Healthcare companies are under constant pressure to deliver high-quality patient care while managing vast amounts of data, complying with regulatory requirements, and adapting to new technologies.
DevOps, a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops), offers significant advantages for healthcare organizations striving to meet these challenges. In this article, we will explore the best practices and benefits of DevOps for healthcare companies.
Regulated Industry
One of the most regulated industry due to compliance standards (HIPAA, HITECH Act, FDA, CMS, JCAHO, etc)
Compliance StandardDescriptionImpact on DevOps PracticesHIPAAHealth Insurance Portability and Accountability ActRequires strict data security and privacy measures, necessitating encryption, access controls, and audit trails. DevOps practices must ensure compliance at all stages.HITECH ActHealth Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health ActEncourages the adoption of electronic health records and sets standards for data breach notification. DevOps practices need to secure electronic health records and establish efficient breach response procedures.FDAFood and Drug AdministrationEnforces regulations on the development and deployment of medical devices and pharmaceutical software. DevOps in healthcare must adhere to rigorous compliance checks, documentation, and validation.CMSCenters for Medicare & Medicaid ServicesRegulates healthcare payment and service delivery. DevOps practices must align with regulations to ensure efficient billing, payments, and service quality.JCAHOJoint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare OrganizationsProvides accreditation for healthcare organizations. DevOps practices play a role in meeting accreditation standards related to patient safety, care quality, and data security.GDPRGeneral Data Protection Regulation (EU)Applies to healthcare organizations that handle EU patient data. DevOps practices must include data protection and consent mechanisms to comply with GDPR requirements.These compliance standards impact DevOps practices by requiring specific security, data protection, documentation, and quality assurance measures tailored to the respective industry's needs.
Specific DevOps Practices Tailored for the Healthcare Industry
HIPAA Compliance
Healthcare organizations deal with sensitive patient data subject to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). DevOps teams must prioritize HIPAA compliance by implementing encryption, access controls, and audit trails in their pipelines.
Automated Testing for Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare applications often need to adhere to strict regulatory standards. Automated testing should include compliance checks to ensure that software meets healthcare-specific regulations and standards.
Patient Data Security - Encryption & Data Masking
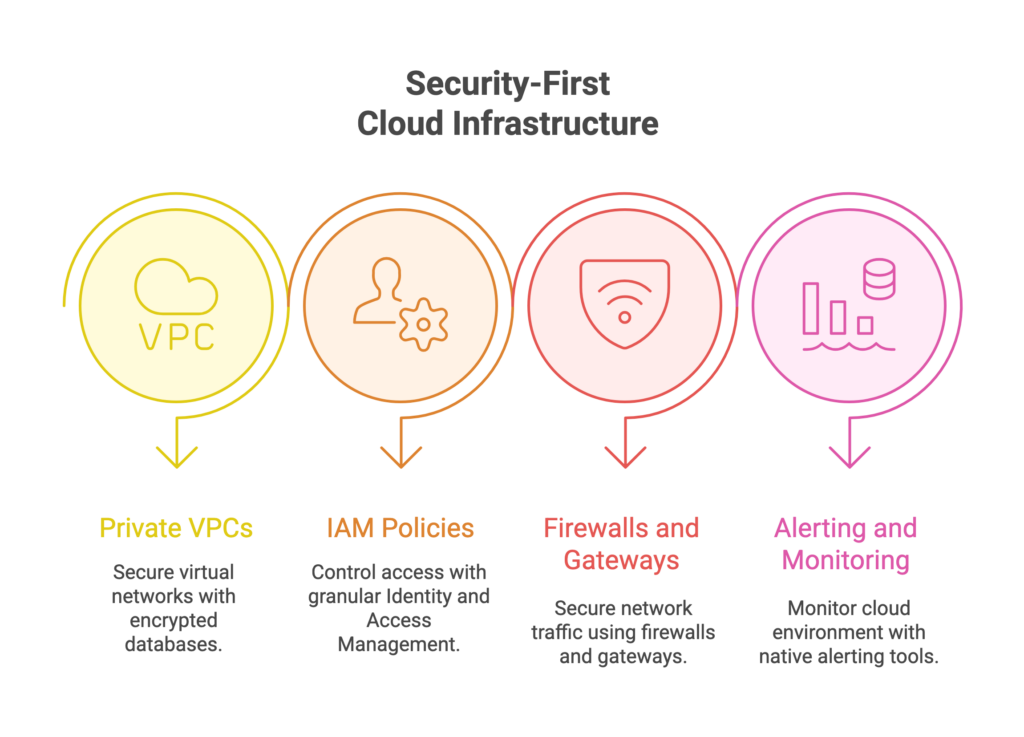
Protecting patient data is a top priority. DevOps should focus on securing data at rest and in transit, and implementing robust identity and access management (IAM) practices.
Utilize strong encryption algorithms to protect sensitive healthcare data when it is stored (at rest) and when it is transmitted (in transit). This ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable and secure.Additionally, implement data masking in non-production environments to protect patient data during development and testing, aligning with stringent healthcare data security requirements.These methods allow for the realistic testing and development of applications without exposing actual patient data. Sensitive elements within the data are replaced with fictional or masked values, preserving data privacy and HIPAA compliance.
Zero Downtime
Healthcare services can't afford downtime. DevOps should aim for zero-downtime deployments, using strategies like blue-green deployments or canary releases to minimize disruptions to patient care.
Disaster Recovery and Redundancy
In the healthcare sector, maintaining high availability is paramount. To safeguard against potential system failures, DevOps must incorporate robust disaster recovery and redundancy measures. These measures are crucial for ensuring uninterrupted operations and patient care, especially in the face of unforeseen disasters or critical system issues. Gart, known for its expertise in this area, offers specialized solutions for Backup & Disaster Recovery to bolster healthcare system resilience.
Change Management and Version Control
Strict change management and version control are essential in healthcare to track modifications, updates, and configurations. DevOps tools can help manage and document these changes effectively.
Collaboration with Clinical Teams
DevOps teams should collaborate closely with clinical professionals to understand their needs and feedback. This ensures that software aligns with clinical workflows and improves patient care.
Performance Monitoring
Implement robust performance monitoring to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact patient care. Real-time monitoring of healthcare systems is crucial for maintaining service levels.
Regulated Data Retention and Backup
Data retention and backup policies need to comply with healthcare data retention regulations. DevOps practices should include automated data backup and secure storage management.
? Looking to streamline your operations, boost security, and scale effectively? Reach out to Gart's DevOps specialists for a transformation. ? Contact Gart Today!
Cross-Functional Training
Encourage cross-functional training between IT staff and healthcare professionals to foster a deeper understanding of healthcare processes and IT requirements.
Non-Disruptive Updates
Develop strategies for non-disruptive software updates to minimize disruptions during critical patient care procedures. Implement rolling updates or feature flags to control new functionalities.
Serverless Agility
With a serverless architecture, healthcare companies are liberated from the burden of managing servers and infrastructure. Serverless platforms seamlessly adjust resource scaling according to demand, ensuring your SaaS application effortlessly adapts to varying user activity levels without the need for manual interventions. You focus on coding, while the cloud does the rest, significantly simplifying operations.
Incident Response Planning
Develop and regularly test incident response plans tailored to healthcare scenarios to ensure quick recovery in case of security breaches or system failures.
Containerization and Microservices
Utilize containerization and microservices to enhance scalability, portability, and resource efficiency, while maintaining healthcare application performance.
Secure Code Practices
Promote secure coding practices within DevOps teams to reduce vulnerabilities in healthcare software, where data security is of utmost importance.
Comprehensive Documentation
Maintain comprehensive documentation for all DevOps processes and configurations, facilitating auditing and ensuring healthcare software integrity.
By integrating these healthcare-specific DevOps practices, healthcare organizations can enhance their ability to provide high-quality patient care while complying with regulatory standards and maintaining data security. These practices ensure that the benefits of DevOps are tailored to the unique demands of the healthcare industry.
DevOps in Healthcare: Best Practices
Automation
DevOps encourages automation across the entire software development and deployment lifecycle. This includes automating code testing, deployment, and monitoring. In healthcare, where patient safety and data security are paramount, automation reduces the risk of human error and enhances compliance with regulatory requirements.
Collaboration
DevOps fosters a culture of collaboration between development and operations teams. Healthcare organizations can benefit from improved communication, leading to faster issue resolution, more efficient deployments, and better overall patient care.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
The CI/CD pipeline is a fundamental DevOps practice. It allows healthcare companies to make rapid and frequent software releases while maintaining high quality. This agility is crucial for adapting to changing healthcare needs.
Security
The healthcare industry is a prime target for cyberattacks due to the sensitive nature of patient data. DevOps integrates security from the beginning of the development process, making it easier to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities. Regular security testing and automated compliance checks enhance data protection.
Monitoring and Feedback
Continuous monitoring and feedback loops in DevOps help healthcare organizations identify and address issues promptly. Real-time insights into system performance and user experience enable proactive problem-solving and ensure the highest level of patient care.
Benefits of DevOps in Healthcare
Improved Patient Care: DevOps practices enhance the quality and reliability of healthcare software, contributing to improved patient care. Faster deployments and quicker issue resolution mean healthcare professionals can access critical tools without disruption.
Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces manual intervention, resulting in cost savings. With healthcare costs continually under scrutiny, DevOps helps companies allocate resources more efficiently.
Regulatory Compliance: DevOps streamlines compliance efforts by automating documentation and ensuring security and privacy requirements are met. This minimizes the risk of penalties associated with non-compliance.
Faster Innovation: The ability to release new features and updates quickly enables healthcare companies to innovate in response to changing patient needs, market demands, and technological advancements.
Data Security: DevOps best practices for security ensure that patient data remains confidential and protected. Timely detection and remediation of vulnerabilities help prevent data breaches.
Enhanced Productivity: By automating time-consuming tasks and promoting collaboration, DevOps frees up resources and allows healthcare professionals to focus on patient care rather than IT issues.
Case Studies: E-Health DevOps Transformation
CI/CD Pipelines and Infrastructure for E-Health Platform
Explore how Gart Solutions transformed a healthcare development company's Electronic Medical Records Software (EMRS) for a government E-Health platform and CRM systems. Gart implemented CI/CD pipelines and on-premises infrastructure, adhering to strict HIPAA and GDPR standards.By leveraging local cloud provider GiGa Cloud's hardware, utilizing VMWare ESXi and Terraform, and implementing data-masking techniques, they ensured secure and compliant data management.
Seamless Rails Application Migration: Transitioning from HealthCareBlocks to AWS with HIPAA Compliance
Gart orchestrated a smooth and comprehensive migration of a Ruby on Rails application from HealthCareBlocks to Amazon AWS. With meticulous attention to detail, Gart prioritized HIPAA compliance, safeguarded data integrity, and ensured the continued seamless operation of the application in its new cloud environment.
Healthcare SaaS: Cloud Engineer's Journey in CI/CD, Terraform, and Cloud Migration
Gart took on the challenge at a high-growth healthcare SaaS company, where the task was to revamp CI/CD pipelines for both .NET and Node.js environments and implement Terraform infrastructure. Alongside these tasks, Gart orchestrated a smooth AWS to Azure migration. Gart's impeccable work ensured PHI access compliance. Gart seamlessly interfaced with a US-based team.
? Are you seeking to streamline your operations, enhance security, and improve scalability? Transform operations and security with Gart's DevOps experts. ? Contact Gart Today!
Conclusion
DevOps has rapidly become a key driver of efficiency, security, and innovation in the healthcare industry. By adopting DevOps best practices, healthcare companies can provide better patient care, reduce costs, meet regulatory requirements, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving field. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing DevOps will be essential for healthcare organizations to thrive in an increasingly digital and data-driven world.

What is Digital Transformation in Healthcare?
Imagine walking into a hospital where your medical records are instantly accessible on a secure digital platform, doctors consult you virtually from anywhere, and AI systems analyze your blood tests to predict diseases before symptoms appear. That’s digital transformation in healthcare.
In simple terms, it refers to leveraging technology to revolutionize how healthcare is delivered, managed, and experienced. It involves integrating digital solutions like electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, AI diagnostics, IoT-connected devices, and robotic surgeries to improve patient care, operational efficiency, and medical outcomes.
Why is it Gaining Momentum Globally?
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated healthcare digitization, but the momentum continues due to:
Rising Patient Expectations:Today’s patients demand convenience, accessibility, and personalized care, just like their experiences with Amazon or Netflix.
Technological Advancements:AI, IoT, and big data analytics have matured, making them viable for large-scale healthcare applications.
Cost Pressures and Resource Constraints:Hospitals face financial constraints and staff shortages. Digital transformation optimizes workflows, reducing costs while improving quality.
Regulatory Push:Governments and health bodies globally are mandating secure digital health records, telemedicine, and interoperability standards to improve national healthcare systems.
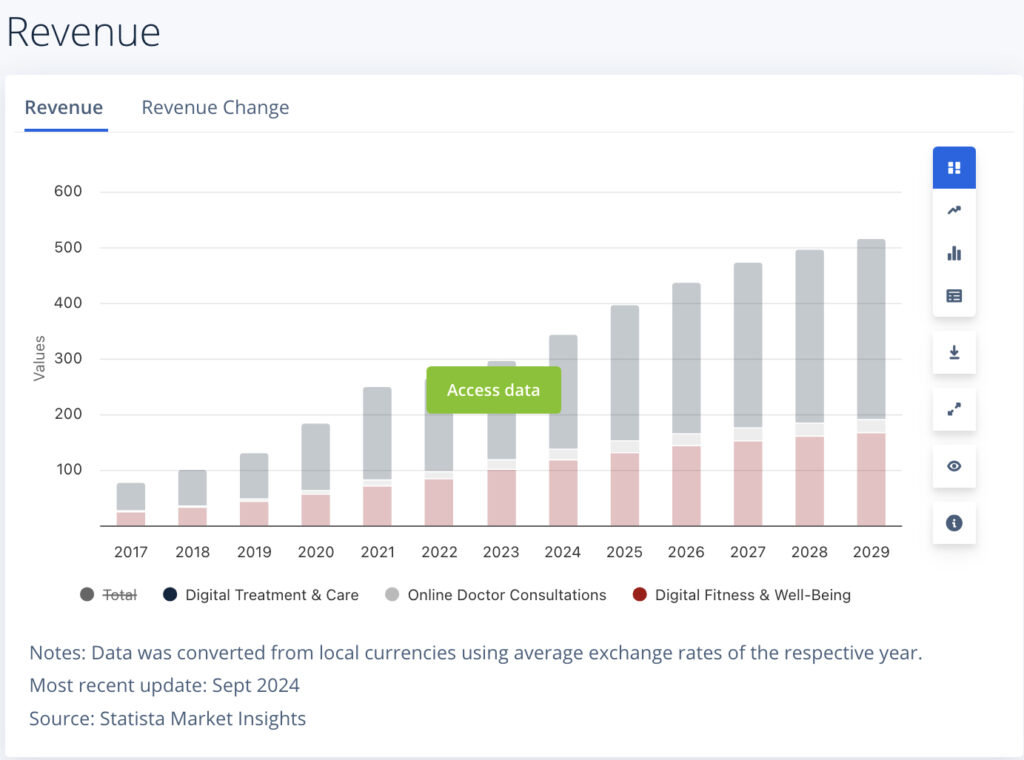
A Statista report projects the global digital healthcare market to reach $504.4 billion by 2025, underscoring how essential digital transformation has become for competitive and efficient healthcare delivery.
88% of healthcare technology leaders prioritize improving the patient experience in their investments (according to a Deloitte survey)
This shift underscores the necessity for healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and administrative staff, to stay abreast of ongoing digital advancements.
Key Drivers of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Emerging Technologies Shaping Healthcare
Technological innovations are the backbone of healthcare’s digital transformation. Here’s how the main technologies are driving change:
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by:
Automating administrative tasks like record-keeping and billing
Enhancing predictive diagnostics by analyzing medical images for early disease detection
Personalizing treatment plans based on patient history, genetics, and lifestyle
Enabling AI-powered chatbots to handle appointment scheduling, symptom checks, and medication reminders, reducing the burden on human staff
For example, AI diagnostic platforms like Google DeepMind Health detect eye diseases with the same accuracy as ophthalmologists, enabling earlier intervention and better outcomes.
IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT-connected health devices include:
Wearables: Smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor heart rate, oxygen saturation, and sleep cycles, alerting users to anomalies.
Remote Patient Monitoring Devices: Track vitals for chronic patients, reducing hospital visits while enabling proactive care.
Connected Hospital Equipment: Optimize operations by tracking equipment usage, availability, and maintenance schedules.
This improves real-time patient monitoring, operational efficiency, and resource utilization, making healthcare delivery smarter and more responsive.
Robotics
Robotics in healthcare enables:
Minimally invasive surgeries: Robotic surgical systems like da Vinci Surgical System enhance precision, reducing recovery time and hospital stays.
Remote surgeries: Surgeons operate robotic instruments from distant locations, expanding access to specialized care globally.
3D Printing
3D printing is transforming:
Prosthetics: Creating customized, affordable prosthetics quickly for amputees.
Implants and Organs: Producing tailor-made implants and researching bioprinted organs for transplantation.
These emerging technologies are not just futuristic concepts – they are real-world solutions enhancing healthcare daily.
Changing Patient Expectations and Demographics
Today’s patients are digital natives, especially younger demographics who expect:
Online appointment booking
Access to digital medical records
Telehealth consultations
Personalized health recommendations
With over 5.3 billion internet users globally, healthcare providers must adapt to digital-first expectations to remain competitive and patient-centric, as the demand for digital healthcare services is rising.
Updated Regulations Driving Adoption
Governments worldwide are introducing regulations to support digital transformation:
HIPAA (US): Mandates data privacy and security for protected health information (PHI).
GDPR (EU): Enforces strict data protection rules for personal data, including health records.
ISO/IEC 27799: Provides guidelines for information security management in healthcare.
Compliance with these standards is not optional. Healthcare providers must adopt digital solutions with built-in security and privacy measures to avoid legal repercussions and build patient trust.
Gart guides you through every step of the compliance process, providing the expertise, tools, and support you need. Contact Us.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
1. Reduced Costs - automating administrative tasks and other processes allows healthcare providers to save time and money while enhancing patient care. Through digital transformation, workflows are streamlined, and operational efficiency is increased, which helps reduce overhead costs.
2. Optimized Workflow - digital transformation has enabled healthcare providers to optimize their workflows. Automating tasks like patient information management and appointment scheduling allows medical staff to focus more on delivering effective patient care. Additionally, digital tools such as AI-powered chatbots can handle simple patient interactions, reducing the burden on physicians.
3. Enhanced Patient Interaction - digital transformation has empowered healthcare providers to interact with patients more effectively. Innovative technologies enable health professionals to easily access patient records, aiding in better diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, digital solutions like telemedicine allow doctors to offer timely medical advice even when they are not physically present at the hospital or clinic.
4. Improved Administration - digitizing processes makes managing administrative tasks more efficient for healthcare organizations. Automation of activities like scheduling appointments, filing insurance claims, and maintaining accurate financial records reduces manual errors while improving accuracy and speed.
Challenges to Healthcare Digital Transformation
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Healthcare deals with highly sensitive patient data. Digital systems, if not secured, can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, risking:
Data breaches exposing personal health information
Compliance violations leading to hefty fines
Loss of patient trust and reputational damage
Implementing robust cybersecurity frameworks, encryption, and continuous monitoring is non-negotiable for digital health systems.
Resistance to Change within Organizations
Healthcare has traditionally been conservative in adopting new technologies. Reasons for resistance include:
Fear of disrupting established workflows
Lack of digital literacy among staff
Concerns about technology reliability during critical care situations
Change management, leadership support, and comprehensive staff training are essential to overcome this barrier.
Interoperability and Legacy System Integration
Most healthcare organizations run on legacy systems that do not integrate easily with modern digital applications. Challenges include:
Data silos are hindering unified patient views
Incompatibility with new software or cloud platforms
High costs and risks are associated with migrating from outdated systems
Adopting interoperability standards like HL7 FHIR and working with experienced technology partners can mitigate these challenges.
Skills Gaps and Staff Shortages
Digital transformation requires staff to be digitally proficient. However, many healthcare professionals:
Lack of training in new digital tools and platforms
Feel overwhelmed by technological complexity, which affects adoption rates
Continuous upskilling programs and user-friendly solutions can bridge the skills gap and enhance digital confidence among healthcare staff.
Successful Cases of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
1. Infrastructure Optimization and Data Management in Healthcare
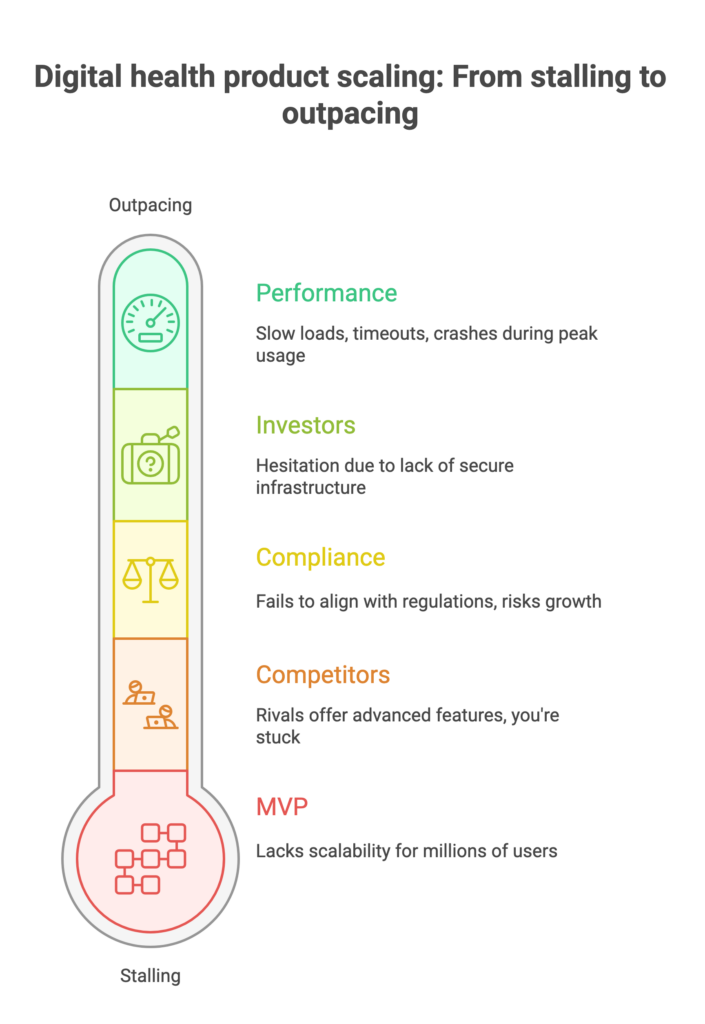
Challenge
A health tech company came with outdated infrastructure that hindered efficient data management and slowed down critical operations. The existing system was not scalable and faced frequent downtimes, affecting the overall patient care experience.
Solution
Gart Solutions implemented a comprehensive infrastructure optimization strategy, including:
Modernizing legacy systems to enhance speed and scalability
Integrating cloud solutions for seamless, secure data management
Ensuring HIPAA compliance for patient data security
Enabling dynamic scaling to meet demand spikes efficiently
Impact
Faster data access, reduced downtimes, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced patient experiences.
Learn details from the Case Study.
2. CI/CD Pipelines and Infrastructure for E-Health Platform
Challenge
An e-health platform aimed to accelerate their development process and improve the reliability of their applications. However, they faced significant challenges with manual deployments, which were time-consuming and error-prone, leading to inconsistent performance and delayed updates.
Solution
Gart Solutions designed and implemented automated CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines tailored to the platform’s unique architecture.
Key implementation steps included:
Automated Build and Testing Pipelines:Code commits automatically triggered builds, testing suites, and static code analysis to catch bugs early.
Infrastructure Optimization:Upgraded and containerized infrastructure to support CI/CD operations efficiently with Kubernetes orchestration for scalability.
Deployment Automation:Introduced automated deployment scripts for seamless rollout of features across production and staging environments without downtime.
Monitoring and Rollback Strategies:Integrated real-time monitoring tools with automated rollback protocols to ensure rapid issue remediation in case of deployment failures.
Impact
Reduced deployment times from days to hours
Significantly minimized human errors, enhancing application stability
Improved development velocity, allowing frequent feature releases
Increased user satisfaction due to faster bug fixes and feature updates
This case demonstrates that CI/CD pipelines aren’t just DevOps best practices – they are strategic enablers of digital agility in healthcare platforms, ensuring compliance, security, and innovation at scale.
Struggling with digital transformation for your healthcare project? Get expert guidance and IT Consultancy for your project free of charge. “Quick wins” – guaranteed. Contact Us.
How Digital Transformation Enhances Patient Experience
Telehealth and Remote Consultations
Imagine consulting your doctor while sipping coffee at home, with prescriptions emailed within minutes. That’s the new healthcare reality.
Telehealth is among the most impactful transformations in healthcare, enabling:
Remote Consultations: Patients consult doctors without visiting clinics, saving time, reducing exposure to infections, and increasing accessibility for remote populations.
Mental Health Services: Telepsychiatry platforms provide discreet, accessible therapy sessions, crucial in an era of rising mental health challenges.
Chronic Disease Management: Regular remote check-ins for diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic conditions enable proactive care, preventing complications and hospital admissions.
During the pandemic, telehealth usage surged by over 154% compared to pre-pandemic levels (CDC data) and continues to grow as patients demand convenience and digital-first care experiences.
Personalized Medicine and AI Diagnostics
Digital transformation enables hyper-personalized treatments tailored to individual patient profiles by leveraging:
AI Diagnostics:AI algorithms analyze radiology images, blood tests, and genetic data to detect diseases earlier than traditional methods. For example, IBM Watson Health analyzes patient records to recommend tailored treatment options for oncologists.
Genomic Medicine:Advances in data processing allow healthcare providers to customize medications and treatments based on patient genetics, enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Predictive Analytics:Big data analytics predict patient risks, enabling early interventions for conditions like sepsis, cardiac events, or diabetic complications.
Patients no longer experience generic treatment plans but benefit from precision medicine designed for their unique biological and lifestyle factors, resulting in improved outcomes and satisfaction.
Get a sample of IT Audit
Sign up now
Get on email
Loading...
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Conclusion
Healthcare organizations understand that digital transformation is crucial for enhancing healthcare services and strengthening patient relationships. Beyond technology investments, this transformation necessitates a shift in organizational culture and employee engagement, requiring enterprise-wide involvement.
Leading health organizations are adopting six key strategies to advance digitally:
Establish digital leadership and governance aligned with business strategies.
Cultivate a digital culture supported by leadership at all organizational levels.
Develop next-generation talent with a focus on workforce quality and quantity.
Integrate cybersecurity at all stages for robust risk management.
Emphasize flexibility and scalability to adapt to evolving technologies.
Implement measurable, accountable KPIs to track the success of digital initiatives.
Successfully navigating digital transformation in healthcare requires expertise and a business-first approach of IT Consulting.
Gart Solutions can guide healthcare providers through the process of Digital Transformation, accelerating the adoption of digital healthcare technologies and improvement of patient outcomes.
Contact Gart today to learn more about how we can help you solve the challenges of digital transformation in healthcare.

AI and machine learning are revolutionizing healthcare, especially in the realm of medical devices, bringing in new ways to diagnose and treat patients. But with this fast-paced innovation comes the tricky task of regulating technology that’s constantly evolving.
Agencies like the FDA in the U.S. and regulatory bodies in Europe are working to keep up, finding ways to make sure these high-tech tools are safe, reliable, and effective. By creating flexible guidelines, building collaborative partnerships, and focusing on real-world monitoring, regulators are adapting to the unique challenges of AI-driven healthcare — aiming to support innovation while keeping patient safety front and center.
Differences in Regulatory Approaches to AI in Healthcare: US vs. Europe
1. Regulatory Structure and Oversight
United States: In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the main body overseeing AI in medical devices. It operates under a centralized system with clear processes for classifying devices, assessing risks, and approving them. The FDA’s Digital Health Center of Excellence focuses on AI and machine learning (ML) in healthcare, offering resources and guidance for developers. The FDA itself reviews medical AI devices to make sure they’re safe and effective.
Europe: The European Union (EU) and the United Kingdom (UK) follow a more decentralized system, using third-party certifying bodies for conformity assessments instead of direct government oversight. The EU’s regulatory framework is developed by the European Commission, aiming to create consistent regulations across member states for a smooth internal market. In the UK, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) works with the Department of Health to oversee AI in healthcare.
"Unlike in America, we don’t really have a single agency overseeing medical devices development in Europe... The European Commission drives the policy, aiming for harmonization across member states to support a single market."
Lincoln Tsang, a UK-based legal expert
2. Risk-Based Frameworks for Classification
US FDA: The FDA categorizes AI-based medical devices by their risk level and intended use, with a focus on potential patient impact. Lower-risk devices, like general wellness apps, face minimal oversight, while higher-risk tools, particularly those that influence clinical decisions, go through strict evaluation. The FDA’s guidance highlights functionality, deployment context, and patient safety as key factors in deciding the risk level and regulatory needs.
European and UK Standards: Similar to the FDA, regulators in Europe and the UK classify devices based on functionality, intended use, and patient impact. Both the EU and UK use a risk-based approach to assess whether AI software qualifies as a medical device, examining the potential harm and healthcare role of the device. Unlike the FDA’s centralized model, the EU uses third-party bodies for assessments, adding industry involvement to the review process.
3. Approval Pathways and Compliance Assistance
The FDA offers several resources to help developers, including guidance documents, informal consultations, and a Digital Health Policy Navigator to clarify regulatory requirements. A key tool is the Predetermined Change Control Plan (PCCP), which lets developers update AI models without resubmitting for approval, as long as updates follow pre-approved guidelines.
The EU and UK support emerging tech through policy papers and adaptable guidelines. While EU regulators are considering adaptive AI-specific regulation, they currently use general guidance rather than structured pathways like the FDA’s PCCP. Both regions prioritize flexibility, updating guidelines and consulting with industry to keep up with rapid tech advancements in AI and digital health.
"We understand the impact this has on companies, particularly for smaller companies and startups, which we see a lot of in the digital health space. Predictability in regulation is crucial."
Sonja Fulmer, Deputy Director, Digital Health Center of Excellence
4. International Harmonization Efforts
Recognizing the global reach of AI, the FDA, Health Canada, and the UK’s MHRA collaborate to align standards and practices. This teamwork simplifies the approval process for companies across borders. Through groups like the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), these agencies work on creating standards that support global interoperability, safety, and clarity. The IMDRF also offers guidance on issues like machine learning practices, promoting a unified regulatory approach worldwide.
Third-Party Compliance Audits for Healthcare Startups
Third-party compliance audits are key for healthcare startups to ensure their products meet regulatory standards before hitting the market. Companies like Gart Solutions offer specialized compliance audits and consulting services to help startups align with the rules set by bodies like the FDA in the U.S. and certification organizations in the EU.
These third-party services support startups by helping them:
Assess Regulatory ReadinessThrough preliminary audits and gap assessments, firms like Gart Solutions help startups identify their current compliance status and highlight areas needing improvement.
Prepare for Formal CertificationBy simulating official audit conditions, third-party firms enable startups to address potential issues in advance of formal evaluations by agencies like the FDA or European certifying bodies.
Monitor Ongoing ComplianceSince regulations, particularly around adaptive AI, are constantly evolving, third-party auditors often conduct periodic reviews to ensure products stay compliant. For AI-enabled devices, these audits can also include checks on algorithmic fairness, data quality, and post-market performance.
Benefits of Compliance Audits for Startups
Partnering with third-party compliance firms offers several advantages:
Cost Savings: Catching compliance issues early can prevent expensive delays and rework during regulatory approval.
Streamlined Approvals: A thorough pre-audit can smooth the formal certification process, reducing friction with regulatory bodies.
Increased Trust and Transparency: Third-party audits show a startup’s dedication to safety and transparency, boosting stakeholder and consumer confidence.
In regions like the EU, where third-party assessments are a regulatory standard, companies like Gart Solutions help fill the gap for startups that may not have in-house compliance expertise. This support is especially valuable for AI-driven healthcare startups, where standards are both strict and rapidly changing.
Get a sample of IT Audit
Sign up now
Get on email
Loading...
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Why Postmarket Surveillance Matters
Postmarket surveillance plays a vital role in regulating AI in medical devices. For high-stakes uses like sepsis detection tools, the FDA requires a monitoring plan to track real-world performance, ensuring devices remain safe and effective across diverse patient populations. This process means manufacturers need to keep an eye on model bias, data quality, and overall device performance in everyday clinical settings. By actively managing these factors, postmarket surveillance helps reduce risks from data issues or model bias, supporting consistent, reliable performance over time.
Trends and the Future of Regulation
With AI becoming a bigger part of healthcare, regulators are likely to move toward more flexible, adaptive policies. Emerging challenges, like continuous-learning AI algorithms, are pushing agencies to rethink how they manage the entire lifecycle of these technologies. Quality assurance, postmarket surveillance, and adaptable regulations are all set to play a larger role as AI advances.
The FDA is working on guidelines for adaptive AI, expected to be released soon, which will help developers as they build continuously learning algorithms. Meanwhile, regulatory bodies in the UK and EU are exploring similar frameworks suited to their own standards, promoting international alignment and consistency.
Conclusion
The regulatory landscape for AI in healthcare is advancing rapidly to keep pace with technological developments. With their risk-based frameworks, both the FDA and European regulators are focused on ensuring the safety and efficacy of AI-enabled medical devices while supporting innovation. Through resources like the Digital Health Center of Excellence and international harmonization initiatives, agencies are setting the stage for a future where AI can safely and effectively transform healthcare, with robust postmarket surveillance and flexible change management strategies forming the backbone of this evolving regulatory framework.