- IT Infrastructure Security Table
- Common Threats to IT Infrastructure Security
- Real-World Case Study: How Gart Transformed IT Infrastructure Security for a Client
- Best Practices for IT Infrastructure Security
- Securing Network Infrastructure
- Server Infrastructure
- Cloud Infrastructure Security
- Incident Response and Recovery
- Emerging Trends and Technologies in IT Infrastructure Security
From sensitive data storage to critical communication networks, the integrity and security of these digital foundations are paramount. This is where IT infrastructure security plays a crucial role.
IT infrastructure security encompasses a comprehensive set of measures and practices designed to protect the hardware, software, networks, and data that constitute an organization’s technology ecosystem. Its significance cannot be overstated, as the ever-evolving threat landscape poses significant risks to businesses of all sizes and industries.
With cyberattacks becoming more sophisticated and frequent, it is imperative for organizations to recognize the importance of fortifying their IT infrastructure against potential breaches, intrusions, and disruptions. The consequences of inadequate security measures can be detrimental, leading to financial loss, reputational damage, and legal ramifications.
Whether you are a small startup or a multinational corporation, understanding and implementing robust IT infrastructure security practices is essential for maintaining the trust of your customers, safeguarding critical data, and ensuring smooth business operations.
IT Infrastructure Security Table
| Aspect | Description |
| Threats | Common threats include malware/ransomware, phishing/social engineering, insider threats, DDoS attacks, data breaches/theft, and vulnerabilities in software/hardware. |
| Best Practices | Implementing strong access controls, regularly updating software/hardware, conducting security audits/risk assessments, encrypting sensitive data, using firewalls/intrusion detection systems, educating employees, and regularly backing up data/testing disaster recovery plans. |
| Network Security | Securing wireless networks, implementing VPNs, network segmentation/isolation, and monitoring/logging network activities. |
| Server Security | Hardening server configurations, implementing strong authentication/authorization, regularly updating software/firmware, and monitoring server logs/activities. |
| Cloud Security | Choosing a reputable cloud service provider, implementing strong access controls/encryption, monitoring/auditing cloud infrastructure, and backing up data stored in the cloud. |
| Incident Response/Recovery | Developing an incident response plan, detecting/responding to security incidents, conducting post-incident analysis/implementing improvements, and testing incident response/recovery procedures. |
| Emerging Trends/Technologies | Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML) in security, Zero Trust security model, blockchain technology for secure transactions, and IoT security considerations. |
Common Threats to IT Infrastructure Security
Understanding common threats to IT infrastructure security is crucial for organizations to implement appropriate measures and defenses. By staying informed about emerging attack vectors and adopting proactive security practices, businesses can strengthen their resilience against these threats and protect their valuable digital assets.
Malware and Ransomware Attacks
Malware and ransomware attacks present considerable risks to the security of IT infrastructure. Malicious programs like viruses, worms, and Trojan horses can infiltrate systems through diverse vectors such as email attachments, infected websites, or software downloads. Once within the infrastructure, malware can compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, and even grant unauthorized access to malicious actors. Ransomware, a distinct form of malware, encrypts vital files and extorts a ransom for their decryption, potentially resulting in financial losses and operational disruptions.
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing and social engineering attacks target individuals within an organization, exploiting their trust and manipulating them into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. These attacks often come in the form of deceptive emails, messages, or phone calls, impersonating legitimate entities. By tricking employees into sharing passwords, clicking on malicious links, or disclosing confidential data, cybercriminals can gain unauthorized access to the IT infrastructure and carry out further malicious activities.
Insider Threats
Insider threats refer to security risks that arise from within an organization. They can occur due to intentional actions by disgruntled employees or unintentional mistakes made by well-meaning staff members. Insider threats can involve unauthorized data access, theft of sensitive information, sabotage, or even the introduction of malware into the infrastructure. These threats are challenging to detect, as insiders often have legitimate access to critical systems and may exploit their privileges to carry out malicious actions.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks aim to disrupt the availability of IT infrastructure by overwhelming systems with a flood of traffic or requests. Attackers utilize networks of compromised computers, known as botnets, to generate massive amounts of traffic directed at a target infrastructure. This surge in traffic overwhelms the network, rendering it unable to respond to legitimate requests, causing service disruptions and downtime. DDoS attacks can impact businesses financially, tarnish their reputation, and impede normal operations.
Data Breaches and Theft
Data breaches and theft transpire when unauthorized individuals acquire entry to sensitive information housed within the IT infrastructure. This encompasses personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Perpetrators may exploit software vulnerabilities, weak access controls, or inadequate encryption to infiltrate the infrastructure and extract valuable data. The ramifications of data breaches are far-reaching and encompass legal liabilities, financial repercussions, and harm to the organization’s reputation.
Vulnerabilities in Software and Hardware
Software and hardware vulnerabilities introduce weaknesses in the IT infrastructure that can be exploited by attackers. These vulnerabilities can arise from coding errors, misconfigurations, or outdated software and firmware. Attackers actively search for and exploit these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access, execute arbitrary code, or perform other malicious activities. Regular patching, updates, and vulnerability assessments are critical to mitigating these risks and ensuring a secure IT infrastructure
Real-World Case Study: How Gart Transformed IT Infrastructure Security for a Client
The entertainment software platform SoundCampaign approached Gart with a twofold challenge: optimizing their AWS costs and automating their CI/CD processes. Additionally, they were experiencing conflicts and miscommunication between their development and testing teams, which hindered their productivity and caused inefficiencies within their IT infrastructure.
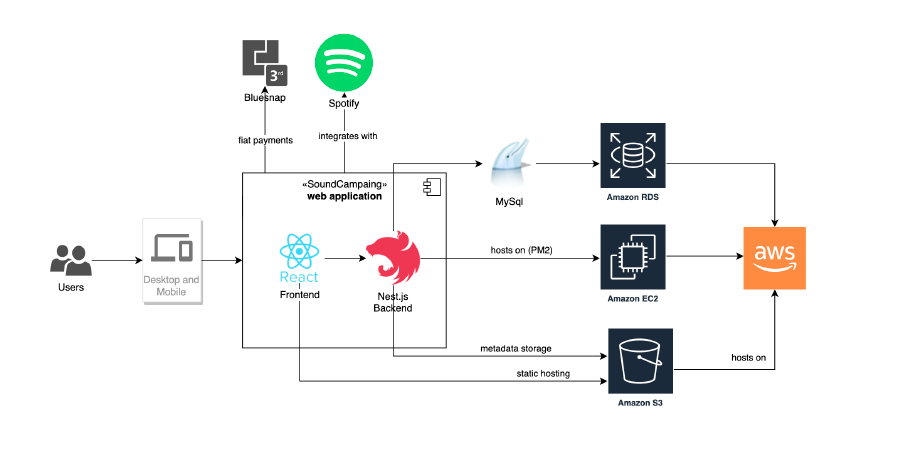
As a trusted DevOps company, Gart devised a comprehensive solution that addressed both the cost optimization and automation needs, while also improving the client’s IT infrastructure security and fostering better collaboration within their teams.
To streamline the client’s CI/CD processes, Gart introduced an automated pipeline using modern DevOps tools. We leveraged technologies such as Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes to enable seamless code integration, automated testing, and deployment. This eliminated manual errors, reduced deployment time, and enhanced overall efficiency.
Recognizing the importance of IT infrastructure security, Gart implemented robust security measures to minimize risks and improve collaboration within the client’s teams. By implementing secure CI/CD pipelines and automated security checks, we ensured a clear and traceable code deployment process. This clarity minimized conflicts between developers and testers, as it became evident who made changes and when. Additionally, we implemented strict access controls, encryption mechanisms, and continuous monitoring to enhance overall security posture.
Are you concerned about the security of your IT infrastructure? Protect your valuable digital assets by partnering with Gart, your trusted IT security provider.
Best Practices for IT Infrastructure Security
It is important to adopt a holistic approach to security, combining technical measures with user awareness and regular assessments to maintain a robust and resilient IT infrastructure
- Strong access controls and authentication mechanisms
- Regular software and hardware updates and patches
- Monitoring and auditing of network activities
- Encryption of sensitive data
- Implementation of firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Security awareness training for employees
- Regular data backups and testing of disaster recovery plans
Implementing robust access controls and authentication mechanisms is crucial to ensuring that only authorized individuals can access critical systems and resources. This involves implementing strong password policies, utilizing multi-factor authentication, and effectively managing user access. By enforcing these measures, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect against potential security breaches.
Regularly updating software and hardware is essential to address known vulnerabilities and maintain the security of systems against emerging threats. Timely application of patches and updates helps mitigate the risk of exploitation and strengthens the overall security posture of the IT infrastructure.
Continuous monitoring and auditing of network activities play a pivotal role in detecting suspicious behavior and potential security incidents. By implementing advanced monitoring tools and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, organizations can proactively identify and respond to threats in real-time, minimizing the impact of security breaches.
Data encryption is a fundamental practice for safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access and interception. Employing encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the data, providing an additional layer of protection against potential data breaches.
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are critical components of network security. Firewalls establish barriers between networks, preventing unauthorized access and blocking malicious traffic. IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activities and alerts administrators to potential threats, allowing for immediate response and mitigation.
Educating employees about security best practices and increasing awareness of potential risks are essential in creating a strong security culture. Conducting regular security awareness training empowers employees to recognize and mitigate security threats, such as phishing attacks and social engineering attempts, thereby strengthening the overall security posture of the organization.
Regular data backups and rigorous testing of disaster recovery plans are crucial for ensuring business continuity and data recoverability. Performing scheduled data backups and verifying their integrity guarantees that critical data can be restored in the event of a data loss incident. Additionally, testing and updating disaster recovery plans periodically ensures their effectiveness and readiness to mitigate the impact of any potential disruptions.
Securing Network Infrastructure
By securing wireless networks, implementing VPNs, employing network segmentation and isolation, and monitoring network activities, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their network infrastructure. These measures help prevent unauthorized access, protect data in transit, limit the impact of potential breaches, and enable proactive detection and response to security incidents.
Securing wireless networks is essential to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data. Organizations should employ strong encryption protocols, such as WPA2 or WPA3, to secure Wi-Fi connections. Changing default passwords, disabling broadcasting of the network’s SSID, and using MAC address filtering can further enhance wireless network security. Regularly updating wireless access points with the latest firmware patches is also crucial to address any known vulnerabilities.
Implementing virtual private networks (VPNs) provides a secure and encrypted connection for remote access to the network infrastructure. VPNs create a private tunnel between the user’s device and the network, ensuring that data transmitted over public networks remains confidential. By utilizing VPN technology, organizations can protect sensitive data and communications from eavesdropping or interception by unauthorized individuals.
Network segmentation and isolation involve dividing the network infrastructure into separate segments to restrict access and contain potential security breaches. By segmenting the network based on function, department, or user roles, organizations can limit lateral movement for attackers and minimize the impact of a compromised system. Each segment can have its own access controls, firewalls, and security policies, increasing overall network security.
Monitoring and logging network activities are crucial for detecting and responding to potential security incidents in a timely manner. By implementing network monitoring tools and systems, organizations can track and analyze network traffic for any suspicious or malicious activities. Additionally, maintaining detailed logs of network events and activities helps in forensic investigations, incident response, and identifying patterns of unauthorized access or breaches.
Our team of experts specializes in securing networks, servers, cloud environments, and more. Contact us today to fortify your defenses and ensure the resilience of your IT infrastructure.
Server Infrastructure
Hardening server configurations involves implementing security best practices and removing unnecessary services, protocols, and features to minimize the attack surface. This includes disabling unused ports, limiting access permissions, and configuring firewalls to allow only necessary network traffic. By hardening server configurations, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect against common vulnerabilities.
Implementing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms is crucial for securing server infrastructure. This involves using complex and unique passwords, enforcing multi-factor authentication, and implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive resources. Strong authentication and authorization mechanisms help prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining privileged access to servers and sensitive data.
Regularly updating server software and firmware is essential for addressing known vulnerabilities and ensuring that servers are protected against emerging threats. Organizations should stay current with patches and security updates released by server vendors, including operating systems, applications, and firmware. Timely updates help safeguard servers from potential exploits and protect the infrastructure from security breaches.
Monitoring server logs and activities is a critical security practice for detecting suspicious or malicious behavior. By implementing robust logging mechanisms, organizations can capture and analyze server logs to identify potential security incidents, anomalies, or unauthorized access attempts. Regularly reviewing server logs, coupled with real-time monitoring, enables proactive detection and timely response to security threats.
Cloud Infrastructure Security
By choosing a reputable cloud service provider, implementing strong access controls and encryption, regularly monitoring and auditing cloud infrastructure, and backing up data stored in the cloud, organizations can enhance the security of their cloud infrastructure. These measures help protect sensitive data, maintain data availability, and ensure the overall integrity and resilience of cloud-based systems and applications.
Choosing a reputable and secure cloud service provider is a critical first step in ensuring cloud infrastructure security. Organizations should thoroughly assess potential providers based on their security certifications, compliance with industry standards, data protection measures, and track record for security incidents. Selecting a trusted provider with robust security practices helps establish a solid foundation for securing data and applications in the cloud.
Implementing strong access controls and encryption for data in the cloud is crucial to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. This includes using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized users can access cloud resources. Additionally, sensitive data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest within the cloud environment to safeguard it from potential interception or compromise.
Regular monitoring and auditing of cloud infrastructure is vital to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Organizations should implement tools and processes to monitor cloud resources, network traffic, and user activities for any suspicious or anomalous behavior. Regular audits should also be conducted to assess the effectiveness of security controls, identify potential vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with security policies and regulations.
Backing up data stored in the cloud is essential for ensuring business continuity and data recoverability in the event of data loss, accidental deletion, or cloud service disruptions. Organizations should implement regular data backups and verify their integrity to mitigate the risk of permanent data loss. It is important to establish backup procedures and test data recovery processes to ensure that critical data can be restored effectively from the cloud backups.
Incident Response and Recovery
A well-prepared and practiced incident response capability enables timely response, minimizes the impact of incidents, and improves overall resilience in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Developing an Incident Response Plan
Developing an incident response plan is crucial for effectively handling security incidents in a structured and coordinated manner. The plan should outline the roles and responsibilities of the incident response team, the procedures for detecting and reporting incidents, and the steps to be taken to mitigate the impact and restore normal operations. It should also include communication protocols, escalation procedures, and coordination with external stakeholders, such as law enforcement or third-party vendors.
Detecting and Responding to Security Incidents
Prompt detection and response to security incidents are vital to minimize damage and prevent further compromise. Organizations should deploy security monitoring tools and establish real-time alerting mechanisms to identify potential security incidents. Upon detection, the incident response team should promptly assess the situation, contain the incident, gather evidence, and initiate appropriate remediation steps to mitigate the impact and restore security.
Conducting Post-Incident Analysis and Implementing Improvements
After the resolution of a security incident, conducting a post-incident analysis is crucial to understand the root causes, identify vulnerabilities, and learn from the incident. This analysis helps organizations identify weaknesses in their security posture, processes, or technologies, and implement improvements to prevent similar incidents in the future. Lessons learned should be documented and incorporated into updated incident response plans and security measures.
Testing Incident Response and Recovery Procedures
Regularly testing incident response and recovery procedures is essential to ensure their effectiveness and identify any gaps or shortcomings. Organizations should conduct simulated exercises, such as tabletop exercises or full-scale incident response drills, to assess the readiness and efficiency of their incident response teams and procedures. Testing helps uncover potential weaknesses, validate response plans, and refine incident management processes, ensuring a more robust and efficient response during real incidents.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in IT Infrastructure Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are emerging trends in IT infrastructure security. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, detect patterns, and identify anomalies or potential security threats in real-time. AI and ML can be used for threat intelligence, behavior analytics, user authentication, and automated incident response. By leveraging AI and ML in security, organizations can enhance their ability to detect and respond to sophisticated cyber threats more effectively.
Zero Trust Security Model
The Zero Trust security model is gaining popularity as a comprehensive approach to IT infrastructure security. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, Zero Trust assumes that no user or device should be inherently trusted, regardless of their location or network. It emphasizes strong authentication, continuous monitoring, and strict access controls based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Implementing a Zero Trust security model helps organizations reduce the risk of unauthorized access and improve overall security posture.
Blockchain Technology for Secure Transactions
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing secure transactions by providing a decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger. Its cryptographic mechanisms ensure the integrity and immutability of transaction data, reducing the reliance on intermediaries and enhancing trust. Blockchain can be used in various industries, such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare, to secure transactions, verify identities, and protect sensitive data. By leveraging blockchain technology, organizations can enhance security, transparency, and trust in their transactions.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security Considerations
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to proliferate, securing IoT devices and networks is becoming a critical challenge. IoT devices often have limited computing resources and may lack robust security features, making them vulnerable to exploitation. Organizations need to consider implementing strong authentication, encryption, and access controls for IoT devices. They should also ensure that IoT networks are separate from critical infrastructure networks to mitigate potential risks. Proactive monitoring, patch management, and regular updates are crucial to address IoT security vulnerabilities and protect against potential IoT-related threats.
These advancements enable organizations to proactively address evolving threats, enhance data protection, and improve overall resilience in the face of a dynamic and complex cybersecurity landscape.
Supercharge your IT landscape with our Infrastructure Consulting! We specialize in efficiency, security, and tailored solutions. Contact us today for a consultation – your technology transformation starts here.
See how we can help to overcome your challenges









