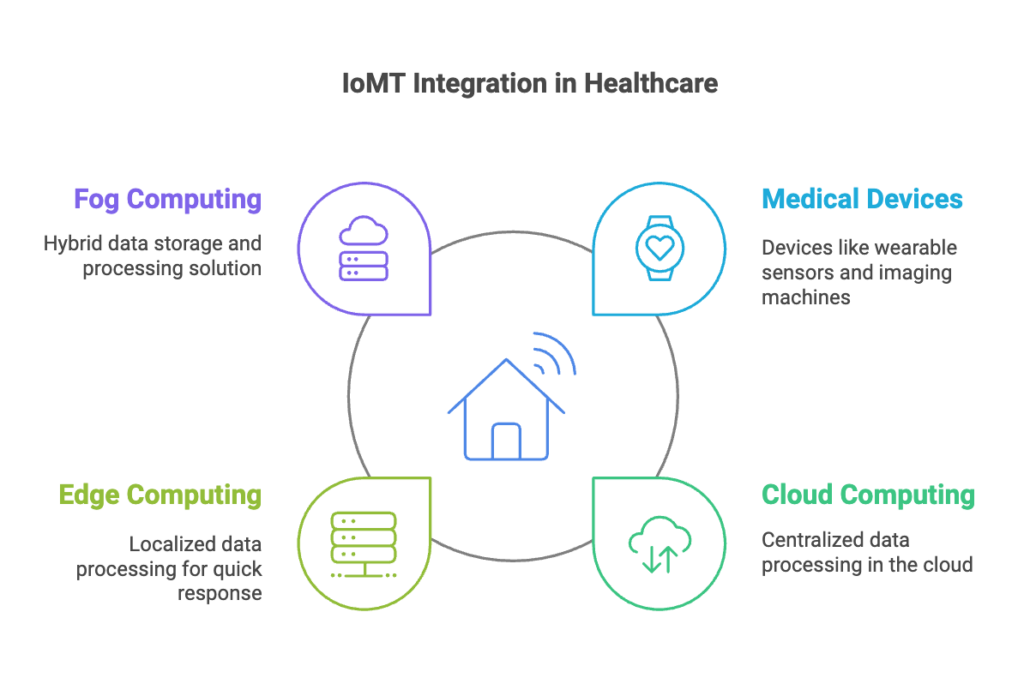
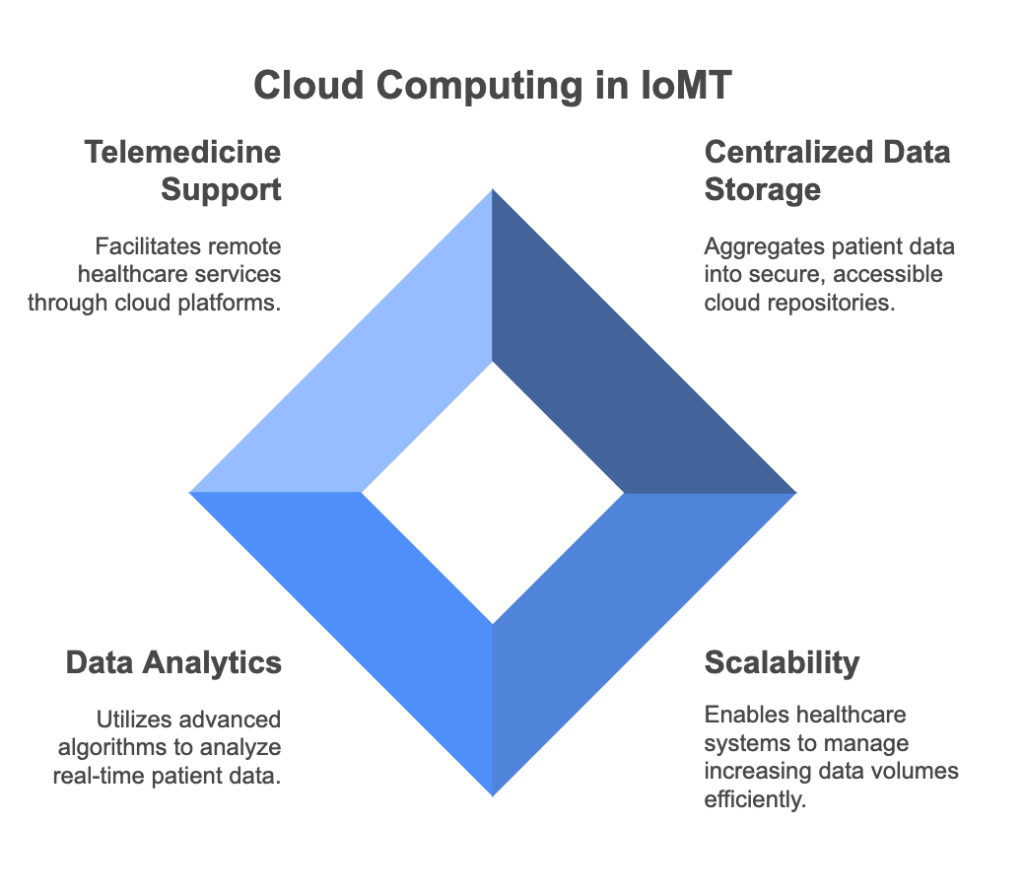
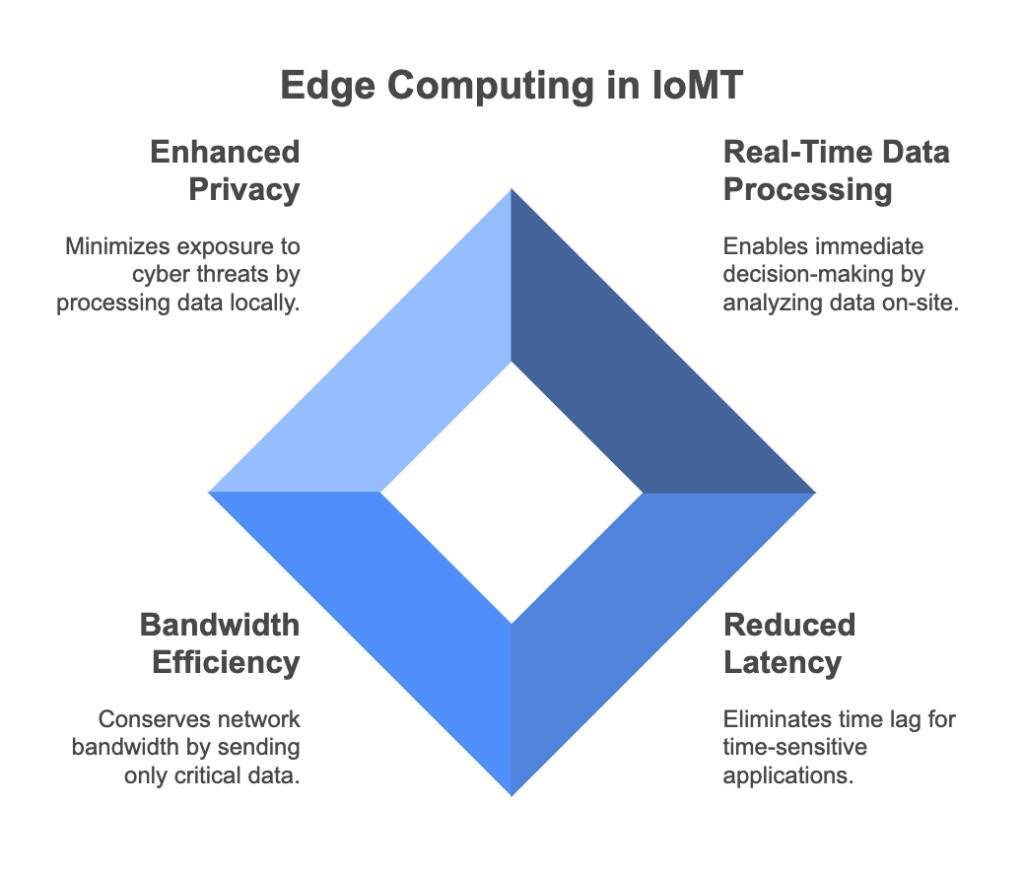
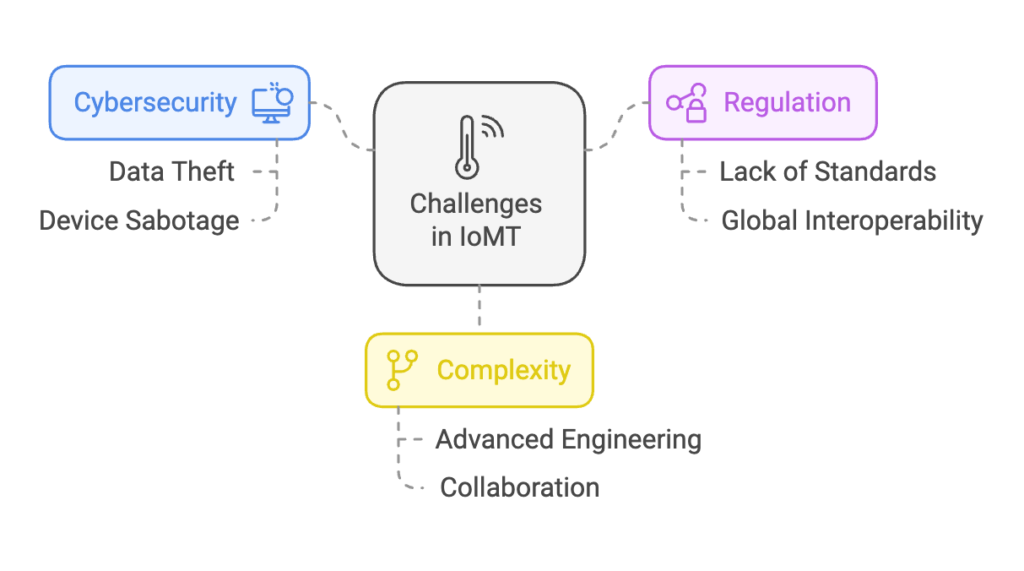
The healthcare sector is gearing up for big changes, and cloud technology is quickly becoming a vital part of its IT backbone. As data demands grow and patient care and security needs become more complex, the cloud offers a scalable, efficient solution to improve healthcare operations.
In this article, we’ll dive into how cloud computing is reshaping healthcare IT—covering what it is, the main challenges, practical applications, and the game-changing potential.
Defining Cloud for Healthcare
"A cloud-based architecture can help overcome many of these challenges, turning IT from a backend support function into a strategic enabler of healthcare."
Jason Jones
The term “cloud” is often associated with innovation but also confusion, as various industries interpret it differently. In healthcare, cloud computing refers to delivering IT services—storage, applications, and networking—through remote servers rather than traditional on-premise systems.
Private Cloud: internal infrastructure managed by an organization.
Public Cloud: external services, e.g., AWS, Azure, offering flexible, on-demand resources but with security considerations.
Hybrid Cloud: combination of private and public, enabling flexible use for storage, scalability, and backup.
Cloud technology can be configured in several ways to meet the specific needs of healthcare providers:
Private Cloud
Managed internally within the organization, a private cloud offers control and security for sensitive healthcare data, ensuring that resources are exclusively used by the organization.
Public Cloud
"In healthcare, especially, we need systems that are horizontally and infinitely scalable based on organizational needs."
Tony Nunes, Pharmacoepidemiologist, Assistant Professor
Hosted by third-party providers like AWS or Microsoft Azure, public clouds offer scalable resources on demand, though concerns about data privacy and security often restrict their use for healthcare’s most sensitive information.
Hybrid Cloud
"The hybrid cloud approach really has become something that’s evolving to a point where today, a majority of healthcare providers...are looking to balance between an on-prem private cloud solution and a hybrid cloud public workload solution."
Chris Mohen
Combining private and public cloud, a hybrid model provides flexibility by allowing healthcare providers to scale with external resources while maintaining strict control over critical data.
For healthcare, the hybrid cloud often represents an ideal balance, offering an adaptable infrastructure that aligns with data privacy regulations while providing scalability. Steven Lazer, CTO of Healthcare at Dell EMC, suggests that healthcare has essentially been engaging in cloud practices for years under different labels, such as affiliate services, where remote access was given to necessary services
Lazer advocates for a “cloud-smart” approach, where healthcare organizations strategically place applications in the cloud or on-premises based on each application's unique needs. This model enhances flexibility, scalability, and data security while supporting both traditional and emerging healthcare needs.
Key Challenges in Cloud Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, healthcare’s journey to the cloud is marked by challenges that require careful planning and robust solutions:
Data Privacy and Security
Healthcare data is a prime target for cyberattacks, so security is essential. Although cloud providers offer strong protections, healthcare organizations must ensure strict access controls and encryption to comply with regulations like HIPAA.
Legislations related to Cloud security and healthcare:
Legal RequirementsPrivacy & Data ProtectionCybersecurityCloud SecurityHealthEU- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)- Network and Information Security Directive (NIS Directive)- None- Medical Device Regulation (MDR)- European Union Cybersecurity Act- Electronic Cross-Border Health Services Directive- Medical Device Directive (MDD)National- National data protection or privacy laws- National information and data security laws- National cloud security laws- National healthcare-related laws for data protection and cybersecurity
Security remains a paramount concern as healthcare organizations adopt cloud technologies:
Data Encryption: Both symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods are essential to secure data at rest and in transit.
Access Controls: Multi-factor authentication and role-based access control ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive patient information.
Compliance with Regulations: Healthcare organizations must comply with frameworks such as HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in Europe, and local privacy laws. Ensuring compliance helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
Continuous Monitoring: Tools such as Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms are vital for identifying and responding to threats in real-time.
Costs
Setting up and managing a cloud environment can be expensive, especially for hybrid models. But as bandwidth costs drop and security improves, the long-term gains in efficiency and scalability are making cloud solutions more affordable.
"As a CFO, I no longer am over-investing in our IT environments... Cloud has allowed us to consolidate and use only what is needed, without pools of unused storage or compute capacity."
Tony Nunes
Resistance to Change
Switching to cloud disrupts traditional IT roles, needing collaboration between IT and clinical teams. This shift requires cultural adjustments to align data access with security needs.
The bigger challenge isn’t technology—we can solve a lot of problems with technology—but rather, it’s the people and the process.
Jason Jones
Knowledge Gaps
Some organizations hesitate to adopt cloud tech due to limited understanding of how it integrates or improves their current systems. Demonstrating real-world successes can help show the cloud’s potential.
Dan Trott, a healthcare strategist with Dell EMC, highlights that while security used to be the foremost concern, now the greatest obstacle is educating stakeholders on how cloud solutions healthcare can work for them and how they can maximize cloud-based resources for better outcomes.
Healthcare Cloud Use Cases
The potential applications for cloud in healthcare are vast, ranging from managing data-heavy imaging systems to electronic health records (EHRs) and research initiatives.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Cloud-based EHRs enable seamless sharing of patient data among healthcare providers. Advanced encryption and access controls ensure data privacy and security.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: Cloud technologies facilitate remote consultations and monitoring, expanding healthcare access in underserved regions. For instance, blockchain-based models enhance secure data sharing in telemedicine platforms.
Health Management and Predictions: Predictive analytics powered by cloud computing aids in identifying health trends and managing chronic diseases. Machine learning algorithms on cloud platforms have been used for mortality predictions and early disease detection.
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics: Cloud platforms allow the storage and analysis of high-resolution imaging data, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Collaboration and Research: Cloud services enable collaboration across healthcare providers, enhancing clinical research and innovation. Centralized platforms support multi-disciplinary teams in analyzing data efficiently.
Patient Population Analysis with Cloud Computing
Cloud computing revolutionizes patient population analysis by providing robust tools for aggregating, processing, and analyzing vast datasets from diverse demographics. Through centralized storage of electronic health records (EHRs), patient demographics, and social determinants of health, cloud platforms enable healthcare providers to identify disease patterns, predict outbreaks, and design targeted public health interventions. Advanced analytics tools hosted on cloud platforms, combined with real-time data from Internet of Things (IoT) devices, allow healthcare systems to monitor patient vitals and derive insights at scale.
The integration of Container as a Service (CaaS) and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines further enhances population health analytics. CaaS enables the deployment and scaling of containerized applications, allowing healthcare organizations to run complex analytics tools and machine learning models efficiently. CI/CD ensures these applications are continuously updated and refined, fostering innovation and reducing downtime for critical services. For instance, a population health model can seamlessly incorporate new data sources or algorithm improvements without disrupting operations.
Moreover, cloud platforms promote interoperability, consolidating data from clinics, laboratories, and pharmacies into a unified system. This integrated approach helps address disparities in healthcare delivery by enabling targeted interventions in underserved populations. Security measures, such as encryption and pseudonymization, ensure patient privacy while permitting researchers and policymakers to access de-identified datasets for broader health studies. By leveraging CaaS and CI/CD alongside cloud computing, healthcare systems can transition from reactive to proactive care strategies, improving public health outcomes with greater agility and efficiency.
Medical Imaging
"Medical imaging represents 80-85% of the total amount of data any one hospital has to manage and store."
Dan Trott
Medical imaging is essential in healthcare, helping doctors diagnose, plan treatments, and monitor progress. As imaging tech has advanced, so has the size and complexity of imaging data, creating new challenges around storage, access, and security.
Here’s how cloud storage is transforming medical imaging:
Easier Storage & ScalabilityCloud storage handles large amounts of imaging data without the need for physical hardware. This scalability is especially helpful for smaller facilities that don’t want to invest in new servers as data needs grow.
Better Security & ComplianceLeading cloud providers offer strong security, like encryption and multi-factor authentication, often surpassing what on-site systems can do. These solutions are designed to meet healthcare regulations, making compliance easier.
Improved Data Sharing & CollaborationCloud-based imaging supports easy data sharing across healthcare facilities, which is crucial for patients seeing multiple providers. This ensures every provider has access to the same, up-to-date images.
Disaster Recovery & BackupCloud solutions automatically back up imaging data across locations, protecting against data loss from hardware failures or natural disasters.
Fast Image AccessStoring images in the cloud allows providers to access them instantly from anywhere, which is especially valuable in emergencies when quick access can impact patient outcomes.
Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are digital versions of patient charts and are a key part of modern healthcare. Unlike paper records, EHRs provide a complete, real-time, and secure way to manage patient information across different healthcare settings.
Using the cloud to store and manage EHRs is a big step forward, though it’s complicated by strict privacy laws and the need for strong security. While some providers offer hosted models, fully cloud-based EHR solutions are still a challenge due to the sensitivity of patient data. Here’s how cloud technology is helping to advance EHRs:
Scalability and Cost-EffectivenessCloud-based EHRs are more affordable and scalable, making them ideal for smaller practices and rural healthcare providers. By storing data in the cloud, organizations can reduce physical storage needs and avoid the high costs of running their own servers and data centers.
Improved Data Sharing and InteroperabilityCloud systems allow data to be accessed from anywhere, supporting better interoperability across healthcare facilities. This enables patient data to follow the patient through different providers, ensuring consistent care no matter the location.
"What the cloud provides is a way of outsourcing that information... putting it into a very large data center that has significant cost efficiency and volume efficiency."
Dan Trott
Enhanced Data SecurityMany cloud providers offer top-level security features like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time monitoring. These protections often go beyond what traditional on-site systems provide, addressing security concerns while meeting healthcare regulations.
Automatic Updates and MaintenanceCloud-based EHR providers handle system updates and maintenance, so healthcare providers always have the latest security and functionality enhancements without disrupting their workflow. This is especially helpful for organizations without dedicated IT resources.
Disaster Recovery and Data BackupCloud storage includes built-in data backup and disaster recovery options, meaning patient information stays safe even if there’s a hardware failure or natural disaster. This added redundancy is essential for protecting patient data and keeping services running smoothly.
Clinical Research and Development
A cloud-based infrastructure is valuable for research-intensive organizations as it allows researchers to quickly scale resources for data processing. Data silos can be eliminated, providing a more seamless research process and helping projects launch faster. For instance, grants often require complex data environments, which can be set up more efficiently in a cloud environment.
These use cases demonstrate how the cloud supports efficiency and innovation by reducing physical storage needs and enhancing data security.
Cloud as a Disruptor in Healthcare IT
The move to cloud computing is shaking up healthcare IT and redefining traditional roles. With the cloud, healthcare providers can use “bimodal IT,” where stable systems work alongside fast, DevOps-driven setups. This approach meets both steady operational needs and the quick-paced demands of data-driven patient care.
"This concept of 'bimodal IT'—where you can use infrastructure in a consolidated way while still delivering essential services—really enables healthcare to enhance the quality and value of the care system."
Steven Lazer
Changing IT Roles
Cloud computing in healthcare pushes IT teams to move from specialized, separate roles (like storage or security) to a more service-oriented and collaborative approach. This shift brings IT closer to clinical workflows, enabling faster data sharing and quicker response times for patient care.
Cost Savings
Consolidating IT into unified cloud platforms cuts down on “maintenance-only” spending. For example, Dell EMC estimates significant cost reductions when switching to cloud systems, allowing more resources to go toward innovative patient care solutions.
Delivering Higher Value
With cloud solutions, healthcare IT can focus on real impact rather than routine tasks. For example, a developer environment can be set up and taken down in just 48 hours, allowing rapid innovation while keeping resources directed at high-impact areas.
"The next step of evolution we’re going to see in cloud is around the concept of a virtual private cloud—using shared infrastructure but isolated resources."
Steven Lazer
Мirtual private clouds are the next phase, where organizations can gain the scalability benefits of public cloud while maintaining the security of private cloud through isolated resources on shared infrastructure.
Cloud computing in healthcare is rapidly evolving, with emerging technologies enhancing its capabilities:
Zero Trust Architecture: Adopting a Zero Trust model ensures no implicit trust for any user or system, enhancing security in cloud environments.
AI and Machine Learning: Real-time threat detection and advanced predictive models are becoming integral to healthcare cloud solutions.
Blockchain Integration: Blockchain provides decentralized and immutable data storage, enhancing trust and transparency in healthcare operations.
Confidential Computing: Techniques to secure data during processing are gaining traction, enabling sensitive operations without exposing data to risks.
Cloud is disrupting the old IT model, building a fast, scalable, and integrated infrastructure that directly supports better care delivery.
Conclusion: The Future of Cloud in Healthcare
"Cloud really becomes a disruptor of the status quo within IT."
Tony Nunes
As healthcare organizations continue adopting cloud solutions, they are poised to deliver more reliable, efficient, and scalable services to patients. The cloud enables them to break free from traditional IT limitations, reduce costs, enhance data security, and improve operational resilience. As demonstrated by the success at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center and other institutions, healthcare is ready to move into a new era where the cloud not only supports IT but also becomes integral to patient-centered care and operational excellence.
Through a thoughtful approach to cloud adoption, healthcare organizations can unlock new potential for innovation, efficiency, and patient satisfaction, transforming how care is delivered in a digitally connected world.
The following experts contributed valuable insights and perspectives, which were instrumental in the creation of this article:
Tony Nunes: 22+ years in healthcare IT.
Chris Mohen: Experience in clinical areas and transformative IT solutions.
Steven Lazer: Global Healthcare & Life Sciences CTO - Dell Technologies at Dell Technologies
Jason Jones: 15+ years, focusing on cloud strategies for healthcare.
Dan Trott: Extensive experience since 2010, working with clinical and IT solutions.

What is Digital Transformation in Healthcare?
Imagine walking into a hospital where your medical records are instantly accessible on a secure digital platform, doctors consult you virtually from anywhere, and AI systems analyze your blood tests to predict diseases before symptoms appear. That’s digital transformation in healthcare.
In simple terms, it refers to leveraging technology to revolutionize how healthcare is delivered, managed, and experienced. It involves integrating digital solutions like electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, AI diagnostics, IoT-connected devices, and robotic surgeries to improve patient care, operational efficiency, and medical outcomes.
Why is it Gaining Momentum Globally?
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated healthcare digitization, but the momentum continues due to:
Rising Patient Expectations:Today’s patients demand convenience, accessibility, and personalized care, just like their experiences with Amazon or Netflix.
Technological Advancements:AI, IoT, and big data analytics have matured, making them viable for large-scale healthcare applications.
Cost Pressures and Resource Constraints:Hospitals face financial constraints and staff shortages. Digital transformation optimizes workflows, reducing costs while improving quality.
Regulatory Push:Governments and health bodies globally are mandating secure digital health records, telemedicine, and interoperability standards to improve national healthcare systems.
A Statista report projects the global digital healthcare market to reach $504.4 billion by 2025, underscoring how essential digital transformation has become for competitive and efficient healthcare delivery.
88% of healthcare technology leaders prioritize improving the patient experience in their investments (according to a Deloitte survey)
This shift underscores the necessity for healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and administrative staff, to stay abreast of ongoing digital advancements.
Key Drivers of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Emerging Technologies Shaping Healthcare
Technological innovations are the backbone of healthcare’s digital transformation. Here’s how the main technologies are driving change:
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by:
Automating administrative tasks like record-keeping and billing
Enhancing predictive diagnostics by analyzing medical images for early disease detection
Personalizing treatment plans based on patient history, genetics, and lifestyle
Enabling AI-powered chatbots to handle appointment scheduling, symptom checks, and medication reminders, reducing the burden on human staff
For example, AI diagnostic platforms like Google DeepMind Health detect eye diseases with the same accuracy as ophthalmologists, enabling earlier intervention and better outcomes.
IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT-connected health devices include:
Wearables: Smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor heart rate, oxygen saturation, and sleep cycles, alerting users to anomalies.
Remote Patient Monitoring Devices: Track vitals for chronic patients, reducing hospital visits while enabling proactive care.
Connected Hospital Equipment: Optimize operations by tracking equipment usage, availability, and maintenance schedules.
This improves real-time patient monitoring, operational efficiency, and resource utilization, making healthcare delivery smarter and more responsive.
Robotics
Robotics in healthcare enables:
Minimally invasive surgeries: Robotic surgical systems like da Vinci Surgical System enhance precision, reducing recovery time and hospital stays.
Remote surgeries: Surgeons operate robotic instruments from distant locations, expanding access to specialized care globally.
3D Printing
3D printing is transforming:
Prosthetics: Creating customized, affordable prosthetics quickly for amputees.
Implants and Organs: Producing tailor-made implants and researching bioprinted organs for transplantation.
These emerging technologies are not just futuristic concepts – they are real-world solutions enhancing healthcare daily.
Changing Patient Expectations and Demographics
Today’s patients are digital natives, especially younger demographics who expect:
Online appointment booking
Access to digital medical records
Telehealth consultations
Personalized health recommendations
With over 5.3 billion internet users globally, healthcare providers must adapt to digital-first expectations to remain competitive and patient-centric, as the demand for digital healthcare services is rising.
Updated Regulations Driving Adoption
Governments worldwide are introducing regulations to support digital transformation:
HIPAA (US): Mandates data privacy and security for protected health information (PHI).
GDPR (EU): Enforces strict data protection rules for personal data, including health records.
ISO/IEC 27799: Provides guidelines for information security management in healthcare.
Compliance with these standards is not optional. Healthcare providers must adopt digital solutions with built-in security and privacy measures to avoid legal repercussions and build patient trust.
Gart guides you through every step of the compliance process, providing the expertise, tools, and support you need. Contact Us.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
1. Reduced Costs - automating administrative tasks and other processes allows healthcare providers to save time and money while enhancing patient care. Through digital transformation, workflows are streamlined, and operational efficiency is increased, which helps reduce overhead costs.
2. Optimized Workflow - digital transformation has enabled healthcare providers to optimize their workflows. Automating tasks like patient information management and appointment scheduling allows medical staff to focus more on delivering effective patient care. Additionally, digital tools such as AI-powered chatbots can handle simple patient interactions, reducing the burden on physicians.
3. Enhanced Patient Interaction - digital transformation has empowered healthcare providers to interact with patients more effectively. Innovative technologies enable health professionals to easily access patient records, aiding in better diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, digital solutions like telemedicine allow doctors to offer timely medical advice even when they are not physically present at the hospital or clinic.
4. Improved Administration - digitizing processes makes managing administrative tasks more efficient for healthcare organizations. Automation of activities like scheduling appointments, filing insurance claims, and maintaining accurate financial records reduces manual errors while improving accuracy and speed.
Challenges to Healthcare Digital Transformation
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Healthcare deals with highly sensitive patient data. Digital systems, if not secured, can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, risking:
Data breaches exposing personal health information
Compliance violations leading to hefty fines
Loss of patient trust and reputational damage
Implementing robust cybersecurity frameworks, encryption, and continuous monitoring is non-negotiable for digital health systems.
Resistance to Change within Organizations
Healthcare has traditionally been conservative in adopting new technologies. Reasons for resistance include:
Fear of disrupting established workflows
Lack of digital literacy among staff
Concerns about technology reliability during critical care situations
Change management, leadership support, and comprehensive staff training are essential to overcome this barrier.
Interoperability and Legacy System Integration
Most healthcare organizations run on legacy systems that do not integrate easily with modern digital applications. Challenges include:
Data silos are hindering unified patient views
Incompatibility with new software or cloud platforms
High costs and risks are associated with migrating from outdated systems
Adopting interoperability standards like HL7 FHIR and working with experienced technology partners can mitigate these challenges.
Skills Gaps and Staff Shortages
Digital transformation requires staff to be digitally proficient. However, many healthcare professionals:
Lack of training in new digital tools and platforms
Feel overwhelmed by technological complexity, which affects adoption rates
Continuous upskilling programs and user-friendly solutions can bridge the skills gap and enhance digital confidence among healthcare staff.
Successful Cases of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
1. Infrastructure Optimization and Data Management in Healthcare
Challenge
A health tech company came with outdated infrastructure that hindered efficient data management and slowed down critical operations. The existing system was not scalable and faced frequent downtimes, affecting the overall patient care experience.
Solution
Gart Solutions implemented a comprehensive infrastructure optimization strategy, including:
Modernizing legacy systems to enhance speed and scalability
Integrating cloud solutions for seamless, secure data management
Ensuring HIPAA compliance for patient data security
Enabling dynamic scaling to meet demand spikes efficiently
Impact
Faster data access, reduced downtimes, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced patient experiences.
Learn details from the Case Study.
2. CI/CD Pipelines and Infrastructure for E-Health Platform
Challenge
An e-health platform aimed to accelerate their development process and improve the reliability of their applications. However, they faced significant challenges with manual deployments, which were time-consuming and error-prone, leading to inconsistent performance and delayed updates.
Solution
Gart Solutions designed and implemented automated CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines tailored to the platform’s unique architecture.
Key implementation steps included:
Automated Build and Testing Pipelines:Code commits automatically triggered builds, testing suites, and static code analysis to catch bugs early.
Infrastructure Optimization:Upgraded and containerized infrastructure to support CI/CD operations efficiently with Kubernetes orchestration for scalability.
Deployment Automation:Introduced automated deployment scripts for seamless rollout of features across production and staging environments without downtime.
Monitoring and Rollback Strategies:Integrated real-time monitoring tools with automated rollback protocols to ensure rapid issue remediation in case of deployment failures.
Impact
Reduced deployment times from days to hours
Significantly minimized human errors, enhancing application stability
Improved development velocity, allowing frequent feature releases
Increased user satisfaction due to faster bug fixes and feature updates
This case demonstrates that CI/CD pipelines aren’t just DevOps best practices – they are strategic enablers of digital agility in healthcare platforms, ensuring compliance, security, and innovation at scale.
Struggling with digital transformation for your healthcare project? Get expert guidance and IT Consultancy for your project free of charge. “Quick wins” – guaranteed. Contact Us.
How Digital Transformation Enhances Patient Experience
Telehealth and Remote Consultations
Imagine consulting your doctor while sipping coffee at home, with prescriptions emailed within minutes. That’s the new healthcare reality.
Telehealth is among the most impactful transformations in healthcare, enabling:
Remote Consultations: Patients consult doctors without visiting clinics, saving time, reducing exposure to infections, and increasing accessibility for remote populations.
Mental Health Services: Telepsychiatry platforms provide discreet, accessible therapy sessions, crucial in an era of rising mental health challenges.
Chronic Disease Management: Regular remote check-ins for diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic conditions enable proactive care, preventing complications and hospital admissions.
During the pandemic, telehealth usage surged by over 154% compared to pre-pandemic levels (CDC data) and continues to grow as patients demand convenience and digital-first care experiences.
Personalized Medicine and AI Diagnostics
Digital transformation enables hyper-personalized treatments tailored to individual patient profiles by leveraging:
AI Diagnostics:AI algorithms analyze radiology images, blood tests, and genetic data to detect diseases earlier than traditional methods. For example, IBM Watson Health analyzes patient records to recommend tailored treatment options for oncologists.
Genomic Medicine:Advances in data processing allow healthcare providers to customize medications and treatments based on patient genetics, enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Predictive Analytics:Big data analytics predict patient risks, enabling early interventions for conditions like sepsis, cardiac events, or diabetic complications.
Patients no longer experience generic treatment plans but benefit from precision medicine designed for their unique biological and lifestyle factors, resulting in improved outcomes and satisfaction.
Conclusion
Healthcare organizations understand that digital transformation is crucial for enhancing healthcare services and strengthening patient relationships. Beyond technology investments, this transformation necessitates a shift in organizational culture and employee engagement, requiring enterprise-wide involvement.
Leading health organizations are adopting six key strategies to advance digitally:
Establish digital leadership and governance aligned with business strategies.
Cultivate a digital culture supported by leadership at all organizational levels.
Develop next-generation talent with a focus on workforce quality and quantity.
Integrate cybersecurity at all stages for robust risk management.
Emphasize flexibility and scalability to adapt to evolving technologies.
Implement measurable, accountable KPIs to track the success of digital initiatives.
Successfully navigating digital transformation in healthcare requires expertise and a business-first approach of IT Consulting.
Gart Solutions can guide healthcare providers through the process of Digital Transformation, accelerating the adoption of digital healthcare technologies and improvement of patient outcomes.
Contact Gart today to learn more about how we can help you solve the challenges of digital transformation in healthcare.

Healthcare technology solutions must navigate a complex web of regulations designed to protect patient data and maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Six significant compliance frameworks that healthcare providers and technology developers must adhere to are HIPAA, CCPA, GDPR, NIST, HiTECH, and PIPEDA.
Let’s take a closer look at each of those frameworks:
HIPAA Compliance
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a critical regulation for any technological solutions developed for the US market. Enacted in 1996, HIPAA mandates the protection of Protected Healthcare Information (PHI). It ensures that electronically protected health information maintains its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Compliance with HIPAA involves implementing robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse of patient data. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular audits to ensure that all processes align with HIPAA standards.
CCPA Compliance
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is another cornerstone of data protection in the United States. Although it primarily targets businesses operating in California, its implications are far-reaching, especially for healthcare providers handling large volumes of personal data. The CCPA focuses on transparency, requiring organizations to inform clients about the data collected, its purpose, and how it will be used. Patients have the right to request a detailed report of their data, demand its deletion, or opt out of data sharing with third parties. Ensuring CCPA compliance necessitates rigorous data management practices and responsive mechanisms to address patient requests promptly.
GDPR Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) represents one of the most stringent data protection laws globally. Introduced in Europe in 2018, GDPR applies to any healthcare apps and services operating within the European Union. Its reach extends to any company processing data related to EU citizens, regardless of the company's location. GDPR emphasizes patient consent, data minimization, and the right to be forgotten. Healthcare providers must ensure that data is collected and processed transparently, securely, and only for specified purposes. Non-compliance can result in severe financial penalties, making adherence to GDPR a top priority for any organization handling personal health data in Europe.
NIST Compliance
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) framework is another collection of standards, tools, and technologies designed to protect users’ data in the United States. According to research, 70% of surveyed organizations consider the NIST framework as the best cybersecurity practice, but many say it requires significant investment. The NIST framework is renowned for its comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, offering guidelines for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber incidents. Implementing NIST standards helps healthcare organizations bolster their security posture, ensuring they can safeguard sensitive health information effectively.
HiTech Compliance
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HiTECH) Act focuses more on the Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems' data security and is also valid in the United States. Enacted in 2009 and integrated into the HIPAA Final Omnibus Rule in 2013, HiTECH aims to promote the adoption and meaningful use of health information technology. Now, HIPAA-compliant applications are considered HiTECH compliant. This alignment simplifies compliance efforts for healthcare providers, ensuring they meet rigorous standards for data protection and patient privacy across multiple regulatory frameworks.
PIPEDA Compliance
The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) governs cloud storage and other medical software working in the Canadian market. Compliance with PIPEDA is crucial for any healthcare technology solutions operating in Canada. An interesting fact is that if your app is compliant with PIPEDA, it’s most likely compliant with the GDPR since these two laws are quite similar. PIPEDA emphasizes obtaining consent for data collection, ensuring data accuracy, and implementing safeguards to protect personal information. Compliance with PIPEDA helps organizations build trust with Canadian patients and ensures robust data protection practices.
Project Example: Gart's Expertise in ISO 27001 Compliance
Challenges:
Our client, Spiral Technology, faced significant challenges related to data security and cloud migration. The primary concerns were ensuring compliance with ISO 27001 standards and seamlessly transitioning their data and operations to the cloud without compromising security or disrupting their services.
Proposed Solutions:
ISO 27001 Compliance
Gart Solutions provided expert guidance and support to Spiral Technology, helping them achieve ISO 27001 certification. This involved implementing comprehensive security measures, conducting thorough risk assessments, and establishing robust data protection protocols.
Seamless Cloud Migration
To address the challenge of cloud migration, Gart Solutions developed a detailed migration plan that minimized downtime and ensured data integrity, utilizing advanced encryption and secure data transfer methods to protect sensitive information during the transition.
Continuous Monitoring and Audits
For post-migration, Gart Solutions set up continuous monitoring and regular audits to maintain ISO 27001 compliance and address any emerging security threats promptly.
More details about this Case Study – by the link.
Interested in being prepared for a compliance audit & certification - contact Us!
We will help you to understand the specifics and be prepared, as well as from a technology integration and data management perspective.
Conclusion
Compliance in healthcare is an ongoing challenge that requires constant vigilance, investment in technology, and a thorough understanding of regulatory requirements.
By adhering to HIPAA, CCPA, GDPR, NIST, HiTECH, and PIPEDA, healthcare providers can protect patient data, build trust, and avoid costly penalties. As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive in compliance efforts will remain essential for success in the healthcare industry.