What is SOX compliance and why does it matter?
SOX compliance refers to adhering to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, a U.S. law requiring public companies to maintain accurate financial reporting and strong internal controls. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, reputational damage, and executive liability.
SOX Compliance is all about following the rules set by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, a U.S. law designed to protect investors by making sure companies report their financial information accurately. This law came into play after major scandals like those at Enron and WorldCom shook public trust in corporate finances. By enforcing stronger internal controls and holding company executives accountable for the accuracy of their reports, SOX aims to improve transparency and prevent financial fraud in publicly traded companies, both in the U.S. and for some foreign firms listed here.
SOX Audit Penalties
Non-compliance with SOX can result in severe consequences, including:
- Financial Penalties: Companies may face fines or removal from stock exchanges for failure to comply.
- Personal Liability: Executives (CEOs, CFOs) may face personal fines up to $5 million and up to 20 years in prison for willfully submitting inaccurate financial reports.
- Reputational Damage: Non-compliance can result in a loss of investor confidence and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act: What is a SOX Audit?
Enforcement Date: July 30, 2002
Applicability: All U.S. public companies, companies looking to go public, and their auditors.
SOX applies to companies planning an initial public offering (IPO), including special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs). It mandates corporate reforms designed to increase accountability in financial disclosures, ensuring there is a transparent and reliable reporting process for investors.
The audit must be performed by an independent external auditor and cannot overlap with other company audits, ensuring there is no conflict of interest. If a company fails to meet the audit’s requirements, it may face significant legal and financial consequences, such as losing public trust and penalties.
The Purpose of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act
In the early 2000s, a series of financial scandals shattered public trust in large corporations. Fraudulent financial reporting at companies like Enron and WorldCom led to billions in losses for investors. In response, Congress passed the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) to restore faith in corporate America by mandating strict reforms in corporate governance and financial disclosure.
Main Goals of SOX:
- Improve the accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures.
- Hold senior executives accountable for the integrity of financial reports.
- Establish strong internal controls over financial reporting to detect fraud and irregularities.
- Enhance the role of independent auditors.
Key SOX Compliance Sections
Some of the critical sections of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act include:
- Section 302: Corporate responsibility for financial reports. This holds senior executives (CEO, CFO) accountable for the accuracy of financial reports.
- Section 401: Disclosures in financial reporting, ensuring transparency and accuracy in public financial records.
- Section 404: Management’s assessment of internal controls, which requires an annual audit to test and verify internal controls.
- Section 409: Real-time issuer disclosures, ensuring timely public notification of any material changes in financial condition.
- Section 802: Criminal penalties for altering or falsifying documents.
- Section 906: Corporate responsibility for accurate financial reports, enforcing transparency and holding executives accountable.
While SOX consists of 11 sections (or “titles”), Sections 302 and 404 are the most critical for compliance.
Section 302: Corporate Responsibility for Financial Reports
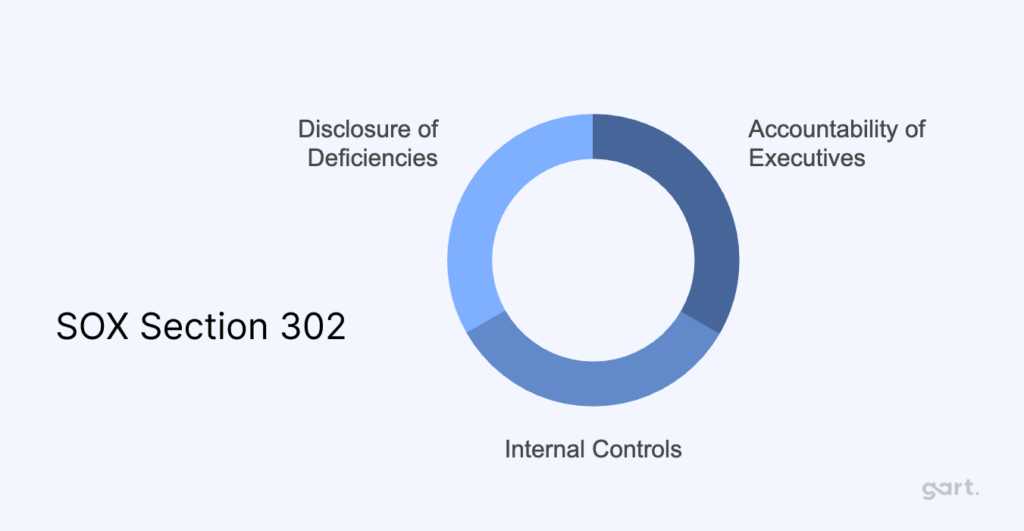
Accountability of Executives
This section mandates that the CEO and CFO are personally responsible for the accuracy of financial reports. They must certify that the company’s financial statements are accurate and complete.
Internal Controls
These executives must establish and maintain adequate internal controls to ensure accurate financial reporting. This includes evaluating and certifying the effectiveness of these controls.
Disclosure of Deficiencies
Any significant deficiencies, fraud, or material changes in internal controls must be disclosed in financial reports.
Section 404: Management Assessment of Internal Controls
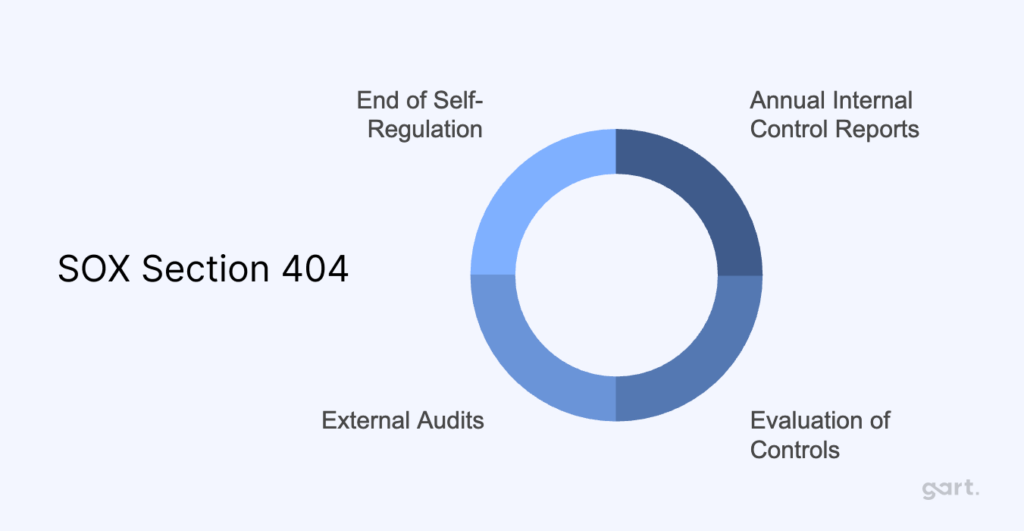
- Annual Internal Control Reports: Companies must include a detailed report on the effectiveness of internal controls over financial reporting in their annual reports.
- Evaluation of Controls: Management is responsible for assessing and maintaining adequate internal control structures and must provide an attestation on their effectiveness.
- External Audits: Independent auditors must review the company’s internal controls, ensuring they are functioning correctly. The audit must be performed with a high degree of professional skepticism and independence.
- End of Self-Regulation: The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) was established under SOX to oversee audit standards and prevent self-regulation, which had previously allowed fraud to go undetected.
The Importance of Internal Controls
A large part of SOX compliance centers on internal controls over financial reporting (ICFR). Internal controls refer to the processes and procedures that ensure the accuracy of a company’s financial information. A SOX audit examines the design and effectiveness of these controls.
Some key areas covered under SOX audits include:
- Access controls: Ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive financial information.
- Data management: Protecting data integrity and ensuring accurate financial reporting.
- IT controls: Verifying that the company’s IT systems (network, databases, applications) are secure and functioning properly.
SOX places heavy reliance on technology, particularly for managing IT assets and securing sensitive financial data.
SOX Compliance Checklist
Here’s a summary of what needs to be done to ensure compliance with SOX:
- Data Integrity: Implement measures to prevent financial data tampering.
- Audit Timeline: Establish and adhere to a clear audit schedule.
- Data Access Controls: Verify who has access to what data and ensure accountability.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regularly test the effectiveness of internal controls, not just during audits.
- Fraud Detection: Implement processes for identifying and responding to fraud attempts.
- Security Breach Reporting: Ensure transparency in reporting any security breaches.
- Automation: Implement automated controls wherever possible to enhance reliability and accuracy.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess risks to identify new or emerging threats to financial reporting.
The Challenges of SOX Compliance
Meeting SOX compliance can be tough for many companies, especially when it was first introduced. One of the biggest initial challenges was the high cost associated with compliance, particularly with Section 404. Implementing strong internal controls and conducting regular audits was not only time-consuming but also expensive.
As time has gone on, the costs of compliance have continued to rise. New requirements from external audits and the introduction of frameworks like COSO have added to the financial burden. Companies must invest heavily in technology and hire skilled personnel to keep up with these demands, leading to worries about the growing financial impact of SOX.
Another major hurdle is the significant resource burden that compliance creates. Organizations need talented individuals who can manage internal controls, conduct audits, and maintain detailed documentation. This is especially challenging for smaller companies, which often struggle to find the manpower and budget necessary to meet these compliance requirements.
How We at Gart Solutions Can Help with SOX Compliance
At Gart Solutions, we understand that navigating the challenges of SOX compliance can be daunting. That’s why we’re dedicated to helping businesses meet the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Here’s how we support your organization:
Cloud Infrastructure and Security
SOX compliance demands a secure infrastructure to protect financial data. We provide cloud services that ensure your data is safely stored and managed. Our key offerings include:
- Data Encryption: We encrypt your data both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: We implement multi-layered access management, like role-based access and multi-factor authentication, ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
- Audit Logs and Monitoring: We create detailed audit trails and monitoring systems to track user activities, essential for transparency.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup Solutions: We ensure your financial data is securely backed up and have a disaster recovery plan in place to prevent data loss.
DevOps Automation for SOX Compliance
Our DevOps practices introduce automation that is critical for maintaining compliance. Here’s how we enhance SOX compliance:
- Automated Deployment Pipelines: We streamline the deployment of financial reporting systems, minimizing the risk of errors and downtime.
- Configuration Management: We automate the setup of IT systems to ensure everything is consistently and correctly configured.
- Continuous Monitoring: We use DevOps tools to continuously monitor your environment and alert you to any unusual activity, aligning with SOX’s real-time reporting requirements.
- Compliance-as-Code: We apply Infrastructure-as-Code principles to maintain a compliant infrastructure that is always ready for audits.
IT Controls and Risk Management
Strong IT controls are vital for SOX compliance, particularly regarding data access and financial reporting. We help implement these controls by:
- User Access Management: We enforce strict access control to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to financial data.
- Change Management: We establish processes to track and document all changes to IT systems, which meets SOX requirements for well-documented internal controls.
- Audit-Ready Infrastructure: We create infrastructure solutions that are always optimized for compliance, making audits straightforward.
Data Integrity and Automation
We know that maintaining data integrity is crucial for financial reporting. Our services ensure your data is accurate and secure:
- Automated Data Validation: We implement automated checks that validate the accuracy of financial data before it’s reported.
- Automated Backup and Version Control: Our solutions automate data backups and track changes, making audits easier.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): We utilize CI/CD pipelines to systematically test and deploy updates, reducing the risk of manual errors.
Real-Time Monitoring and Incident Response
Monitoring financial systems and reporting incidents is essential under SOX. We provide real-time monitoring services to help you quickly address any risks:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): We use SIEM tools to give you real-time visibility into potential security incidents.
- Incident Response Automation: Our automation ensures that any issues are addressed swiftly, maintaining data integrity.
Audit Preparation and Reporting
Preparing for SOX audits can be overwhelming, but we make it easier:
- Automated Compliance Reports: We automate the generation of necessary reports for audits, such as access logs and system changes.
- Documenting Internal Controls: Our solutions help you document your processes, ensuring you’re always audit-ready.
- Audit Trail Maintenance: We ensure you have a complete and accurate audit trail for all financial transactions and system changes.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
Cybersecurity is crucial for SOX compliance, and our services help protect your financial data from breaches:
- Vulnerability Assessments: We regularly conduct assessments to identify and mitigate security risks in your financial systems.
- Data Encryption and Protection: We ensure all sensitive financial data is encrypted to safeguard it from unauthorized access.
- Compliance with IT Security Standards: We align your IT security protocols with industry standards that support SOX’s requirements.
By partnering with us at Gart Solutions, you can navigate the complexities of SOX compliance while enhancing your financial integrity and operational efficiency. Let us help you achieve and maintain compliance with confidence!
See how we can help to overcome your challenges









