With the increasing prominence of cloud computing, more and more organizations are recognizing the advantages of utilizing multiple cloud providers through multi-cloud solutions. A survey conducted by Gartner revealed that 81% of public cloud users reported utilizing two or more cloud providers.
This approach allows businesses to leverage the unique strengths and capabilities offered by different cloud providers, enabling them to optimize performance, enhance resilience, and effectively manage costs. However, managing multiple clouds simultaneously presents its own set of challenges and complexities.
If you find these concepts overwhelming or complex, there’s no need to worry. In this blog post, we delve into the world of multi-cloud management, exploring the strategies and best practices that organizations can employ to navigate this intricate landscape successfully.
Multicloud vs. Hybrid Cloud
| Multicloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Utilizes multiple cloud providers simultaneously | Combines public and private clouds |
| Offers flexibility in choosing and switching providers | Utilizes benefits of both environments |
| Workloads can be distributed across different cloud platforms | Workloads can be distributed between on-premises and cloud |
| Avoids vendor lock-in | Allows data and workload sharing between environments |
| Scalability based on workload demands | Scalability by utilizing on-premises and cloud resources |
| Cost optimization through selecting cost-effective services | Cost optimization by choosing the most appropriate environment |
| Management complexity due to multiple providers | Complexity in managing integration and data consistency |
| Requires robust security measures across multiple environments | Security measures for both on-premises and cloud |
| Offers customization and best-of-breed solutions | Combines control and flexibility of private cloud with scalability of public cloud |
| Allows leveraging specialized services from different providers | Balances data sensitivity, compliance, performance, and cost |
Real-Life Case Study Multi-Cloud
Optimizing Costs and Operations for Cloud-Based SaaS E-Commerce Platform
The client had a legacy on-premises architecture that was not efficient, and the challenge was to modernize their SaaS e-commerce platform and move it to the cloud. The solution involved redeveloping and replicating the platform’s architecture in Kubernetes for multiple cloud environments, including AWS, Azure, and Minikube. This made the platform cloud-agnostic and able to work with any cloud provider. The integration of various monitoring and analytical tools further enhanced the platform’s capabilities.
The results of the project include optimized costs by migrating to the cloud, avoiding vendor lock-in, improved efficiency through streamlined deployment processes, and expanded product offering through third-party integrations. The case study showcases how the client leveraged multi-cloud capabilities to achieve these benefits and improve their SaaS e-commerce platform’s operations and cost-effectiveness.
Ready to harness the full potential of multi-cloud solutions for your business? Contact Gart now and embark on your journey towards optimized performance, enhanced flexibility, and cost efficiency.
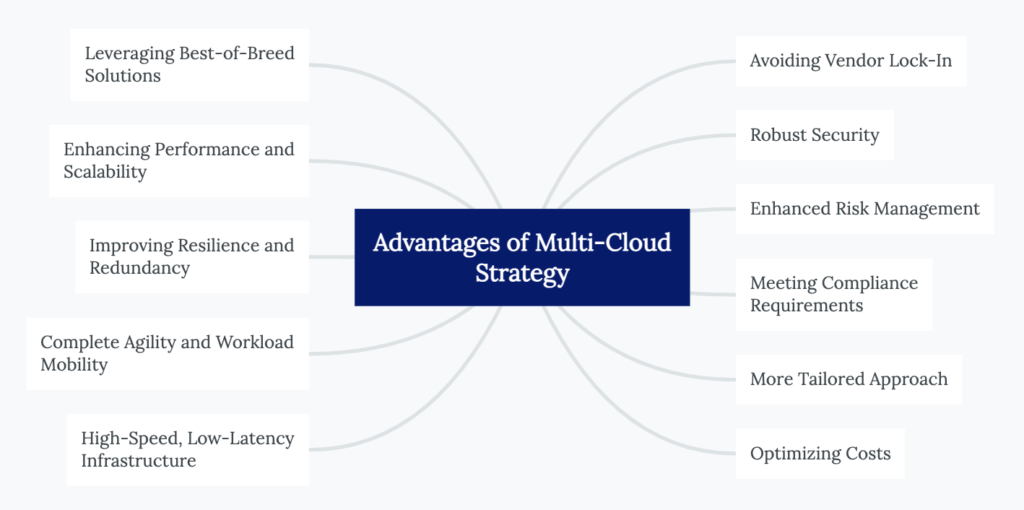
Advantages of Multi-Cloud Strategy
If you’re hesitant about embracing a multi-cloud approach, consider the advantages it offers in terms of unlocking limitless opportunities and flexibility for your IT strategy. Adopting a multi-cloud strategy empowers organizations to avoid vendor lock-in, leverage the best solutions available, enhance performance and scalability, improve resilience and redundancy, and optimize costs.
By harnessing the strengths of multiple cloud providers, organizations can build a robust and flexible cloud infrastructure that aligns with their specific needs and goals.
Challenges in Multi-Cloud Management
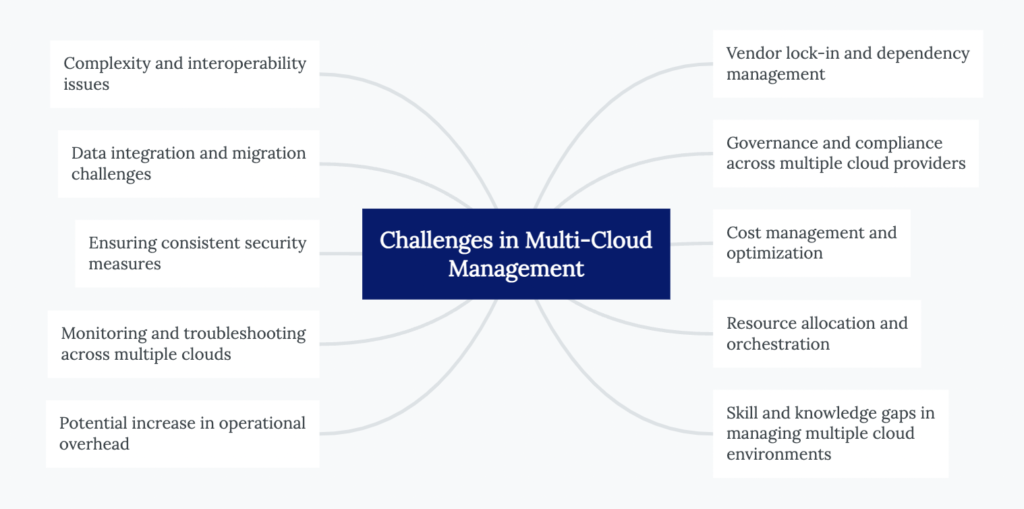
While there are numerous advantages to utilizing multiple cloud models and vendors, it is important to acknowledge that multi-cloud management is not without its limitations.
Managing multiple cloud environments can introduce complexity due to different architectures, APIs, and management tools. Ensuring seamless interoperability between clouds and integrating various systems and applications can be challenging.
Moving and integrating data across multiple clouds requires careful planning and execution. Organizations may face compatibility issues, data format conversions, and data synchronization challenges when transferring and consolidating data between different cloud platforms.
Maintaining consistent security measures across multiple clouds can be demanding. It involves implementing standardized security controls, access management, encryption, and monitoring practices that align with the organization’s security policies and compliance requirements.
Monitoring performance, detecting issues, and troubleshooting problems across multiple cloud environments can be complex. Organizations need effective monitoring tools and practices to gain visibility into each cloud platform and identify and resolve issues promptly.
Managing multiple clouds can potentially increase the operational overhead for IT teams. It requires expertise in different cloud technologies, administration tasks across various platforms, and coordination with multiple cloud providers, which can strain resources and impact efficiency.
Key Considerations for Multi-Cloud Management
By considering these key aspects of multi-cloud management, organizations can effectively plan, implement, and maintain a resilient and optimized multi-cloud environment that aligns with their business goals and maximizes the benefits of multiple cloud providers:
Cloud Strategy Development
Cloud strategy development refers to the process of formulating a comprehensive plan that outlines an organization’s approach to utilizing cloud computing technologies and services. It involves defining the objectives, goals, and desired outcomes of adopting cloud solutions, as well as identifying the specific strategies, guidelines, and best practices to be followed. It involves aligning cloud initiatives with business goals, defining the desired outcomes, and determining the optimal mix of cloud services and deployment models.
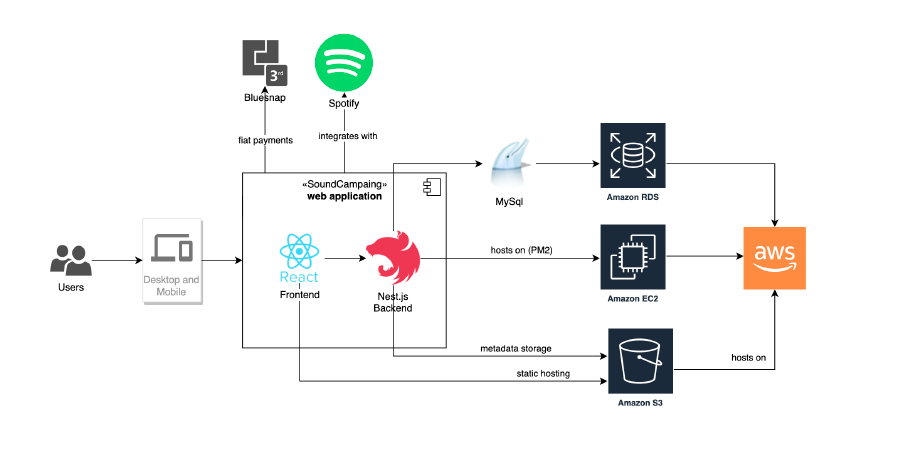
Example of solution architecture for Gart’s client SoundCampaign
Cloud Provider Selection Criteria
Choosing the right cloud providers is crucial. Organizations should consider factors such as
- Service Offerings
- Performance
- Reliability
- Security Capabilities
- Scalability
- Pricing Models
- Geographical Coverage
- Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Architecture and Deployment Considerations
Designing a well-architected multi-cloud environment requires careful planning. Considerations include workload distribution, data integration, network connectivity, application portability, and the ability to scale resources seamlessly across different cloud platforms.
Resource Provisioning and Orchestration
Efficient resource provisioning and orchestration across multiple clouds are key considerations. Organizations should automate processes for deploying, managing, and scaling resources, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Data Management and Governance
Managing data across multiple clouds requires robust data management and governance practices. This includes defining data classification, access controls, data protection measures, data integration, data backup and recovery, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Security and Compliance Measures
Implementing robust security measures and ensuring compliance across multiple clouds is critical. This involves establishing identity and access management controls, encryption mechanisms, network security, monitoring, auditing, and adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Managing costs effectively in a multi-cloud environment is essential. Organizations should analyze resource utilization, optimize workload placement, leverage pricing models (e.g., reserved instances, spot instances), and regularly review and optimize cloud spending.
Read more: Azure Cost Optimization for a Software Development Company.
Monitoring and Performance Management
Implementing comprehensive monitoring and performance management practices helps track the performance of applications, services, and infrastructure across multiple clouds. Proactive monitoring, performance optimization, and timely issue resolution are essential for ensuring optimal operations.
Vendor Management and Relationships
Managing relationships with cloud providers is crucial. Organizations should track service-level agreements, stay informed about provider roadmaps, engage in open communication, and understand the support and escalation processes to effectively address issues and leverage provider expertise.
Training and Expertise Development
Investing in training and developing expertise is key to successful multi-cloud management. It involves ensuring the IT team has the necessary skills and knowledge to manage and optimize cloud resources, understand different cloud platforms, and keep up with evolving technologies and best practices.
Best Multi-Cloud Management Tools
| Tool | Key Characteristics |
| CloudHealth by VMware | Comprehensive cloud cost management and optimization |
| RightScale by Flexera | Multi-cloud governance and cost optimization |
| Turbonomic | AI-driven cloud resource optimization and workload management |
| Scalr | Policy-based cloud governance and automation |
| CloudBolt | Unified hybrid and multi-cloud management platform |
| Morpheus | Cloud management with built-in governance and self-service capabilities |
| DivvyCloud | Multi-cloud security and compliance automation |
| FlexDeploy | Cloud-native DevOps and application release automation |
| HyperGrid | Intelligent multi-cloud management with focus on automation |
| Morro Data | Cloud-native data management and collaboration platform |
Multi-Cloud Management Framework
A multi-cloud management framework provides a structured approach to effectively manage and govern multi-cloud environments. It serves as a guide for organizations to navigate the complexities and challenges of multi-cloud adoption. The framework typically includes the following key components:
- Cloud Strategy Development. Defining a clear cloud strategy aligned with business objectives and identifying the goals and outcomes to be achieved through multi-cloud management.
- Cloud Provider Selection Criteria. Establishing criteria for selecting cloud providers based on factors such as service offerings, pricing models, performance, security, compliance, and support.
- Architecture and Deployment Considerations. Designing a scalable and flexible architecture that accommodates multi-cloud environments, considering factors like workload placement, data management, network connectivity, and integration.
- Resource Provisioning and Orchestration. Implementing mechanisms for efficient provisioning, allocation, and management of resources across multiple clouds, ensuring optimal utilization and scalability.
- Data Management and Governance. Implementing policies and practices for secure and compliant handling of data, including data integration, data protection, data privacy, and data governance across multiple cloud platforms.
- Security and Compliance Measures. Establishing robust security measures, access controls, identity management, encryption, and monitoring practices to ensure data and infrastructure security in a multi-cloud environment, while adhering to regulatory compliance requirements.
- Cost Optimization Strategies. Implementing strategies to optimize costs by monitoring and optimizing resource usage, leveraging cost-effective services, and eliminating unnecessary expenses across multiple cloud providers.
- Monitoring and Performance Management. Implementing monitoring tools and practices to gain visibility into the performance, availability, and health of resources and applications across multiple cloud platforms, enabling proactive issue detection and resolution.
- Vendor Management and Relationships. Establishing effective vendor management practices, including contract negotiations, performance monitoring, and maintaining productive relationships with cloud service providers.
- Training and Expertise Development. Investing in training and skill development programs to ensure the IT team has the necessary knowledge and expertise to manage and operate in a multi-cloud environment effectively.
By following a multi-cloud management framework, organizations can navigate the complexities of multi-cloud environments, optimize performance, ensure security and compliance, control costs, and achieve the desired benefits of a multi-cloud strategy.
Conclusion
Effective multi-cloud management is of utmost importance as organizations expand and incorporate new applications and services into their IT environments. Despite the continuous growth of cloud adoption and increasing data volumes, businesses still rely on conventional methods, such as passwords, which pose security risks to their diverse environments, remote workers, and multiple applications.
For seamless multi-cloud management and robust security, turn to Gart today. Contact us to explore how we can assist you in achieving your goals.
Seize the future of business in the cloud! Our expert Cloud Consulting Services offer seamless migration, cost optimization, and scalable solutions. Transform your digital landscape today.









