In today's digital world, businesses rely heavily on their IT infrastructure to operate effectively. Any downtime or performance issues can result in lost productivity, revenue, and brand reputation. This is where infrastructure monitoring comes in.
What Is Infrastructure Monitoring?
Infrastructure monitoring plays a vital role in collecting and analyzing data from various components of a tech stack, including servers, virtual machines, containers, and databases. This data is then analyzed to provide insights into the health and performance of the infrastructure. The tools also provide alerts and notifications when issues are detected, enabling IT teams to take corrective action.
By utilizing infrastructure monitoring practices, organizations can proactively identify and address issues that may impact users and mitigate risks of potential losses in terms of time and money.
Modern software applications must be reliable and resilient to meet clients' needs worldwide. Companies like Amazon are making an average of $14,900 every second in sales, therefore, even 30 seconds of downtime would have cost them thousands of dollars.
For software to keep up with demand, infrastructure monitoring is crucial. It allows teams to collect operational and performance data from their systems to diagnose, fix, and improve them.
Monitoring often includes physical servers, virtual machines, databases, network infrastructure, IoT devices and more. Full-featured monitoring systems can also alert you when something is wrong in your infrastructure.
In this article, we'll explain how infrastructure monitoring works, its primary use cases, typical challenges, use cases and best practices of infrastructure monitoring.
Infrastructure Monitoring: What Should You Monitor?
Infrastructure monitoring is essential for tracking the availability, performance, and resource utilization of backend components, including hosts and containers. By installing monitoring agents on hosts, engineers collect infrastructure metrics and send them to a monitoring platform for analysis. This allows organizations to ensure the availability and proper functioning of critical services for users.
Identifying which parts of your infrastructure to monitor depends on factors such as SLA requirements, system location, and complexity. Google has its Four Golden Signals (latency, traffic, errors, and saturation), which can help your team narrow down important metrics (review the official Google Cloud Monitoring Documentation). AWS, Azure also provides its best practices for monitoring.
Common System Monitoring Metrics Include
Sеrvеrs: Monitor sеrvеr CPU usagе, mеmory usagе, disk I/O, and nеtwork traffic.
Nеtwork: Monitor nеtwork latеncy, packеt loss, bandwidth usagе, and throughput.
Applications: Monitor application rеsponsе timе, еrror ratеs, and transaction volumеs.
Databasеs: Monitor databasе pеrformancе, including quеry rеsponsе timе and transaction throughput.
Sеcurity: Monitor sеcurity еvеnts, including failеd logins, unauthorizеd accеss attеmpts, and malwarе infеctions.
This list of metrics for each system isn't exhaustive. Rather, you should determine your business requirements and expectations for different parts of the infrastructure. These baselines will help you better understand what metrics should be monitored and establish guidelines for setting alerting thresholds.
Use Cases of Infrastructure Monitoring
Operations teams, DevOps engineers and SREs (site reliability engineers) generally use infrastructure monitoring to:
1. Troublеshoot pеrformancе issues
Infrastructure monitoring is instrumental in preventing incidents from escalating into outages. By using an infrastructure monitoring tool, engineers can quickly identify failed or latency-affected hosts, containers, or other backend components during an incident. In the event of an outage, they can pinpoint the responsible hosts or containers, facilitating the resolution of support tickets and addressing customer-facing issues effectively.
2. Optimize infrastructure use
Proactive cost reduction is another significant benefit of infrastructure monitoring. By analyzing the monitoring data, organizations can identify overprovisioned or underutilized servers and take necessary actions such as decommissioning them or consolidating workloads onto fewer hosts. Furthermore, infrastructure monitoring enables the redistribution of requests from underprovisioned hosts to overprovisioned ones, ensuring balanced utilization across the infrastructure.
Learn from this case study how Gart helped with AWS Cost Optimization and CI/CD Automation for the Entertainment Software Platform.
3. Forecast backend requirements
Historical infrastructure metrics provide valuable insights for predicting future resource consumption. For example, if certain hosts were found to be underprovisioned during a recent product launch, organizations can leverage this information to allocate additional CPU and memory resources during similar events. By doing so, they reduce strain on critical systems, minimizing the risk of revenue-draining outages.
4. Configuration assurancе tеsting
One of the prominent use cases of infrastructure monitoring is enhancing the testing process. Small and mid-size businesses utilize infrastructure monitoring to ensure the stability of their applications during or after feature updates. By monitoring the infrastructure, they can proactively detect any issues that may arise and take corrective measures, ensuring that their applications remain robust and reliable.
Ready to level up your Infrastructure Management? Contact us today and let our experienced team empower your organization with streamlined processes, automation, and continuous integration.
Infrastructure Monitoring Best Practices
Infrastructure monitoring best practices involve a combination of key strategies and techniques to ensure efficient and effective monitoring of your infrastructure. Here are some recommended practices to consider:
1. Opt for automation
To enhance Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR), leverage from the best infrastructure monitoring tools that offer automation capabilities. By adopting AIOps for infrastructure monitoring, you can achieve comprehensive end-to-end observability across your entire stack, facilitating quicker issue detection and resolution.
3. Install the agent across your entire environment
Rather than installing the monitoring agent on specific applications and their supporting environments, it is advisable to deploy it across your entire production environment. This approach provides a more holistic view of your infrastructure's health and performance, enabling you to make informed decisions based on comprehensive data.
Google Ops Agent Overview | AWS Systems Manager OpsCenter
3. Set up and prioritize alerts
Given the potential for numerous alerts in an infrastructure monitoring system, it's crucial to prioritize them effectively. As an SRE, focus on identifying and addressing the most critical alerts promptly, ensuring that essential issues are promptly resolved while minimizing distractions caused by less urgent notifications.
Google Cloud Monitoring Alerting Policy | AWS Alerting Policy
4. Create custom dashboards
Take advantage of the customization options available in infrastructure monitoring tools. Tools like Middleware offer the ability to create custom dashboards tailored to specific roles and requirements. By leveraging these capabilities, you can streamline your monitoring experience, presenting relevant information to different stakeholders in a clear and accessible manner.
5. Test your tools
Before integrating new applications or tools for infrastructure monitoring, testing is vital. This practice ensures that the monitoring setup functions correctly and all components are working as expected. By performing test runs, you can identify and address any potential issues before they impact your live environment.
6. Configure native integrations
If your infrastructure includes AWS resources, it is beneficial to configure native integrations with your infrastructure monitoring solution. For example, setting up the AWS EC2 integration allows for the automatic import of tags and metadata associated with your instances. This integration facilitates data filtering, provides real-time views, and enables scalability in line with your cloud infrastructure.
7. Activate integrations for comprehensive monitoring
Extend your infrastructure monitoring beyond CPU, memory, and storage utilization. Activate pre-configured integrations with services such as AWS CloudWatch, AWS Billing, AWS ELB, MySQL, NGINX, and more. These integrations enable monitoring of the services supporting your hosts and provide access to dedicated dashboards for each integrated service.
8. Create filter set for efficient resource management
Utilize the filter set functionality offered by your monitoring solution to organize hosts, cluster roles, and other resources based on relevant criteria. By applying filters based on imported EC2 tags or custom tags, you can optimize resource monitoring, proactively detect and resolve issues, and gain a comprehensive overview of your infrastructure's performance.
9. Set up alert conditions based on filtered data
Instead of creating individual alert conditions for each host, leverage the filtering capabilities to create alert conditions based on filtered data. This approach automates the addition and removal of hosts from the alert conditions as they match the specified tags. By aligning alerts with your infrastructure's tags, you ensure scalability and efficient alert management.
Our Monitoring Case Study
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, infrastructure monitoring is critical for ensuring the performance and availability of IT infrastructure. By following best practices and partnering with a trusted provider like Gart, organizations can detect issues proactively, optimize performance and be sure the IT infrastructure is 99,9% available, robust, and meets your current and future business needs. Leverage external expertise and unlock the full potential of your IT infrastructure through IT infrastructure outsourcing!
Let’s work together!
See how we can help to overcome your challenges
Contact us

Ready to take your IT infrastructure to the next level? Discover the ultimate arsenal of monitoring tools and software in this blog post. From real-time insights to proactive alerts, we unveil the best IT infrastructure monitoring solutions that will empower your business operations and supercharge your success. Get ready to elevate your monitoring game and unlock the full potential of your infrastructure in today's digital landscape.
IT Infrastructure Monitoring Tools Comparison Table
SoftwareKey FeaturesSupported PlatformsPricingSolarWinds NPMReal-time network monitoring, bandwidth tracking, alertingWindowsPaid, with free trialPRTG Network MonitorNetwork, server, and application monitoring, customizable dashboardsWindows, LinuxFreemium, paid plansNagios XINetwork, server, and application monitoring, customizable dashboardsWindows, LinuxPaid, with free trialZabbixNetwork, server, and application monitoring, scalabilityWindows, LinuxFree and open-sourceDatadogCloud-based monitoring, infrastructure, application, and logsWindows, LinuxPaid, with free trialDynatraceFull-stack monitoring, automatic discovery, AI-powered insightsWindows, LinuxPaid, with free trialIT Infrastructure Monitoring Tools & Software Table
Best IT Infrastructure Monitoring Software
Resource Management Framework (RMF)
We've created the Resource Management Framework (RMF), a scalable, cloud-agnostic solution for infrastructure monitoring, specifically designed for digital landfill management. RMF features a user-friendly dashboard, automated alerts, and seamless integration with tools like Microsoft Teams, enabling real-time monitoring and proactive issue resolution. Its flexibility ensures scalability across various cloud platforms, making it ideal for managing environmental operations globally.
Sematext Monitoring
Sematext Monitoring is a comprehensive monitoring solution that provides visibility into applications, infrastructure, and logs. It offers real-time insights, proactive alerting, and powerful analytics to ensure efficient operations.
Pros:
End-to-end monitoring: Sematext allows monitoring of applications, infrastructure components, and logs from a single platform.
Real-time insights: It provides real-time data and analytics, enabling quick identification and resolution of issues.
Proactive alerting: Sematext offers customizable alerting mechanisms, ensuring timely notifications for critical events.
Powerful analytics: The tool provides advanced analytics and visualizations for deep performance analysis.
Easy integration: It seamlessly integrates with various technologies, including cloud platforms, containers, and popular frameworks.
Cons:
Learning curve: Users may require some time to familiarize themselves with the tool's features and configurations.
Pricing: The pricing structure of Sematext Monitoring may not be suitable for smaller organizations or those with budget constraints.
Complexity for simple setups: The extensive feature set of Sematext Monitoring may feel overwhelming for simpler infrastructure setups.
Sematext infrastructure monitoring tool offers different pricing plans based on the specific monitoring needs of the organization. It typically operates on a subscription-based model with pricing determined by factors such as infrastructure size, data retention requirements, and additional features. It's advisable to contact Sematext directly for detailed pricing information tailored to your organization's needs.
Need infrastructure monitoring services? Contact us today to ensure the optimal performance and reliability of your IT infrastructure.
The Elastic Stack
The Elastic Stack is a powerful and versatile set of open-source tools designed for log management, data analytics, and visualization. It consists of Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats, providing a comprehensive solution for collecting, storing, searching, and analyzing data.
Pros:
Scalable and flexible: The Elastic Stack can scale to handle large amounts of data and is adaptable to different use cases and environments.
Full-text search capabilities: Elasticsearch, the core component, offers robust search functionality for fast and efficient data retrieval.
Rich data visualization: Kibana allows users to create interactive visualizations and dashboards, enabling easier data exploration and insights.
Integration capabilities: The Elastic Stack can integrate with various data sources, systems, and third-party tools, enhancing its versatility.
Active community and support: With a large and active user community, there is extensive documentation, resources, and community support available.
Cons:
Complexity: The Elastic Stack can be complex to set up and configure, especially for users with limited experience or expertise.
Resource-intensive: Running and maintaining the Elastic Stack may require significant hardware resources and expertise.
Learning curve: Due to its extensive feature set, there may be a learning curve for users new to the Elastic Stack.
The Elastic Stack is available as open-source software, which means the core components are free to use. However, Elastic, the company behind the Elastic Stack, offers additional features, management tools, and support through various subscription plans. The pricing for these commercial offerings is based on factors such as data volume, deployment size, and desired features. It's recommended to visit the Elastic website or contact their sales team for detailed pricing information.
Prometheus
Prometheus is a popular open-source monitoring and alerting system designed for gathering and analyzing metrics from various components in a distributed IT infrastructure. It is known for its scalability, flexibility, and robust features.
Pros:
Powerful metrics collection: Prometheus can efficiently collect metrics from different sources, including applications, servers, and network devices.
Flexible query language: It offers a flexible query language called PromQL, enabling users to retrieve and analyze metrics with ease.
Dynamic alerting and notification: Prometheus allows the creation of custom alert rules and supports integrations with various notification channels.
Scalable architecture: It is designed to handle large-scale environments and provides horizontal scalability options.
Active community and ecosystem: Prometheus has a thriving community, resulting in extensive documentation, integrations, and support.
Cons:
Initial learning curve: Getting started with Prometheus may require some familiarity with its concepts and query language.
Complex configuration: Setting up Prometheus for complex environments can be challenging and time-consuming.
Limited long-term storage: By default, Prometheus offers limited long-term data retention, although this can be extended with additional components or integrations.
Prometheus is an open-source tool and available for free. However, it's important to consider the costs associated with hosting, maintaining, and scaling the infrastructure required to run Prometheus effectively. Organizations may also need to allocate resources for dedicated personnel or seek professional support if required.
Zabbix
Zabbix is a robust open-source monitoring solution that provides comprehensive visibility into the performance and health of IT infrastructure components. It offers a wide range of features for monitoring networks, servers, applications, and other devices.
Pros:
Extensive monitoring capabilities: Zabbix supports monitoring of diverse infrastructure components, including network devices, servers, virtual machines, databases, and more.
Flexible and customizable: It allows for extensive customization and flexible configuration options to adapt to various monitoring needs.
Advanced alerting and notification: Zabbix provides customizable alerting mechanisms, enabling timely notifications for critical events via email, SMS, or other channels.
Rich visualization and reporting: The tool offers a variety of visualizations, graphs, and reporting options to analyze and present monitoring data effectively.
Active community and ecosystem: Zabbix has a large and active user community, resulting in continuous development, frequent updates, and extensive documentation.
Cons:
Steeper learning curve: Setting up and configuring Zabbix may require a learning curve, especially for users with limited monitoring experience.
Resource-intensive: Running Zabbix may require adequate hardware resources, especially for larger infrastructures or high-frequency data collection.
Interface complexity: The user interface of Zabbix can be overwhelming for some users due to the abundance of features and configuration options.
Zabbix is an open-source tool available for free. However, it's essential to consider costs related to hosting, maintaining, and scaling the infrastructure required to run Zabbix effectively. Organizations may also need to allocate resources for dedicated personnel or seek professional support if required.
SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor (SAM)
SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor (SAM) is a comprehensive monitoring solution designed to monitor servers, applications, and their underlying infrastructure. It offers a wide range of features to optimize performance, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the availability of critical systems.
Pros:
Easy deployment and configuration: SAM provides a user-friendly interface and offers automated discovery, making it quick and straightforward to set up monitoring for servers and applications.
Extensive monitoring capabilities: It supports monitoring for a variety of applications, servers, databases, virtualization platforms, and cloud environments, providing comprehensive visibility into the entire infrastructure.
Powerful alerting and remediation: SAM enables the creation of custom alerts based on specific performance thresholds, ensuring prompt notifications and proactive problem resolution.
Intuitive dashboards and reporting: The solution offers intuitive dashboards and reporting features to visualize performance metrics and generate insightful reports.
Integration with other SolarWinds products: SAM seamlessly integrates with other SolarWinds products, allowing for enhanced monitoring capabilities across the IT environment.
Cons:
Complexity for larger environments: Managing and configuring SAM in larger environments can be complex and may require additional resources and expertise.
Licensing costs: SolarWinds SAM is a paid solution, and the pricing can be a consideration for organizations with budget constraints.
SolarWinds SAM operates on a licensing model, with pricing based on the number of monitored components and the desired features. The exact pricing information can be obtained by contacting the SolarWinds sales team or visiting their website.
N-able RMM
N-able RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) is a comprehensive IT infrastructure monitoring and management platform designed to simplify and streamline the management of IT environments. It provides a wide range of features to monitor, automate, and support IT infrastructure and endpoints.
Pros:
Centralized monitoring and management: N-able RMM offers a centralized platform to monitor and manage multiple devices, servers, applications, and networks from a single interface.
Proactive issue detection: It provides proactive monitoring capabilities, alerting administrators to potential issues before they escalate, enabling timely resolution and minimizing downtime.
Automation and scripting: N-able RMM allows for automation of routine tasks and scripting, reducing manual effort and increasing operational efficiency.
Patch management: The platform includes patch management features to ensure that systems and software are up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
Remote control and support: It offers remote access and support capabilities, allowing administrators to troubleshoot issues and provide remote assistance to end-users.
Third-party integrations: N-able RMM integrates with other tools and systems, such as ticketing systems and PSA (Professional Services Automation) platforms, enhancing workflow and collaboration.
Cons:
Initial learning curve: The complexity of N-able RMM may require some time for administrators to familiarize themselves with the platform and its features.
Resource-intensive: Depending on the size of the IT environment, running N-able RMM may require sufficient hardware resources and bandwidth.
Pricing: N-able RMM is a commercial solution, and the pricing is based on factors such as the number of devices and endpoints being monitored. It's advisable to consult with the N-able sales team for detailed pricing information.
N-able RMM follows a subscription-based pricing model. The cost varies depending on factors such as the number of devices, the desired features, and additional services required. For accurate pricing details, it is recommended to contact the N-able sales team or visit their website.
Datadog Infrastructure Monitoring
Datadog Infrastructure Monitoring is a robust cloud-based monitoring solution designed to provide comprehensive visibility into the performance and health of IT infrastructure components. It offers a wide range of features to monitor servers, databases, containers, and cloud environments.
Datadog Infrastructure Monitoring allows organizations to collect and analyze metrics, traces, and logs from various sources, providing real-time insights into the health and performance of their infrastructure. It offers advanced monitoring capabilities, customizable dashboards, and intelligent alerting to ensure proactive issue detection and resolution.
Pros:
Comprehensive monitoring: Datadog Infrastructure Monitoring supports monitoring for diverse infrastructure components, including servers, databases, containers, and cloud services, providing a holistic view of the IT environment.
Real-time visibility: The solution offers real-time metrics and visualizations, enabling administrators to monitor infrastructure performance and quickly identify potential issues.
Powerful alerting and collaboration: Datadog allows the creation of custom alerts based on specific metrics, and provides integrations with collaboration tools, facilitating prompt notifications and efficient incident response.
Scalable and flexible: The platform can scale to accommodate growing infrastructure needs, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes. It also supports multi-cloud and hybrid environments.
Integration ecosystem: Datadog integrates with a wide range of popular technologies, including cloud providers, containers, orchestration tools, and application frameworks, enhancing its capabilities and versatility.
Cons:
Complexity for beginners: Datadog's extensive feature set and configuration options may have a steeper learning curve for users new to the platform.
Pricing: Datadog is a commercial solution with pricing based on factors such as the number of hosts, metrics, and additional features required. It's advisable to consult with the Datadog sales team for detailed pricing information.
ManageEngine OpManager
ManageEngine OpManager is a comprehensive IT infrastructure monitoring and management software designed to monitor network devices, servers, applications, and other IT resources. It offers a wide range of features to ensure the optimal performance and availability of IT infrastructure.
ManageEngine OpManager provides a unified platform for monitoring and managing IT infrastructure. It offers real-time monitoring, alerting, and reporting capabilities to help organizations maintain a robust and secure IT environment. With its intuitive interface and extensive feature set, OpManager simplifies network monitoring and troubleshooting processes.
Pros:
End-to-end monitoring: OpManager allows monitoring of network devices, servers, virtual machines, applications, databases, and other IT resources, providing comprehensive visibility into the entire infrastructure.
Automated discovery and mapping: The software automatically discovers network devices and maps their interconnections, making it easier to visualize the network topology.
Proactive alerting and remediation: OpManager sends real-time alerts for critical events, enabling administrators to take immediate action and resolve issues before they impact operations.
Performance analytics: The solution provides in-depth performance analytics, enabling administrators to identify bottlenecks, track resource utilization, and optimize the performance of IT infrastructure components.
Extensive reporting: OpManager offers pre-built and customizable reports to gain insights into the performance, availability, and health of the monitored infrastructure.
Integration capabilities: It integrates with other ManageEngine products and third-party tools, allowing seamless workflow integration and enhancing overall IT operations.
Cons:
Complexity for large deployments: OpManager may require additional configuration and resources to handle large-scale deployments or complex network environments.
Pricing: ManageEngine OpManager is a commercial product, and the pricing is based on factors such as the number of devices and the desired features. For detailed pricing information, it is recommended to contact the ManageEngine sales team.
PRTG Network Monitor
PRTG Network Monitor offers real-time monitoring of network devices, servers, applications, and services. It uses various protocols to collect data and provides an intuitive web-based interface to visualize and analyze the monitored data. With PRTG, you can proactively detect network issues, troubleshoot problems, and optimize network performance.
Pros:
Easy to use: PRTG Network Monitor features a user-friendly interface with simple configuration and setup, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced administrators.
Comprehensive monitoring: It supports a wide range of network devices, including routers, switches, servers, and virtual machines. It also offers application monitoring and can monitor bandwidth utilization, response times, and other network performance metrics.
Customizable alerts and notifications: PRTG allows you to set up custom alerts and notifications based on specific thresholds, ensuring you are promptly notified of any issues that may affect your network.
Reporting and analysis: The solution offers built-in reporting capabilities, allowing you to generate customized reports on network performance and usage trends. This helps with capacity planning and troubleshooting.
Scalability: PRTG is scalable and can adapt to networks of any size, from small businesses to large enterprises, making it suitable for various environments.
Active community and support: PRTG has an active user community and provides comprehensive support resources, including forums, knowledge base articles, and user manuals.
Cons:
Complexity for advanced configurations: While PRTG offers ease of use for basic configurations, more advanced configurations and setups may require additional expertise and time.
Pricing: PRTG Network Monitor offers various pricing options based on the number of sensors required. The pricing structure can become more expensive as the number of sensors and monitored devices increases. It's recommended to consult with the PRTG sales team for detailed pricing information.
Nagios
Nagios offers a flexible and extensible monitoring framework that allows users to monitor various aspects of their IT infrastructure. It utilizes a plugin-based architecture, enabling users to customize and expand its functionality according to their specific monitoring needs.
Pros:
Versatility: Nagios can monitor a wide range of network devices, servers, applications, and services, making it suitable for diverse IT environments.
Extensibility: With its plugin architecture, Nagios can be extended to support additional monitoring capabilities and integrate with third-party tools, enhancing its functionality.
Customization: Users have the flexibility to define custom monitoring checks and thresholds, tailoring the monitoring to their specific requirements.
Alerting and notification: Nagios provides robust alerting mechanisms, allowing users to receive notifications via various channels (email, SMS, etc.) when issues are detected.
Community support: Nagios has a large and active community of users who contribute plugins, provide support, and share knowledge and best practices.
Cons:
Configuration complexity: Nagios configuration can be complex, especially for larger deployments or complex monitoring scenarios. It requires knowledge and expertise to set up and maintain effectively.
User interface: The user interface of Nagios may not be as intuitive or visually appealing as some commercial monitoring solutions, requiring users to spend time learning and navigating the interface.
Nagios is an open-source software and available for free. However, there are also commercial versions and plugins available that offer additional features, support, and services.
WhatsUp Gold
WhatsUp Gold offers network, server, and application monitoring for efficient infrastructure management. Gain real-time visibility, receive alerts, and analyze data to optimize performance.
With its intuitive interface and powerful features, WhatsUp Gold simplifies network monitoring, troubleshooting, and reporting processes.
Key Features:
Network monitoring: WhatsUp Gold offers real-time monitoring of network devices, interfaces, and traffic, providing visibility into network performance and availability.
Application monitoring: It enables monitoring of applications and services to ensure they are functioning properly and meeting performance metrics.
Server monitoring: WhatsUp Gold monitors servers, tracks resource utilization, and alerts administrators of any issues impacting server performance or availability.
Device monitoring: The software can monitor various devices, such as switches, routers, printers, and wireless access points, providing insights into device health and performance.
Alerting and notification: WhatsUp Gold sends customizable alerts and notifications when issues are detected, allowing administrators to take prompt action.
Reporting and analysis: The solution offers pre-built and customizable reports, allowing administrators to generate insights into network performance, availability, and historical trends.
Pros of infrastructure monitoring tool:
Easy-to-use interface: WhatsUp Gold provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it accessible for both experienced administrators and beginners.
Comprehensive monitoring capabilities: It supports monitoring of a wide range of infrastructure components, including networks, servers, applications, and devices, providing a holistic view of the IT environment.
Proactive issue detection: WhatsUp Gold enables proactive monitoring and alerts administrators to potential issues before they impact operations, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Scalability: The software can scale to accommodate growing infrastructure needs, making it suitable for small to large enterprises.
Integration capabilities: WhatsUp Gold integrates with various third-party tools and technologies, allowing seamless integration into existing IT environments.
Cons of infrastructure monitoring tool:
Advanced features may require additional configuration: Some advanced features and configurations may require additional expertise or technical knowledge to set up and utilize effectively.
Pricing: WhatsUp Gold is a commercial product, and pricing may vary based on the desired features, the number of monitored devices, and the level of support. It's advisable to contact the Ipswitch sales team for detailed pricing information.
Pricing: WhatsUp Gold offers different pricing plans based on the number of monitored devices and the desired feature set. For accurate pricing details and to explore the available options, it is recommended to contact the Ipswitch sales team or visit their website.
New Relic
New Relic provides full-stack observability for applications and infrastructure. Monitor performance, traces, errors, and logs. Gain insights for efficient troubleshooting and performance optimization.
Key features of New Relic infrastructure monitoring tool:
Application Performance Monitoring (APM): New Relic provides detailed insights into the performance of applications, helping identify bottlenecks, slow response times, and errors. It offers code-level visibility and traces transactions across various components.
Infrastructure Monitoring: The software enables monitoring of servers, virtual machines, containers, and cloud resources. It provides real-time metrics, alerts for resource utilization, and helps optimize infrastructure performance.
Real User Monitoring (RUM): New Relic allows monitoring of user interactions with web applications, providing insights into user experience, page load times, and performance issues from different geographical locations and devices.
Synthetic Monitoring: It offers synthetic testing to simulate user interactions and monitor application availability and performance from different locations. This helps identify performance issues before they impact actual users.
Distributed Tracing: New Relic provides end-to-end visibility into complex distributed systems, allowing users to trace requests across multiple services and identify performance bottlenecks and latency issues.
Error and Log Analysis: The software aggregates and analyzes application errors and logs, providing insights into root causes and aiding in troubleshooting and debugging.
Scalability and Auto-Instrumentation: New Relic scales with your infrastructure and supports dynamic environments, providing automatic instrumentation for many popular frameworks and platforms.
Dashboards and Reporting: It offers customizable dashboards and reports, allowing users to visualize and share monitoring data, track performance trends, and generate insights for stakeholders.
Integration and Collaboration: New Relic integrates with various tools and platforms, enabling seamless collaboration across teams and providing a centralized view of monitoring data.
Alerting and Notification: The software allows setting up customizable alerts and notifications based on predefined thresholds, ensuring timely response to critical incidents.
Mobile Application Monitoring: New Relic provides monitoring capabilities for mobile applications, helping track performance, crashes, and user behavior.
API Monitoring: It offers monitoring of APIs to ensure their availability, response times, and adherence to SLAs.
Dynatrace
Dynatrace is an AI-powered observability platform that offers real-time monitoring of applications, infrastructure, and user experiences. Get automatic discovery, intelligent problem resolution, and proactive performance monitoring.
Key features of dynatrace infrastructure monitoring software:
Full-Stack Observability: Dynatrace provides end-to-end visibility across the entire technology stack, including infrastructure, applications, and user experiences. It offers deep insights into application performance, dependencies, and resource utilization.
AI-Powered Root Cause Analysis: Dynatrace utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to automatically detect anomalies, identify root causes of performance issues, and provide actionable insights for troubleshooting and optimization.
Real-Time User Experience Monitoring: The software captures and analyzes user interactions, providing real-time visibility into user experience and performance across different devices, browsers, and locations. It helps identify performance bottlenecks and optimize user satisfaction.
Automatic Baselining and Anomaly Detection: Dynatrace establishes baselines for performance metrics and automatically detects anomalies and deviations from normal behavior. It proactively alerts users to abnormal patterns, enabling quick identification and resolution of issues.
Continuous Performance Optimization: Dynatrace offers continuous performance optimization recommendations based on AI-driven analysis. It suggests optimizations to enhance application performance, resource utilization, and user experience.
AppDynamics
AppDynamics provides application performance monitoring and infrastructure visibility. Monitor application health, user experiences, and infrastructure dependencies for optimal operations.
Key features of AppDynamics infrastructure monitoring tool:
Application Performance Monitoring (APM): AppDynamics provides deep visibility into application performance, allowing users to identify and diagnose performance bottlenecks, errors, and latency issues. It offers code-level diagnostics and transaction tracing to pinpoint the root causes of performance problems.
Business Transaction Monitoring: The software enables monitoring of end-to-end business transactions, helping organizations understand how application performance impacts critical business processes and user experiences. It provides insights into response times, conversions, and other key business metrics.
Infrastructure Monitoring: AppDynamics offers infrastructure monitoring capabilities, allowing users to monitor the health, availability, and performance of servers, virtual machines, containers, and cloud resources. It provides real-time metrics and alerts for resource utilization and infrastructure-related issues.
Real-Time Analytics and Dashboards: AppDynamics provides powerful analytics and customizable dashboards to visualize and analyze monitoring data. It offers real-time insights into application and infrastructure performance, allowing users to track key metrics and performance trends.
Dynamic Baseline and Anomaly Detection: AppDynamics establishes dynamic baselines for performance metrics and automatically detects anomalies and deviations from normal behavior. It proactively alerts users to abnormal patterns, facilitating quick troubleshooting and issue resolution.
End-User Monitoring: The software allows monitoring and measuring the experiences of end users, capturing data on page load times, user actions, and errors. It helps organizations understand how users interact with their applications and identify areas for improvement.
Scalability and Cloud Readiness: AppDynamics is designed to scale with the growth of applications and infrastructure. It supports cloud-native environments and provides visibility into dynamic and distributed architectures.
Site24x7 Infrastructure Monitoring
Site24x7 Infrastructure Monitoring offers comprehensive monitoring for servers, networks, and cloud resources. Monitor performance, track uptime, and receive alerts for efficient infrastructure management.
Key features of Site24x7 IT infrastructure monitoring software:
Server Monitoring: Site24x7 allows monitoring of servers across different platforms and operating systems. It provides real-time visibility into server performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network traffic.
Network Monitoring: The software monitors network devices, interfaces, and traffic, helping identify network bottlenecks, latency issues, and connectivity problems. It provides insights into bandwidth utilization, packet loss, and network latency.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM): Site24x7 offers APM capabilities to monitor the performance of web applications and APIs. It tracks response times, transactions, and user experiences, enabling organizations to optimize application performance and user satisfaction.
Cloud Monitoring: Site24x7 supports monitoring of cloud infrastructure and services from providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It provides visibility into resource utilization, availability, and performance of cloud-based applications and services.
Website Monitoring: The software offers website monitoring features to track website availability, response times, and performance from different geographical locations. It helps identify website downtime, errors, and slow page load times.
Alerting and Notification: Site24x7 sends customizable alerts and notifications via various channels (email, SMS, mobile push notifications) when performance thresholds are breached or critical issues are detected. It ensures timely response and minimizes downtime.
Reports and Dashboards: Site24x7 provides pre-built and customizable reports and dashboards to visualize and analyze monitoring data. It offers historical trends, SLA compliance reports, and executive-level summaries for effective decision-making.
Integration and Automation: Site24x7 integrates with popular IT tools and platforms, enabling seamless data exchange and automation. It supports integrations with incident management systems, IT service management (ITSM) tools, and collaboration platforms.
In Closing
To wrap up, selecting the right IT infrastructure monitoring software is vital for maintaining optimal system performance, availability, and security. The featured solutions in this blog post offer a range of powerful features, from real-time monitoring to automation and scalability. When making your choice, consider your specific requirements, including ease of use, integration capabilities, and pricing models. Remember, if you need assistance with your infrastructure monitoring needs, Gart is here to help. Our team of experts can provide guidance and support to ensure your systems are effectively monitored and optimized. Contact us today to learn more about how Gart can assist you in achieving reliable and efficient IT operations.
Revolutionize your IT infrastructure with our expert consulting! From seamless optimizations to robust security measures, we tailor solutions to elevate your technology backbone. Ready to transform?

In the relentless pursuit of success, businesses often find themselves caught in the whirlwind of IT infrastructure management. The demands of keeping up with ever-evolving technologies, maintaining robust security, and optimizing operations can feel like an uphill battle.
What is IT Infrastructure Outsourcing?
Imagine you’re running a marathon, but you’re also carrying your heavy backpack. That’s what managing IT infrastructure in-house often feels like for many companies. You’re trying to focus on winning the race (your business goals), but the weight of maintaining servers, networks, data centers, and security is slowing you down.
IT infrastructure outsourcing is like handing over that backpack to a professional support team running beside you. They carry it efficiently, ensuring everything inside remains organized, protected, and accessible, allowing you to focus solely on your pace and strategy.
At its core, IT infrastructure outsourcing means entrusting a specialized external provider with the management, maintenance, and optimization of your IT systems and hardware, including:
Servers and storage
Networks and connectivity
Data centers and cloud infrastructure
Security protocols and compliance requirements
Instead of managing all these internally, you leverage the expertise and resources of professionals dedicated solely to this domain.
Why is IT Infrastructure Outsourcing Becoming Essential Today?
Today’s business landscape demands agility, security, and innovation – all while keeping costs under control. Here’s why outsourcing IT infrastructure has shifted from being a strategic option to a critical necessity:
Rapid Technological AdvancementsIT evolves so fast that in-house teams struggle to keep up with emerging tools, frameworks, and security protocols. Outsourcing partners invest heavily in continuous skill upgrades, ensuring your business benefits from the latest advancements without the learning curve.
Cybersecurity Threats Are RisingThe sophistication of cyberattacks increases daily. Outsourcing ensures your infrastructure is protected by advanced threat detection systems and experts monitoring for vulnerabilities 24/7.
Need for Scalability and FlexibilityWhether it’s Black Friday traffic spikes or sudden global expansions, businesses must scale their IT resources seamlessly. Outsourcing provides elasticity without the delays and overhead of in-house provisioning.
Pressure to Focus on Core BusinessEvery hour spent fixing servers is an hour not spent innovating or delighting customers. Outsourcing allows businesses to focus on strategic initiatives while leaving technical operations to experts.
In essence, IT infrastructure outsourcing is not about relinquishing control – it’s about gaining freedom to drive your business forward faster.
Breaking Down IT Infrastructure Outsourcing
At its simplest, IT infrastructure outsourcing is the strategic delegation of your company’s IT infrastructure management to a trusted external provider. This includes:
Hardware management: Procuring, installing, configuring, and maintaining servers, storage devices, and network hardware.
Software management: Managing operating systems, infrastructure software, and middleware.
Network management: Ensuring secure, reliable, and optimized connectivity within and beyond your organization.
Security management: Implementing and maintaining cybersecurity measures to protect systems and data.
Cloud infrastructure management: Designing, deploying, and maintaining cloud resources in platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
It’s like hiring a specialized external team to maintain, upgrade, and optimize the entire “engine room” of your business so your internal teams can steer the ship confidently towards strategic goals.
Components Included in IT Infrastructure Outsourcing
Here’s a breakdown of what infrastructure outsourcing usually covers:
Servers:Physical and virtual servers host your applications, databases, and services.
Networks:LAN, WAN, VPNs, and connectivity solutions ensure data flows securely and efficiently.
Storage Systems:Data storage solutions, backup infrastructure, and disaster recovery planning.
Data Centers:Management of on-premises data centers or leveraging third-party colocation and cloud facilities.
Security Systems:Firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention, endpoint security, and compliance management.
Cloud Infrastructure:Public, private, or hybrid cloud management, including architecture design, resource provisioning, monitoring, and cost optimization.
By outsourcing these components, companies gain access to specialized expertise, advanced technologies, and robust security protocols without the overhead of building these capabilities internally.
Benefits of IT Infrastructure Outsourcing
Outsourcing IT infrastructure brings numerous benefits that contribute to business growth and success.
Manage Cloud Complexity
Over the past two years, there’s been a surge in cloud commitment, with more than 86% of companies reporting an increase in cloud initiatives.
Implementing cloud initiatives requires specialized skill sets and a fresh approach to achieve comprehensive transformation. Often, IT departments face skill gaps on the technical front, lacking experience with the specific tools employed by their chosen cloud provider.
Cloud migration and management aren’t as simple as clicking “deploy.” Each cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP) has unique architectures, tools, and services requiring specialized skills and certifications.
Many organizations lack the expertise needed to develop a cloud strategy that fully harnesses the potential of leading platforms such as AWS or Microsoft Azure, utilizing their native tools and services.
For instance:
AWS requires expertise in services like EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda, and VPC configurations.
Azure demands proficiency in Resource Groups, Virtual Networks, Azure AD, and cost management tools.
GCP needs knowledge of Compute Engine, Kubernetes Engine, Cloud Functions, and BigQuery integrations.
Without this expertise, companies risk:
Cost overruns due to improper provisioning
Security misconfigurations exposing critical data
Failed migrations disrupting business operations
Outsourcing to experienced infrastructure providers ensures cloud initiatives are implemented efficiently, securely, and cost-effectively.
Access to Specialized Expertise
Outsourcing IT infrastructure allows businesses to tap into the expertise of professionals who specialize in managing complex IT environments.
As a CTO, I understand the importance of having a skilled team that can handle diverse technology domains, from network management and system administration to cybersecurity and cloud computing.
Outsourcing partners bring in strategic cloud architecture design that aligns with your business goals:
Hybrid or multi-cloud setups for redundancy and compliance
Auto-scaling and elasticity to handle traffic spikes seamlessly
Disaster recovery and high availability architectures to minimize downtime risks
Cost optimization strategies like reserved instances, spot instances, and resource right-sizing
These capabilities are critical as over 86% of companies have increased their cloud initiatives in the last two years, according to Gartner, but lack in-house expertise to fully leverage them.
"Gart finished migration according to schedule, made automation for infrastructure provisioning, and set up governance for new infrastructure. They continue to support us with Azure. They are professional and have a very good technical experience"
Under NDA, Software Development Company
Enhanced Focus on Core Competencies
Outsourcing IT infrastructure liberates businesses from the burden of managing complex technical operations, allowing them to focus on their core competencies. I firmly believe that organizations thrive when they can allocate their resources towards activities that directly contribute to their strategic goals.
By entrusting the management and maintenance of IT infrastructure to a trusted partner like Gart, businesses can redirect their internal talent and expertise towards innovation, product development, and customer-centric initiatives.
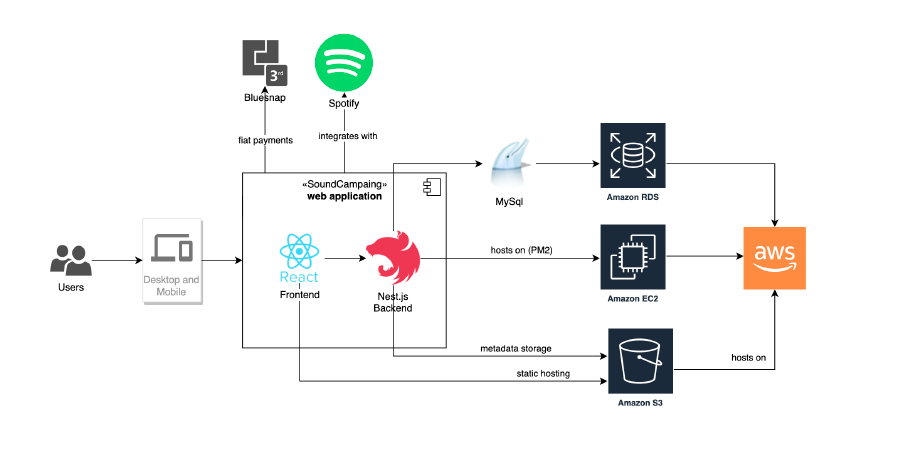
For example, SoundCampaign, a company focused on their core business in the music industry, entrusted Gart with their infrastructure needs.
We upgraded the product infrastructure, ensuring that it was scalable, reliable, and aligned with industry best practices. Gart also assisted in migrating the compute operations to the cloud, leveraging its expertise to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
One key initiative undertaken by Gart was the implementation of an automated CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipeline using GitHub. This automation streamlined the software development and deployment processes for SoundCampaign, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency. It allowed the SoundCampaign team to focus on their core competencies of building and enhancing their social networking platform, while Gart handled the intricacies of the infrastructure and DevOps tasks.
"They completed the project on time and within the planned budget. Switching to the new infrastructure was even more accessible and seamless than we expected."
Nadav Peleg, Founder & CEO at SoundCampaign
Cost Savings and Budget Predictability
Managing an in-house IT infrastructure can be a costly endeavor. By outsourcing, businesses can reduce expenses associated with hardware and software procurement, maintenance, upgrades, and the hiring and training of IT staff.
As an outsourcing provider, Gart has already made the necessary investments in infrastructure, tools, and skilled personnel, enabling us to provide cost-effective solutions to our clients. Moreover, outsourcing IT infrastructure allows businesses to benefit from predictable budgeting, as costs are typically agreed upon in advance through service level agreements (SLAs).
"We were amazed by their prompt turnaround and persistency in fixing things! The Gart's team were able to support all our requirements, and were able to help us recover from a serious outage."
Ivan Goh, CEO & Co-Founder at BeyondRisk
Scaling Quickly with Market Demands
Business is dynamic. Whether it’s expanding into new markets, onboarding thousands of new users overnight, or handling seasonal traffic spikes – your IT infrastructure must scale without delays or failures.
With outsourcing, companies have the flexibility to quickly adapt to these changing requirements. For example, Gart's clients have access to scalable resources that can accommodate their evolving needs.
Outsourcing partners provide:
Elastic server capacity: Add or remove resources instantly.
Flexible storage solutions: Expand databases or object storage without hardware procurement delays.
Network optimization: Enhance bandwidth and connectivity as user demands grow.
For example, Twilio scaled its COVID-19 contact tracing platform rapidly by outsourcing infrastructure to cloud providers. This automatic scaling ensured millions of people were contacted efficiently without infrastructure bottlenecks, a feat nearly impossible with only internal teams.
Whether it's expanding server capacity, optimizing network bandwidth, or adding storage, outsourcing providers can swiftly adjust the infrastructure to support business growth. This scalability and flexibility provide businesses with the agility necessary to respond to market dynamics and seize growth opportunities.
Robust Security Measures
Advanced Threat Detection and Proactive Security
Imagine guarding a fortress with outdated locks and untrained guards. That’s the risk many companies face managing security internally without dedicated resources.
Outsourcing IT infrastructure brings enterprise-level security expertise and tools within reach for businesses of all sizes. Here’s how:
24/7 Monitoring and Threat DetectionOutsourcing partners deploy advanced Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools, intrusion detection systems, and AI-powered threat analytics to monitor your infrastructure around the clock.
Regular Security Audits and Compliance AuditsThey conduct periodic vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and compliance checks to ensure you meet industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 without adding internal workload.
Data Encryption and Access ControlsProviders implement end-to-end encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit, along with strict identity and access management policies to control who accesses sensitive systems.
As the CTO of Gart, I prioritize the implementation of robust security measures, including advanced threat detection systems, data encryption, access controls, and proactive monitoring. We ensure that our clients' sensitive information remains protected from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
"The result was exactly as I expected: analysis, documentation, preferred technology stack etc. I believe these guys should grow up via expanding resources. All things I've seen were very good."
Grigoriy Legenchenko, CTO at Health-Tech Company
Piyush Tripathi About the Benefits of Outsourcing Infrastructure
Looking for answers to the question of IT infrastructure outsourcing pros and cons, we decided to seek the expert opinions on the matter. We reached out to Piyush Tripathi, who has extensive experience in infrastructure outsourcing.
Introducing the Expert
Piyush Tripathi is a highly experienced IT professional with over 10 years of industry experience. For the past ten years, he has been knee-deep in designing and maintaining database systems for significant projects. In 2020, he joined the core messaging team at Twilio and found himself at the heart of the fight against COVID-19. He played a crucial role in preparing the Twilio platform for the global vaccination program, utilizing innovative solutions to ensure scalability, compliance, and easy integration with cloud providers.
What are the potential benefits of IT infrastructure outsourcing?
High scale: I was leading Twilio COVID-19 platform to support contact tracing. This was a fairly quick announcement as the state of New York was planning to use it to help contact trace millions of people in the state and store their contact details. We needed to scale and scale fast. Doing it internally would have been very challenging, as demand could have spiked, and our response could not have been swift enough to respond. Outsourcing it to a cloud provider helped mitigate that; we opted for automatic scaling, which added resources in the infrastructure as soon as demand increased. This gave us peace of mind that even when we were sleeping, people would continue to get contacted and vaccinated.
Potential Risks and Benefits of IT Infrastructure Outsourcing
While outsourcing unlocks significant benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential risks:
Risks:
Infra domain knowledge: if you outsource infra, your team could lose knowledge of setting up this kind of technology. for example, during COVID 19, I moved the contact database from local to cloud so overtime I anticipate that next teams would loose context of setting up and troubleshooting database internals since they will only use it as a consumer.
Limited direct control: since you outsource infrastructure, data, business logic and access control will reside in the provider. in rare cases, for example using this data for ML training or advertising analysis, you may not know how your data or information is being used.
Vendor Lock-in:Relying heavily on a single outsourcing provider may create challenges if switching vendors later becomes necessary. Migrating away can be complex and costly.
Compliance Risks:Data privacy regulations require careful vendor selection. Not knowing how your vendor stores, processes, or uses your data could pose legal and reputational risks, especially for sectors like healthcare and finance.
Gains:
Lower maintenance: since you don't have to keep a whole team, you can reduce maintenance overhead. For example, during my project in 2020, I was trying to increase the adoption of Sendgrid SDK program, and we were able to send 50 billion emails without much maintenance hassle. The reason was that I was working on moving a lot of data pipelines, MTA components to the cloud and which reduced a lot of maintenance.
High scale: this is the primary benefit; traditional infrastructure needs people to plan and provision infrastructure in advance. When I led the project to move our database to the cloud, it was able to support storing a huge amount of data. In addition, it would automatically scale up and down depending on the demand. This was a huge benefit for us because we didn't have to worry that our provisioned infrastructure might not be enough for sudden spikes in demand. Due to this, we were able to help over 100+ million people worldwide get vaccinated.
What are the potential benefits for the internal IT team if they choose to outsource infrastructure?
Reduced Headcount: Outsourcing infrastructure could potentially decrease the need for staff dedicated to its maintenance and control, thus leading to a reduction in headcount within the internal IT team.
Increased Collaboration: If issues arise, the internal IT team will need to collaborate with the external vendor and abide by their policies. This process can create a new dynamic of interaction that the team must adapt to.
Limited Control: The IT team may face additional challenges in debugging issues or responding to audits due to the increased bureaucracy introduced by the vendor. This lack of direct control may impact the team's efficiency and response times.
Types of IT Infrastructure Outsourcing
Outsourcing isn’t a one-size-fits-all strategy. Here are the most common types:
Full Outsourcing
This involves outsourcing the entire IT infrastructure management to an external provider. The vendor handles:
Hardware and software procurement
Installation and configuration
Maintenance, monitoring, and optimization
Security and compliance
Best for:Small to mid-sized businesses that lack internal IT expertise or want to focus entirely on core business functions.
Managed Services
Here, businesses maintain ownership of their infrastructure but outsource specific operational tasks to managed service providers (MSPs), such as:
Network monitoring
Security management
Backup and disaster recovery
Best for:Companies that want to retain partial control but reduce operational burdens and ensure expert management of critical components.
Cloud Infrastructure Outsourcing
With cloud computing’s rise, many companies outsource cloud architecture design, deployment, optimization, and ongoing management to specialized partners.
Best for:Organizations migrating to AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud and lacking certified cloud architects internally to ensure cost-effective and secure deployments.
The Process for Outsourcing IT Infrastructure
Gart aims to deliver a tailored and efficient outsourcing solution for the client's IT infrastructure needs. The process encompasses thorough analysis, strategic planning, implementation, and ongoing support, all aimed at optimizing the client's IT operations and driving their business success.
Free Consultation
Project Technical Audit
Realizing Project Targets
Implementation
Documentation Updates & Reports
Maintenance & Tech Support
The process begins with a free consultation where Gart engages with the client to understand their specific IT infrastructure requirements, challenges, and goals. This initial discussion helps establish a foundation for collaboration and allows Gart to gather essential information for the project.
Then Gart conducts a comprehensive project technical audit. This involves a detailed analysis of the client's existing IT infrastructure, systems, and processes. The audit helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, providing valuable insights to tailor the outsourcing solution.
Based on the consultation and technical audit, we here at Gart work closely with the client to define clear project targets. This includes establishing specific objectives, timelines, and deliverables that align with the client's business objectives and IT requirements.
The implementation phase involves deploying the necessary resources, tools, and technologies to execute the outsourcing solution effectively. Our experienced professionals manage the transition process, ensuring a seamless integration of the outsourced IT infrastructure into the client's operations.
Throughout the outsourcing process, Gart maintains comprehensive documentation to track progress, changes, and updates. Regular reports are generated and shared with the client, providing insights into project milestones, performance metrics, and any relevant recommendations. This transparent approach allows for effective communication and ensures that the project stays on track.
Gart provides ongoing maintenance and technical support to ensure the smooth operation of the outsourced IT infrastructure. This includes proactive monitoring, troubleshooting, and regular maintenance activities. In case of any issues or concerns, Gart's dedicated support team is available to provide timely assistance and resolve technical challenges.
Evaluating the Outsourcing Vendor: Ensuring Reliability and Compatibility
When evaluating an outsourcing vendor, it is important to conduct thorough research to ensure their reliability and suitability for your IT infrastructure outsourcing needs. Here are some steps to follow during the vendor checkup process:
Google Search
Begin by conducting a Google search of the outsourcing vendor's name. Explore their website, social media profiles, and any relevant online presence. A well-established outsourcing vendor should have a professional website that showcases their services, expertise, and client testimonials.
Industry Platforms and Directories
Check reputable industry platforms and directories such as Clutch and GoodFirms. These platforms provide verified reviews and ratings from clients who have worked with the outsourcing vendor. Assess their overall rating, read client reviews, and evaluate their performance based on past projects.
Read more: Gart Solutions Achieves Dual Distinction as a Clutch Champion and Global Winner
Freelance Platforms
If the vendor operates on freelance platforms like Upwork, review their profile and client feedback. Assess their ratings, completion rates, and feedback from previous clients. This can provide insights into their professionalism, technical expertise, and adherence to deadlines.
Online Presence
Explore the vendor's presence on social media platforms such as Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter. Assess their activity, engagement, and the quality of content they share. A strong online presence indicates their commitment to transparency and communication.
Industry Certifications and Partnerships
Check if the vendor holds any relevant industry certifications, partnerships, or affiliations.
Technical Expertise:Review their team’s skills across infrastructure domains – servers, networks, cloud, security, and automation.
Cultural Fit and Communication:Effective communication ensures smooth collaboration. Assess their language proficiency, time zone overlap, and responsiveness during initial consultations.
Scalability and Flexibility:Check if they can scale resources quickly to match your evolving business needs.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs):Evaluate guarantees on uptime, issue resolution times, data security, and exit processes.
By following these steps, you can gather comprehensive information about the outsourcing vendor's reputation, credibility, and capabilities. It is important to perform due diligence to ensure that the vendor aligns with your business objectives, possesses the necessary expertise, and can be relied upon to successfully manage your IT infrastructure outsourcing requirements.
Why Ukraine is an Attractive Outsourcing Destination for IT Infrastructure
Ukraine has emerged as a prominent player in the global IT industry. With a thriving technology sector, it has become a preferred destination for outsourcing IT infrastructure needs.
Ukraine is renowned for its vast pool of highly skilled IT professionals. The country produces a significant number of IT graduates each year, equipped with strong technical expertise and a solid educational background. Ukrainian developers and engineers are well-versed in various technologies, making them capable of handling complex IT infrastructure projects with ease.
One of the major advantages of outsourcing IT infrastructure to Ukraine is the cost-effectiveness it offers. Compared to Western European and North American countries, the cost of IT services in Ukraine is significantly lower while maintaining high quality. This cost advantage enables businesses to optimize their IT budgets and allocate resources to other critical areas.
English proficiency is widespread among Ukrainian IT professionals, making communication and collaboration seamless for international clients. This proficiency eliminates language barriers and ensures effective knowledge transfer and project management. Additionally, Ukraine shares cultural compatibility with Western countries, enabling smoother integration and understanding of business practices.
Long Story Short
IT infrastructure outsourcing empowers organizations to streamline their IT operations, reduce costs, enhance performance, and leverage external expertise, allowing them to focus on their core competencies and achieve their strategic goals.
By delegating complex infrastructure management to specialized providers, businesses can:
Access advanced expertise and technologies
Scale flexibly with market demands
Strengthen cybersecurity and compliance
Focus internal teams on strategic innovation
Optimize costs with predictable budgets
In a world where digital resilience defines market leadership, outsourcing IT infrastructure is your ticket to agility, efficiency, and sustainable success.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your IT infrastructure through outsourcing? Reach out to us and let's embark on a transformative journey together!