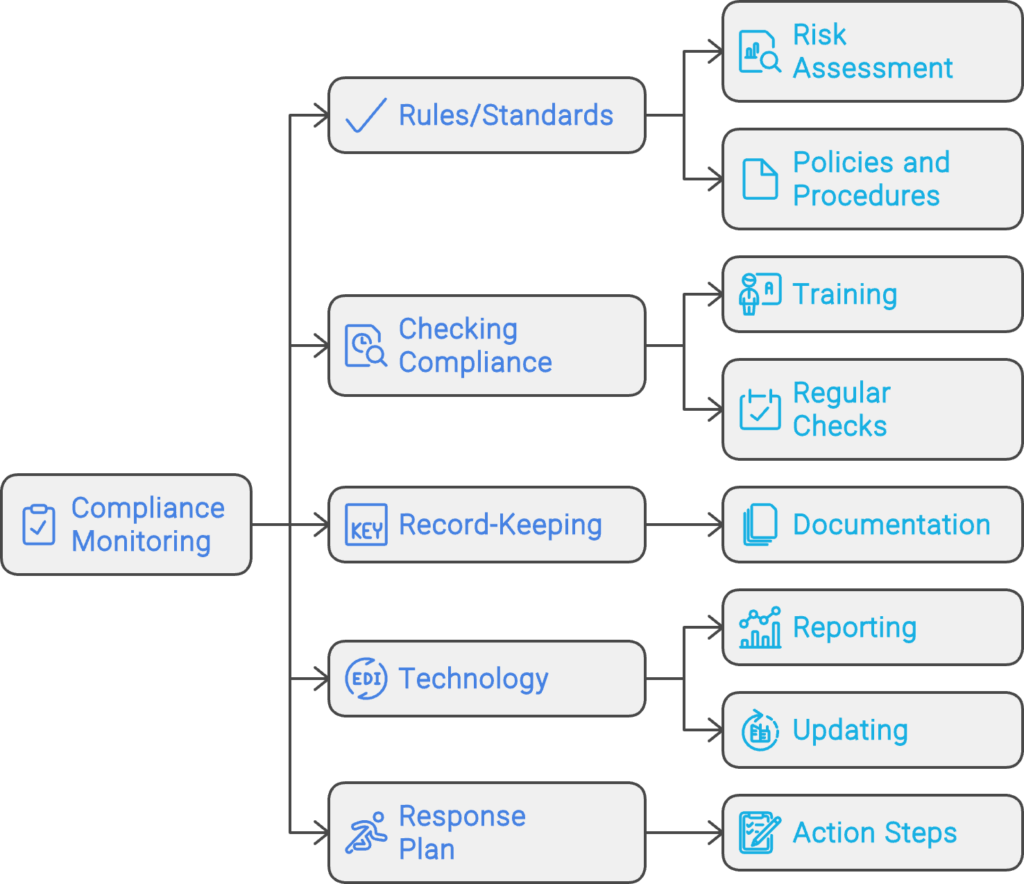
Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) focuses on keeping services reliable and scalable. A crucial part of this discipline is monitoring, which is where the concept of Golden Signals comes into play.
By focusing on just four “Golden Signals,” organizations can cut their incident response time in half. Golden Signals help teams quickly identify and diagnose issues within a system.
This post explores how SRE teams use these metrics — latency, errors, traffic, saturation—to drive reliability and streamline troubleshooting in complex microservices environments.
What are the four golden signals in SRE
SRE principles streamline monitoring by focusing on four key metrics—latency, errors, traffic, and saturation—collectively known as Golden Signals. Instead of tracking numerous metrics across different technologies, focusing on these four metrics helps in quickly identifying and resolving issues.
Latency:
Latency is the time it takes for a request to travel from the client to the server and back. High latency can cause a poor user experience, making it critical to keep this metric in check. For example, in web applications, latency might typically range from 200 to 400 milliseconds. Latency under 300 ms ensures good user experience; errors >1% necessitate investigation. Latency monitoring helps detect slowdowns early, allowing for quick corrective action.
Errors:Errors refer to the rate of failed requests. Monitoring errors is essential because not all errors have the same impact. For instance, a 500 error (server error) is more severe than a 400 error (client error) because the former often requires immediate intervention. Identifying error spikes can alert teams to underlying issues before they escalate into major problems.
Traffic:Traffic measures the volume of requests coming into the system. Understanding traffic patterns helps teams prepare for expected loads and identify anomalies that might indicate issues such as DDoS attacks or unplanned spikes in user activity. For example, if your system is built to handle 1,000 requests per second and suddenly receives 10,000, this surge might overwhelm your infrastructure if not properly managed.
Saturation:Saturation is about resource utilization; it shows how close your system is to reaching its full capacity. Monitoring saturation helps avoid performance bottlenecks caused by overuse of resources like CPU, memory, or network bandwidth. Think of it like a car's tachometer: once it redlines, you're pushing the engine too hard, risking a breakdown.
Challenges associated with monitoring saturation in microservices:
Complexity of Microservice Architectures:In microservice environments, various services are often built on different technologies (e.g., Node.js, databases, Swift). Each service may handle resource usage differently, making it challenging to monitor and understand overall system saturation accurately. Saturation occurs when resources such as CPU, memory, or network bandwidth are fully utilized, leading to degraded performance.
Resource Utilization Visibility:Since each microservice can have its unique metrics, gaining a clear view of overall saturation is difficult. Teams need to aggregate and standardize data from multiple services to accurately assess saturation levels. This can be time-consuming and requires expertise across different technology stacks.
Identification of Bottlenecks:Saturation often results in bottlenecks where some services are overloaded while others are underutilized. Pinpointing which service is causing the bottleneck in a complex system can be difficult without a cohesive monitoring approach like the one provided by SRE Golden Signals.
Dynamic and Variable Loads:In microservice architectures, traffic and resource demands can fluctuate rapidly, making it essential to monitor saturation in real-time. Services must adapt to changes in load, but without proper monitoring, it's easy to miss critical saturation points that can impact overall system performance.
Why Golden Signals Matter
Golden Signals provide a comprehensive overview of a system's health, enabling SREs and DevOps teams to be proactive rather than reactive. By continuously monitoring these metrics, teams can spot trends and anomalies, address potential issues before they affect end-users, and maintain a high level of service reliability.
SRE Golden Signals help in proactive system monitoring
SRE Golden Signals are crucial for proactive system monitoring because they simplify the identification of root causes in complex applications. Instead of getting overwhelmed by numerous metrics from various technologies, SRE Golden Signals focus on four key indicators: latency, errors, traffic, and saturation.
By continuously monitoring these signals, teams can detect anomalies early and address potential issues before they affect the end-user. For instance, if there is an increase in latency or a spike in error rates, it signals that something is wrong, prompting immediate investigation.
What are the key benefits of using "golden signals" in a microservices environment?
The "golden signals" approach is especially beneficial in a microservices environment because it provides a simplified yet powerful framework to monitor essential metrics across complex service architectures.
Here’s why this approach is effective:
▪️Focuses on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
By concentrating on latency, errors, traffic, and saturation, the golden signals let teams avoid the overwhelming and often unmanageable task of tracking every metric across diverse microservices. This strategic focus means that only the most crucial metrics impacting user experience are monitored.
▪️Enhances Cross-Technology Clarity
In a microservices ecosystem where services might be built on different technologies (e.g., Node.js, DB2, Swift), using universal metrics minimizes the need for specific expertise. Teams can identify issues without having to fully understand the intricacies of every service’s technology stack.
▪️Speeds Up Troubleshooting
Golden signals quickly highlight root causes by filtering out non-essential metrics, allowing the team to narrow down potential problem areas in a large web of interdependent services. This is crucial for maintaining service uptime and a seamless user experience.
By applying these golden signals, SRE teams can efficiently diagnose and address issues, keeping complex applications stable and responsive.
How to Monitor Microservices Using Golden Signals
Monitoring microservices requires a streamlined approach, especially in environments where dozens (or hundreds) of services interact across various technology stacks. Golden Signals provide a clear, focused framework for tracking system health across these distributed systems.
1. Start by Defining What You’ll Monitor
Each microservice should have its own observability pipeline for:
Latency – Measure the time it takes for a request to be processed from start to finish.
Errors – Capture both 4xx and 5xx HTTP codes or application-level exceptions.
Traffic – Monitor request rates (RPS/QPS) and message throughput.
Saturation – Track CPU, memory, thread usage, and queue lengths.
Tip: Integrate these signals into SLIs (Service Level Indicators) and SLOs (Service Level Objectives) to measure system reliability over time.
2. Use Unified Observability Tools
Deploy tools that allow you to collect metrics, logs, and traces across all services. Popular platforms include:
Datadog and New Relic: Full-stack observability with built-in Golden Signals support.
Prometheus + Grafana: Open-source, highly customizable metrics + dashboards.
OpenTelemetry: Instrument code once to collect traces, metrics, and logs.
3. Isolate Service Boundaries
Microservices should expose telemetry endpoints (e.g., /metrics for Prometheus or OpenTelemetry exporters). Group Golden Signals by service for clarity:
MicroserviceLatencyError RateTrafficSaturationAuth220ms1.2%5k RPS78% CPUPayments310ms3.1%3k RPS89% Memory
4. Correlate Signals with Tracing
Use distributed tracing to map requests across services. Tools like Jaeger or Zipkin help you:
Trace latency across hops
Find the exact service causing spikes in error rates
Visualize traffic flows and bottlenecks
5. Automate Alerting with Context
Set thresholds and anomaly detection for each signal:
Latency > 500ms? Alert DevOps
Saturation > 90%? Trigger autoscaling
Error Rate > 2% over 5 mins? Notify engineering and create an incident ticket
How can the "one-hop dependency view" assist in troubleshooting?
The "one-hop dependency view" in application performance monitoring (APM) simplifies troubleshooting by focusing only on the services that directly impact the affected service.
Here’s how it helps:
▪️Reduces Investigation Scope
Rather than analyzing the entire microservices topology, the one-hop view narrows the scope to immediate dependencies. This selective approach allows engineers to focus on the most likely sources of issues, saving time in identifying the root cause.
▪️Streamlines Root-Cause Analysis
By examining only the services one level away, the team can apply the golden signals (latency, errors, traffic, saturation) to detect any anomalies quickly. If a direct dependency is experiencing problems, it becomes immediately apparent without unnecessary complexity.
▪️Decreases Mean-Time-to-Recovery (MTTR)
With fewer services to investigate, the MTTR is significantly reduced. Engineers can identify and address the root issue faster, minimizing downtime and maintaining the application’s reliability.
Using the one-hop dependency view helps SRE teams keep the troubleshooting process efficient, especially in complex, interdependent service ecosystems
Practical Application: Using APM Dashboards
Application Performance Management (APM) dashboards integrate Golden Signals into a single view, allowing teams to monitor all critical metrics at once. For example, the operations team can use APM dashboards to get insights into latency, errors, traffic, and saturation. This holistic view simplifies troubleshooting and reduces the mean time to resolution (MTTR).
Here's how they work together:
▪️Centralized Monitoring with APM Dashboards:APM tools provide dashboards that centralize the key Golden Signals—latency, errors, traffic, and saturation. This centralized view allows operations and development teams to monitor the health of their applications in real-time. By displaying these critical metrics in one place, APM tools simplify the identification of performance issues, making it easier to spot trends and anomalies that need attention.
▪️"One Hop" Dependency Views:APM tools often support a "one hop" dependency view, which shows only the immediate downstream services connected to a problematic service. This feature is particularly useful in complex microservice environments where pinpointing the root cause of an issue can be daunting. By focusing on immediate dependencies, teams can quickly assess which services are functioning within normal parameters and which are experiencing issues, thereby speeding up the troubleshooting process.
▪️Proactive Issue Detection and Resolution:Integrating Golden Signals into APM tools allows for proactive monitoring, where issues can be identified before they escalate into more serious problems. For example, if a service’s saturation levels begin trending upwards, the APM tool can alert the team before users experience degraded performance. This proactive approach helps reduce the mean time to resolution (MTTR) and improves overall service reliability.
▪️ Customization for Different Teams:The video also mentions that APM tools can be customized for different stakeholders within the organization. While the operations team may focus on all four Golden Signals, development teams might create specialized dashboards that prioritize the signals most relevant to their services. This tailored approach ensures that both dev and ops teams are aligned and can address issues quickly, often even before they impact the end-users.
In essence, the integration of SRE Golden Signals with APM tools empowers teams to maintain high levels of service performance and reliability by providing clear, actionable insights into the most critical aspects of their systems.
What is the significance of distinguishing 500 vs. 400 errors in SRE monitoring?
The distinction between 500 and 400 errors in SRE monitoring is crucial because it impacts how issues are prioritized and addressed.
Here’s a breakdown:
Error TypeCauseSeverityResponse500 Server-side issueSystem/app failureHighImmediate investigation400 Client-side request issueBad input/authLowerMonitor trends only
500 Errors (Server Errors)
These indicate serious problems on the server side, such as downtime or crashes. They require immediate attention because they prevent users from accessing the service entirely, often resulting in significant disruptions. For instance, a 500 error signals that something is failing within the server's infrastructure, meaning end-users can’t receive a response at all. Therefore, these errors are more critical in incident response and may trigger alerts for the SRE team.
400 Errors (Client Errors)
These typically indicate client-side issues, where a request is invalid or needs adjustment, like when the requested resource doesn’t exist or is restricted. Such errors might be resolved simply by retrying or by the client correcting the request, so they’re usually less urgent. Monitoring 400 errors can still reveal trends or user behavior that may require attention, but they don't indicate systemic issues.
In summary, recognizing the difference allows SREs to prioritize resources on issues that directly affect the system’s reliability and availability (like 500 errors) versus issues that may just need minor adjustments or retries.
SRE Monitoring Dashboard Best Practices
A well-structured SRE dashboard makes or breaks your incident response. It’s not just about displaying data — it’s about surfacing the right insights at the right time. Here's how to do it:
1. Prioritize Golden Signals Above All
Place latency, errors, traffic, and saturation front and center. Avoid clutter—these four are your frontline defense against performance issues.
Example Layout:
Top row: Latency (P50/P95), Error Rate (%), Traffic (RPS), Saturation (CPU, Memory)
Second row: SLIs, SLO burn rates, alerts over time
2. Use Visual Cues Effectively
Color code thresholds: green (healthy), yellow (warning), red (critical)
Sparklines for trend visualization
Heatmaps to spot saturation across clusters or zones
3. Break Down by Environment & Service
Segment dashboards by:
Environment (prod, staging, dev)
Service or team ownership
Availability zone or region
This helps you quickly isolate issues when incidents arise.
4. Integrate Logs and Traces
Link metrics to logs or traces:
Click on a spike in latency → see related trace in Jaeger or logs in Kibana
Integrate dashboards with alert management (PagerDuty, Opsgenie)
5. Provide Different Views for Different Teams
SRE/DevOps view: Full stack overview + real-time alerts
Engineering view: Deep dive into a specific service’s metrics
Management view: SLO dashboards and service health summaries
Use templating (in Grafana or Datadog) so one dashboard serves multiple roles.
6. Regularly Review & Evolve Dashboards
Prune unused panels or metrics
Reassess thresholds quarterly
Add annotations for incidents or deployments
Dashboards should be living documents, not static reports. Learn from the official Google documentation.
Conclusion
Ready to take your system's reliability and performance to the next level? Gart Solutions offers top-tier SRE Monitoring services to ensure your systems are always running smoothly and efficiently. Our experts can help you identify and address potential issues before they impact your business, ensuring minimal downtime and optimal performance.
Discover how Gart Solutions can enhance your system's reliability today! Learn from our IT Monitoring case studies (Monitoring Solution for a B2C SaaS Music Platform and Advanced Monitoring for Digital Landfill Management) to learn more about our SRE Monitoring expertise.
After implementing Golden Signals, our customer reduced MTTR by 60% in under two months.
https://youtu.be/BqPXUxhshTM?si=EWFFu0JNYgJCj7g0

The NIS2 (Network and Information Security Directive) is a comprehensive directive that mandates organizations to implement robust security measures and document compliance to protect critical assets and ensure community continuity.
For organizations subject to NIS2 requirements, CISOs, and IT security officers must ensure robust internal compliance preparedness.
Why NIS2 Compliance Matters
NIS2 aims to enhance the overall level of cybersecurity in the EU by:
Improving the resilience of critical infrastructure.
Enhancing the security of network and information systems.
Ensuring rapid response to and recovery from cyber incidents.
For organizations subject to NIS2 requirements, compliance is not just a legal obligation but a vital component of risk management and operational continuity. Failing to comply can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Who is affected by NIS2?
NIS2 affects all big organizations that work in the European Union and are considered important to society. This includes organizations that:
Have 50 or more employees, or
Make over €10 million in revenue each year
NIS2 puts these organizations into two groups:
Essential organizations - These are very important sectors like energy, healthcare, transportation, and water supply.
Important organizations - These are sectors like manufacturing, food production, waste management, and postal services.
So in simple terms, if your fairly large organization operates in the EU and provides crucial services or products to society, then NIS2 applies to you. The directive aims to ensure these vital entities have strong cybersecurity measures in place.
The penalties for not following NIS2 rules are different depending on whether an organization is labeled as "essential" or "important".
For essential organizations:
They can be fined up to €10 million, or
They can be fined at least 2% of their total worldwide revenue from the previous year, whichever amount is higher.
For important organizations:
They can be fined up to €7 million, or
They can be fined at least 1.4% of their total worldwide revenue from the previous year, whichever amount is higher.
Gart’s NIS2 Solution
Gart offers a solution that simplifies the complexity of NIS2 compliance. The solution provides a systematic approach tailored to your ongoing operations and compliance efforts. By adopting Gart’s solution, you gain access to:
A systematic compliance framework for analyzing and documenting the security of critical assets.
Assurance of effective compliance work throughout your organization, aligned with good security practices and NIS2 requirements by applying ISO/EIC 27001/2 security principles.
Use of questionnaires to review the directive's requirements and ensure all documentation requirements are met, preparing you for audits.
Clear guidance on how to register significant security incidents with CSIRT, ensuring a proactive approach.
Read more: Gart’s Expertise in ISO 27001 Compliance Empowers Spiral Technology for Seamless Audits and Cloud Migration
How Does Gart Solution Support NIS2 Compliance?
NIS2 Requirement 1: Have policies for analyzing risks and information security
Gart can find and evaluate all assets, systems, weaknesses, and cyber/operational risks in critical infrastructure environments. It uses this detailed visibility to automatically create and enforce network security policies that reduce exposure to those identified risks.
In simple terms, Gart's solution allows organizations to:
Discover all their critical assets, systems, and potential vulnerabilities
Assess the cyber and operational risks in their environments
Automatically define security policies to protect against those risks
Enforce those security policies across their networks
NIS2 Requirement 2: Dealing with Security Incidents
Gart Solutions constantly keeps watch over all critical infrastructure systems for any signs of potential threats, both known and new. It analyzes all security alerts in detail to prioritize the most important issues. Gart also integrates with existing security tools like SIEM and SOAR to extend an organization's security processes across all of its critical systems.
In simpler terms, Gart's solution allows organizations to:
Continuously monitor all their vital systems and networks
Quickly detect any potential cyber threats, even new unidentified ones
Understand the context and importance of every security alert
Work seamlessly with their existing security tools and workflows
Expand their incident response capabilities to cover all critical infrastructure
NIS2 Requirement 3: Managing Crises
Gart provides:
A complete, up-to-date list of all critical systems
Logging of all changes and unusual activity in assets and networks
Ability to create and enforce security policies to separate networks and control access
Ready integration with backup and recovery tools
All of these capabilities from Gart help organizations improve their overall crisis management and ensure the continuity of essential operations.
In simpler terms, Gart's solution allows organizations to:
Know exactly what critical assets they have at all times
Track all activity so they can investigate incidents
Lock down systems by enforcing strict security controls
Quickly backup and restore systems if needed
NIS2 Requirement 4: Security of Networks and Information Systems
By utilizing Gart's capabilities, customers can effectively:
Identify vulnerabilities and insecure configurations in their critical networks and systems
Assess and manage the cyber risks to their operational environments
Allow remote access for personnel to do their work securely
In simple terms, Gart helps organizations implement robust security measures for their networks and information systems as required by NIS2. This includes finding and fixing vulnerabilities, evaluating risks, and controlling access - all crucial for securing vital operational technology.
NIS2 Requirement 5: Basic Cybersecurity Practices and Training
Gart's solution helps organizations:
Identify areas where they need to improve their basic cybersecurity habits and procedures based on risk assessments.
Ensure all personnel, whether employees or vendors, follow proper access controls, password management, and other essential cybersecurity practices.
Use the recommendations to develop training programs to raise cybersecurity awareness and skills.
NIS2 Requirement 6: Policies and Procedures for Data Encryption
Gart provides:
1) Encryption of all user data, critical system data, and other sensitive information in compliance with NIS2, GDPR, and other regulations.
2) Alerts when sensitive data like personal health records is being processed in a way that violates security policies or could lead to a data breach.
Here's a rewording in simple language:
NIS2 Requirement 7: Using Multi-Factor Authentication and Secure Communications
Gart helps organizations:
- Enforce strong access controls like multi-factor authentication across their workforce and supply chain vendors/partners
- Allow only authorized and verified personnel to access critical systems remotely or on-site
- Ensure all communications to operational technology are fully secured
- Meet audit requirements by recording all access sessions
Key Features:
Mapping of Critical Assets
We will create an overview of the various types of critical assets within your value chain and document their security levels.
Risk Assessment of Critical Assets, Systems, and Processes
We will conduct a risk assessment based on the current threat landscape, the assets' placement within the value chain, and their potential societal consequences.
GAP Analysis
We will obtain a clear overview of your current compliance level and implementation, identifying the essential control objectives required for NIS2.
Automated Processes
We will automate control follow-ups and communication with internal stakeholders to ensure all relevant tasks are carried out correctly and on time.
Compliance Control and Scope of SoA
We will begin with an initial compliance review, prioritize, and scope the Statement of Applicability (SoA) based on NIS2 requirements.
Create Awareness and Communicate Directly with Stakeholders
We will create awareness and directly communicate with stakeholders to keep everyone informed about policy and procedural changes, ensuring everyone understands their role.
Overview of Reporting to CSIRT
We will establish a process for reporting significant incidents and threats to the organization or its supply chain to CSIRT, protecting critical assets quickly and efficiently.
Ongoing Auditing
We will document internal compliance with NIS2 via dedicated management controls and functionality for auditing critical suppliers.
About the NIS2 Directive or NIS2 framework
The NIS 2 Directive, also referred to as the NIS2 framework, is a European Union regulation aimed at enhancing cybersecurity across the bloc. Here's a breakdown of the key points:
Goals:
Improve overall cybersecurity posture in the EU.
Strengthen existing cybersecurity measures in critical sectors.
Ensure a consistent approach to cybersecurity risk management across member states.
Key Features:
Broader Scope: NIS2 applies to a wider range of sectors compared to the previous NIS Directive. This includes essential services (energy, transport, water, etc.) and important entities in sectors like waste management, postal services, manufacturing, and more.
Enhanced Risk Management: Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures to manage risks to their network and information systems. This includes measures to prevent incidents, minimize their impact, and report them effectively.
Incident Reporting: Entities are required to report significant incidents to relevant authorities. This allows for faster response and improved coordination across member states.
Supply Chain Security: The directive emphasizes the importance of supply chain security. Organizations need to consider the cybersecurity risks associated with their suppliers and vendors.
Cooperation and Information Sharing: Increased cooperation and information sharing among member states and relevant authorities are crucial aspects of NIS2.
Current Status:
Adopted in December 2022 and came into effect in January 2023.
EU member states have until October 17, 2024 to transpose the NIS2 Directive into national law.
By April 17, 2025, member states need to establish a list of essential entities falling under the directive.
Conclusion
The European Union's Network and Information Security Directive, known as NIS2, sets stringent requirements for organizations to safeguard their critical assets and ensure the continuity of essential services.
Gart is here to guide you through every step of the process, providing the expertise, tools, and support you need to achieve and maintain compliance. With our systematic approach, you can focus on your core business operations, confident that your information security is in capable hands.
Are you ready to simplify your NIS2 compliance journey? Contact Gart today to learn more about how we can help you strengthen your information security and achieve regulatory compliance with ease.

Information security is crucial in the business world. Companies choose various approaches to address tasks related to the storage and processing of confidential data. One of them is ISO 27001.
ISO 27001 is an international standard that defines requirements for the creation, implementation, improvement, and maintenance of an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
[lwptoc]
Recently, we successfully prepared our client for ISO 27001 certification. Based on a recent case, we want to share with you the procedure.
This standard establishes frameworks and principles for safeguarding confidential information within an organization, covering various aspects such as
financial data
intellectual property
personal employee data
and other information about third parties.
Over an extended period globally, efforts have been made to create uniform rules for protecting personal data, leading to the adoption of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). All companies processing data of individuals from the European Union must comply with this regulation. While the document exists, there is no certificate confirming adherence to these standards. This is where ISO 27001 comes to the rescue, as its standards partially align with the requirements of GDPR, and compliance can be validated with a certificate.
ISO 27001 for Businesses
The certification of ISO 27001 is becoming increasingly relevant not only for large organizations but also for small and medium-sized companies in the context of technological advancement.
Every modern enterprise, to some extent, has tools for managing information security risks. In simpler terms, every company takes measures to secure its informational assets and restrict access to its systems. The Information Security Management System (ISMS) aligns all components of the organization's information security system to ensure that all system policies, procedures, and strategies work as a cohesive unit.
It's important to note that certificates do not provide an absolute guarantee of security but rather confirm adherence to specific criteria set by the accrediting body. For instance, the presence of an ISO/IEC 27001 certificate does not ensure 100% data security; it simply attests that the company meets certain information security standards.
Need assistance on your ISO 27001 journey? Reach out to Gart for personalized support and ensure your company's information security is top-notch.
Why is standardization important for business? Advantages of ISO 27001 Certification
ISO 27001 certification is a powerful tool for building and maintaining trust in the client-supplier relationship. The competitive advantage gained through ISO 27001 extends beyond marketing, influencing real success and the resilience of the business.
Obtaining the certificate comes with numerous benefits. Firstly, it confirms that the company takes information security seriously, a crucial factor for clients and partners. The certificate enhances trust and demonstrates adherence to established standards.
Cost Savings
It sounds incredible, but the certification process can actually lead to substantial cost savings for the company in the future. When ISO 27001 certification is conducted properly, it results in long-term economic benefits. For instance, Gart's strategic approach streamlines processes, allowing teams to focus on higher-level tasks, ultimately reducing costs associated with compliance audits.
A clear understanding of risks enables cost optimization and the formulation of effective security policies.
Increased Sales
ISO 27001 certification is a significant marketing asset. Clients are drawn to the commitments a business makes by obtaining the certificate. The enhanced reputation attracts new clients and partners, fostering business growth.
Reputation Protection
Certification elevates the level of company security, introducing improved policies and technologies. A modern security system helps avoid the detrimental impact of malicious actors on your business. ISO 27001 certification allows you to demonstrate a commitment to information security, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. It also contributes to attracting clients and serves as a competitive advantage for your business. Regular audits help identify risks and respond to changes in the environment.
How to Prepare Your Company for ISO 27001 Certification?
Achieving ISO 27001 certification is a complex task that requires thorough preparation and involves various types of work. This process demands the involvement of a significant number of employees and entails lengthy and costly preparations.
Therefore, at the initial stage, it is crucial to develop a detailed action plan outlining specific tasks, who will be working on them, when they will be accomplished, and how the project will be executed.
Appoint a dedicated team responsible for the certification process, including representatives from different departments. Conduct training for staff on information security and the implementation of an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Start by understanding the ISO 27001 standard and its requirements. It is essential to carefully study the ISO 27001 standard, which consists of two parts:
The main part, which contains the core content of the standard.
Appendix A, which includes a list of 114 potential control measures.
Ready to elevate your information security standards? Gart is here to guide you through ISO 27001 certification. Let's strengthen your defense against cyber threats together.
Approximate ISO 27001 Preparation Plan
Analysis
Assess the current state of your Information Security Management System (ISMS). Identify gaps between existing practices and ISO 27001 requirements. Also, crucially, determine which part of your organization falls under the scope of ISO 27001.
Documentation
Develop and document policies, processes, and procedures aligned with ISO 27001. Create a Statement of Applicability (SoA) defining the scope of your ISMS.
Risk Assessment
Conduct a thorough risk analysis to identify potential security threats. Develop a risk treatment plan to manage and mitigate the identified risks.
Implementation
Ensure employee training and awareness regarding their roles in preserving information security.
Internal Audit
Conduct an internal audit to assess the effectiveness of implemented measures. Identify areas for improvement and corrective actions. At this stage, you may consider engaging external consultants with the necessary expertise, and companies like Gart offer professional services for ISO 27001 certification preparation.
It's also important to note that ISO 27001 is related to several other standards, such as ISO 22301, ISO 31000, and ISO 27003.
External Audit
Demonstrate compliance with ISO 27001 standards. Select an auditor or certification body to conduct the final audit and issue a certificate if your company meets the requirements. After successfully completing the external audit, obtain the ISO 27001 certificate.
What is the cost of obtaining an ISO 27001 certificate?
The cost of obtaining an ISO 27001 certificate can vary significantly and depends on various factors, including the size of the company, the complexity of its information systems, the industry, geographical location, and other considerations. Typically, it's a bespoke matter that is discussed with the agency or organization overseeing the certification process. Even with an approximate cost estimate, it's advisable to include a contingency reserve in the budget.
ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2 table
AspectISO 27001SOC 2ScopeInformation security management system (ISMS)Controls relevant to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of information stored in the cloudFocusComprehensive security frameworkSpecific emphasis on cloud securityRequirementsBroad range covering risk assessment, policies, procedures, and continual improvementFocus areas include security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacyApplicabilityApplicable to all types of organizationsEspecially relevant for service organizations hosting data in the cloudCertificationISO 27001 certificationSOC 2 complianceBenefitsDemonstrates commitment to information security and data protectionProvides assurance to clients and stakeholders regarding security controls in placeMarket RecognitionGlobally recognized standardIncreasingly recognized and sought after, particularly in tech and service sectorsCustomizabilityHighly customizable to fit organizational needsAllows flexibility in selecting applicable trust services criteriaContinuous ImprovementRequires continual assessment and improvementEncourages ongoing monitoring and refinement of controlsRegulatory ComplianceHelps organizations comply with various regulationsCan assist in meeting regulatory requirements, especially in data privacy and security standards
Conclusion
ISO 27001 certification is not just a compliance requirement; it is a journey towards excellence in the realm of information security. Preparing for ISO 27001 certification is a task that demands dedication, collaboration, and systematic efforts from the entire company.
Ready to embark on your ISO 27001 journey? Contact Gart for expert guidance and let's achieve information security excellence together.