Cybersecurity is a critical concern in today’s interconnected world. Understanding how breaches occur and how they are handled can help organizations improve their defenses. With cyber threats evolving in both frequency and sophistication, businesses must stay vigilant in protecting their critical assets. From ransomware attacks to data breaches, the ability to detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents quickly is vital.
This article delves into key concepts surrounding cybersecurity monitoring, including the “boom” event, proactive threat hunting, and the advanced tools used to mitigate risks. We’ll also explore crucial cybersecurity metrics that every organization should track to stay ahead of potential threats.
What is a “Boom” Event?
The term “boom” refers to a cybersecurity breach. It divides events into “left of boom” (before the breach) and “right of boom” (after the breach).
In cybersecurity, a “boom” event refers to a major breach or attack on a system. This event marks the division of time into two critical periods:
▪️ Left of Boom: This is the time before the attack. During this phase, attackers are often preparing their strategies, conducting reconnaissance, and identifying weak spots in the system.
▪️ Right of Boom: This phase occurs after the breach. It is the time when security teams must detect the attack, respond to it, and recover from its effects.
The Time to Detect and Contain: Cybersecurity Monitoring
According to the Ponemon Institute, the time between an initial breach and its detection, called the Mean Time to Identify (MTTI), is, on average, 200 days. The time to contain the attack, known as the Mean Time to Contain (MTTC), adds another 70 days. Combined, organizations can take nearly 270 days to address a breach. During this period, sensitive data can be leaked, and significant damage may be done.
In addition to the time required to handle breaches, the financial toll is severe. The average cost of a data breach is estimated at $4 million, encompassing lost business, regulatory fines, and recovery expenses. Organizations that can reduce their MTTI and MTTC can significantly lower this cost.
A high-profile breach like the Equifax data breach (2017) or SolarWinds attack (2020) could highlight the consequences of slow detection.
Threat Hunting: Proactively Identifying Risks
To reduce the time between boom and response, organizations are adopting threat hunting strategies. This involves proactively searching for indicators of compromise or attack before alarms go off. Threat hunting is conducted in the “left of boom” phase and can help in discovering breaches earlier.
Threat hunters use several tools and strategies:
- Indicators of Compromise (IOC): These are clues left behind by attackers, such as abnormal login patterns or unauthorized file access.
- Indicators of Attack (IOA): These are signs that an attack may be underway, such as unusual data transfers or failed login attempts.
- Security Intelligence Feeds: These provide up-to-date information on current vulnerabilities being exploited by cybercriminals.
Essential tools for threat hunting include:
- XDR (Extended Detection and Response): This tool integrates data from multiple sources to detect and respond to security threats across an organization’s environment. It helps security teams act on threats before they escalate.
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): This system gathers and analyzes security data from different sources, allowing teams to detect anomalies and potential security incidents early.
- UBA (User Behavior Analytics): UBA focuses on identifying unusual or suspicious activities by analyzing user behavior patterns. It helps in spotting compromised accounts or malicious insiders before they cause significant harm.
These tools work together to provide a comprehensive defense against potential cyber threats.
Top Cybersecurity Metrics for 2024
In short:
📊 Incident Detection Time: Measures how long it takes to identify a threat; faster detection reduces damage.
🛡️ Incident Response Time: Fast response post-detection minimizes damage, aided by automation and trained teams.
🔒 Vulnerability Tracking: Knowing where your system is weak is key, with regular scans and patch fixes.
📈 Patching Compliance Rate: Measures the percentage of patched vulnerabilities, and low rates expose weaknesses.
⚠️ False Positive Rate: Reduces wasted time and alert fatigue by improving threat detection accuracy.
🛠️ Meantime to Recover (MTTR): Tracks recovery time post-incident; shorter MTTR improves security processes.
🚨 Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Fewer DLP incidents indicate better protection against sensitive data leaks.
Organizations need to actively monitor and analyze specific cybersecurity metrics to ensure their systems are responsive and resilient to potential threats. Here, we explore the key metrics for 2024 that every cybersecurity team should be tracking.
1. Incident Detection Time
Incident detection time refers to the duration it takes for a system to detect a potential cyber threat. The shorter the detection time, the faster a team can respond, thereby minimizing the damage. To optimize detection, organizations should utilize Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and advanced threat detection tools. These technologies help spot irregularities in network activity and promptly raise alerts.
2. Incident Response Time
Once a threat is detected, the next critical metric is incident response time—how quickly a team can act to neutralize the threat. Faster responses mean less damage. Automation tools, playbooks, and well-trained incident response teams are invaluable in speeding up this process, ensuring the organization can mitigate the impact of threats quickly and efficiently.
3. Vulnerability Tracking and Aging
It’s essential to regularly assess where the system is most vulnerable. Vulnerability tracking allows organizations to identify and patch potential weak points in their defenses. Vulnerability aging, on the other hand, tracks how long these weaknesses have remained unresolved. The goal is to reduce the amount of time vulnerabilities exist without being addressed, as prolonged exposure increases the risk of attacks.
4. Patching Compliance Rate
Patching compliance measures the percentage of vulnerabilities that are fixed after being identified. A high patching compliance rate indicates that an organization is effectively addressing weaknesses, while a low rate leaves systems vulnerable to attacks. Automating patch management processes and prioritizing critical fixes are best practices for maintaining high compliance.
5. False Positive Rate
In threat detection, too many false positives can lead to “alert fatigue,” where security teams become overwhelmed by non-critical alerts and may miss actual threats. It is vital to ensure that detection systems are fine-tuned to reduce false positives, allowing teams to focus on real threats.
6. Meantime to Recover (MTTR)
MTTR is the average time it takes for a system to fully recover from a cyber incident. Shorter recovery times indicate that an organization has effective disaster recovery processes in place. Regular disaster recovery drills and automated backups can help organizations reduce their MTTR, ensuring they can quickly return to normal operations after an attack.
7. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Incidents
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools monitor and protect sensitive data from being leaked or stolen. Fewer DLP incidents reflect stronger data protection policies and better overall compliance with regulations. Continuous cybersecurity monitoring and strong encryption protocols are essential for reducing the number of DLP incidents.
Optimizing Incident Detection Time with the Latest Tools
Incident detection time can be significantly improved using advanced cybersecurity tools and strategies. Here are a few key methods:
▪️ SIEM Systems: Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools are crucial. They aggregate real-time data from various sources like firewalls, servers, and applications, using advanced analytics to detect unusual behavior or potential threats.
▪️ AI-Powered Threat Detection: AI and machine learning models can analyze vast amounts of data faster than human teams. These models can identify patterns in network activity that indicate potential threats, allowing for faster responses.
▪️ Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR tools monitor and analyze activity at the endpoint level, detecting malicious behavior before it spreads through the network.
▪️ Automated Incident Detection: Automation speeds up the entire detection process, flagging suspicious activities instantly and reducing the reliance on manual cybersecurity monitoring.
By combining these tools with regular network monitoring and training, organizations can significantly reduce incident detection times.
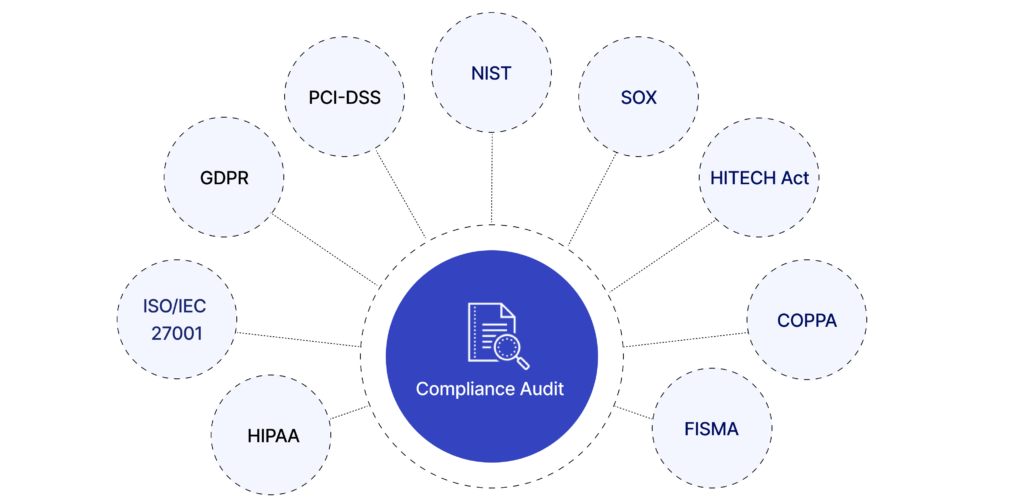
Regulatory and Compliance Implications
Cybersecurity monitoring plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance, particularly in highly regulated industries:
- Ensures protection of sensitive patient data
- Monitors access to electronic health records
- Detects and reports potential data breaches
Finance (PCI-DSS, GDPR):
- Safeguards customer financial information
- Tracks data access and usage patterns
- Ensures data portability and right to erasure compliance
Government Sectors:
- Protects classified information
- Monitors for insider threats
- Ensures compliance with sector-specific regulations
Benefits of compliance-focused cybersecurity monitoring:
- Avoids costly regulatory fines
- Ensures adherence to data protection laws
- Improves auditability with comprehensive logging
- Enhances reporting capabilities for regulatory bodies
Protect your organization from costly regulatory fines and ensure compliance with data protection laws. Our expert compliance audits provide the visibility and control you need to maintain compliance and avoid penalties. Contact Gart today to schedule your audit and safeguard your business.
Need Cybersecurity Monitoring?
Protect your business from evolving cyber threats with advanced cybersecurity monitoring solutions. Gart Solutions offers proactive threat detection, real-time incident response, and compliance support to safeguard your critical assets.
Take a look at our cases of IT Monitoring projects:
Centralized Monitoring for a B2C SaaS Music Platform:
We implemented a real-time monitoring system for both infrastructure and applications using AWS CloudWatch and Grafana for an international music platform. This system allowed for scalable monitoring across different regions, improving visibility, minimizing downtime, and boosting operational performance. The solution delivered a cost-effective, easy-to-use platform designed to support ongoing growth and future scalability.
Monitoring Solutions for Scaling a Digital Landfill Platform:
For the elandfill.io platform, we designed a comprehensive monitoring solution that successfully scaled across multiple countries, including Iceland, France, Sweden, and Turkey. The system enhanced methane emission forecasting, optimized landfill operations, and streamlined compliance with environmental regulations. The cloud-neutral design also ensured the client could choose their cloud provider freely, without being locked into a specific platform.
Don’t wait for a breach — contact Gart today and fortify your cybersecurity defenses!
See how we can help to overcome your challenges








