving strategies was implemented. This included:
Amazon SNS Optimization: A usage audit identified redundant notifications and opportunities for batching messages, leading to lower usage charges.
EC2 and RDS Cost Management: Right-sizing instances, utilizing reserved instances, and implementing auto-scaling ensured efficient resource utilization.
Storage Optimization: Lifecycle policies and data cleanup practices reduced storage costs.
Traffic and Data Transfer Management: Optimized data transfer routes and cost monitoring with alerts helped manage unexpected spikes.
Results: Monthly AWS costs were slashed by 54%, with significant savings across services like Amazon SNS and EC2/RDS. They also established a framework for sustainable cost management, ensuring long-term efficiency.
Partner with Gart for IT Cost Optimization and Sustainable Business
As businesses strive for sustainability, partnering with the right IT provider is crucial for optimizing costs and minimizing environmental impact. Gart emerges as a trusted partner, offering expertise in cloud computing, DevOps, and sustainable IT solutions.
Gart's cloud proficiency spans on-premise-to-cloud migration, cloud-to-cloud migration, and multi-cloud/hybrid cloud management. Our DevOps services include cloud adoption, CI/CD streamlining, security management, and firewall-as-a-service, enabling process automation and operational efficiencies.
Recognized by IAOP, GSA, Inc. 5000, and Clutch.co, Gart adheres to PCI DSS, ISO 9001, ISO 27001, and GDPR standards, ensuring quality, security, and data protection.
By partnering with Gart, businesses can optimize IT costs, reduce their carbon footprint, and foster a sustainable future. Leverage Gart's expertise to align your IT strategies with environmental goals and unlock the benefits of cost optimization and sustainability.

[lwptoc]
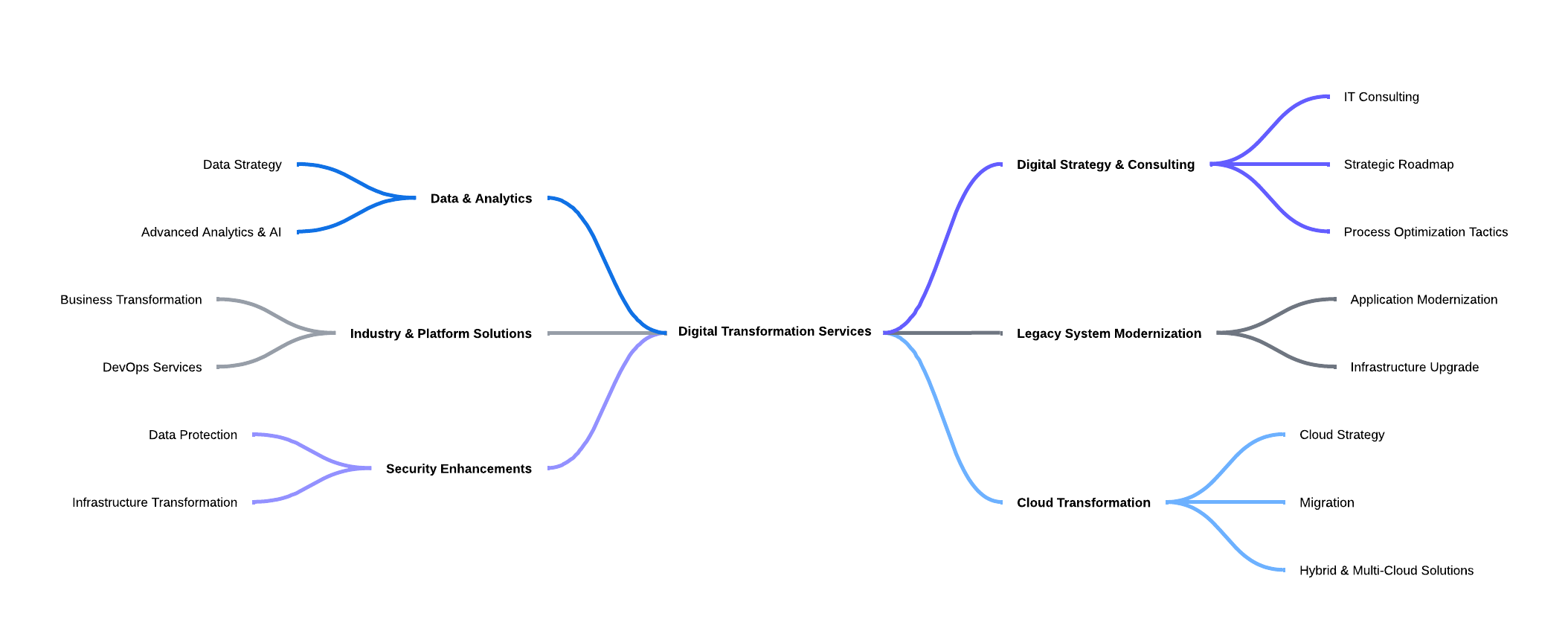
With the development of digital technologies, a well-built IT infrastructure of a company plays an increasingly important role in achieving business goals and objectives. It is indispensable for managing, processing, storing and transferring information within the company. In this article, we will look at the types and models of IT infrastructure, the tasks it performs, its components and how to create it.
What is IT Infrastructure?
IT infrastructure is a combination of information resources and technologies, software and hardware, network components, data storage devices and services of an organization that ensure the operation and management of the company's IT environment. The main goal of IT infrastructure is to ensure the uninterrupted and secure operation of information services, processing, storage and transmission of information. Due to the development of technologies, it is used by companies from different industries: from development to agriculture. We can say that the IT infrastructure of a company is the basis for managing business processes, which directly affects the efficiency and competitiveness of the organization.
What Tasks Does IT Infrastructure Solve?
One of the main tasks that the IT infrastructure of an organization helps to solve is creating conditions for achieving goals and implementing the company's business strategy. This happens, among other things, by reducing costs for IT projects, simplifying scaling, and increasing the company's productivity.
Organizing IT infrastructure within a company helps to increase productivity and reduce costs on IT projects.
Also, the presence of a well-built IT infrastructure in the company implies:
Convenient and secure storage and management of data;
Support for network interaction and organization of collaboration between devices and users;
Optimal distribution of computing resources;
Protection of data from unauthorized access and leaks;
Providing applications and services for managing business processes.
Types and Models of IT Infrastructure
Before starting to organize IT infrastructure within a company, it is necessary to choose a model for its operation. There are three types: traditional, cloud, and hybrid.
Traditional model of IT infrastructure implies an on-premise approach, in which the company purchases its own hardware, places it on its own site, and maintains it by its own employees. It is also possible to place equipment with a provider or rent hardware with monthly payment.
Cloud model provides for the placement of IT infrastructure components with a cloud provider. In this case, the provider maintains uninterrupted operation and provides technical support for the infrastructure, and the company manages it remotely through the control panel interface.
Hybrid model combines traditional and cloud IT infrastructure. In this case, part of the infrastructure is located in the company or with a provider, and part is in cloud services. This allows you to evenly distribute the available capacity.
How to Create an IT Infrastructure from Scratch
When creating an infrastructure, it is important to consider the unique needs of the company, its goals, and budget.
First of all, it is necessary to find out the company's technological needs. Different organizations may have different requirements for IT infrastructure. For example, for some it is important to be able to manage data, for others - to optimally distribute resources.
The next step is to develop a comprehensive IT architecture, which includes hardware and software, as well as network infrastructure. After that, the company can purchase equipment and software, rent them from a provider, or choose a cloud service.
Deployment of IT infrastructure, installation and configuration of hardware and software components can be performed by company employees or provider specialists. The final stage is testing and evaluating the IT infrastructure to ensure optimal performance, security, and functionality.
After the infrastructure creation process is completed, the company must decide who will support and maintain the IT infrastructure. Many companies prefer to outsource this task to third-party specialists in order to focus on their core business.
Gart Solutions company provides Managed IT service, which includes comprehensive infrastructure maintenance:
IT infrastructure management;
Monitoring;
Timely elimination of incidents;
IT infrastructure modernization;
IT Infrastructure support;
Cloud Infrastructure management;
IT Infrastructure consulting
Backup configuration, etc.
This approach allows to ensure continuous operation of the company's IT infrastructure.
Components of IT Infrastructure
What are the main components of the IT infrastructure of an enterprise or company? As a rule, it includes hardware components that provide support for the physical infrastructure, software components that are responsible for functionality, and a network.
Hardware components include servers, data centers, PCs, and other equipment;
Software components are operating systems, CMS, CRM, databases, security software;
The network consists of routers, switches, cables, and software for network operation.
IT infrastructure software is needed to operate and manage hardware components.
IT infrastructure software includes the software and applications that a business uses to function, provide services, and manage internal processes. It also includes additional platforms and services that help solve specialized tasks. For example, this can include CMS and CRM systems, web servers, and email clients.
Conclusion
IT infrastructure is the foundation on which the success of a company is built. The security and flexibility of an enterprise or company depends on what is included in its IT infrastructure. Therefore, when creating it, it is important to consider the current needs, goals, budget of the company and the development plan for the next few years. This determines which infrastructure model to choose and which components should be included.
Since IT infrastructure affects the competitiveness and efficiency of a company, it is better to entrust its creation and support to specialists. Mistakes at the design and launch stage can lead to security, performance and interoperability issues in the future. Gart Solutions company provides a service for the maintenance and updating of IT infrastructure, which can significantly simplify the tasks of companies without a staff of IT specialists.