The NIS2 (Network and Information Security Directive) is a comprehensive directive that mandates organizations to implement robust security measures and document compliance to protect critical assets and ensure community continuity.
For organizations subject to NIS2 requirements, CISOs, and IT security officers must ensure robust internal compliance preparedness.
Why NIS2 Compliance Matters
NIS2 aims to enhance the overall level of cybersecurity in the EU by:
Improving the resilience of critical infrastructure.
Enhancing the security of network and information systems.
Ensuring rapid response to and recovery from cyber incidents.
For organizations subject to NIS2 requirements, compliance is not just a legal obligation but a vital component of risk management and operational continuity. Failing to comply can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Who is affected by NIS2?
NIS2 affects all big organizations that work in the European Union and are considered important to society. This includes organizations that:
Have 50 or more employees, or
Make over €10 million in revenue each year
NIS2 puts these organizations into two groups:
Essential organizations - These are very important sectors like energy, healthcare, transportation, and water supply.
Important organizations - These are sectors like manufacturing, food production, waste management, and postal services.
So in simple terms, if your fairly large organization operates in the EU and provides crucial services or products to society, then NIS2 applies to you. The directive aims to ensure these vital entities have strong cybersecurity measures in place.
The penalties for not following NIS2 rules are different depending on whether an organization is labeled as "essential" or "important".
For essential organizations:
They can be fined up to €10 million, or
They can be fined at least 2% of their total worldwide revenue from the previous year, whichever amount is higher.
For important organizations:
They can be fined up to €7 million, or
They can be fined at least 1.4% of their total worldwide revenue from the previous year, whichever amount is higher.
Gart’s NIS2 Solution
Gart offers a solution that simplifies the complexity of NIS2 compliance. The solution provides a systematic approach tailored to your ongoing operations and compliance efforts. By adopting Gart’s solution, you gain access to:
A systematic compliance framework for analyzing and documenting the security of critical assets.
Assurance of effective compliance work throughout your organization, aligned with good security practices and NIS2 requirements by applying ISO/EIC 27001/2 security principles.
Use of questionnaires to review the directive's requirements and ensure all documentation requirements are met, preparing you for audits.
Clear guidance on how to register significant security incidents with CSIRT, ensuring a proactive approach.
Read more: Gart’s Expertise in ISO 27001 Compliance Empowers Spiral Technology for Seamless Audits and Cloud Migration
How Does Gart Solution Support NIS2 Compliance?
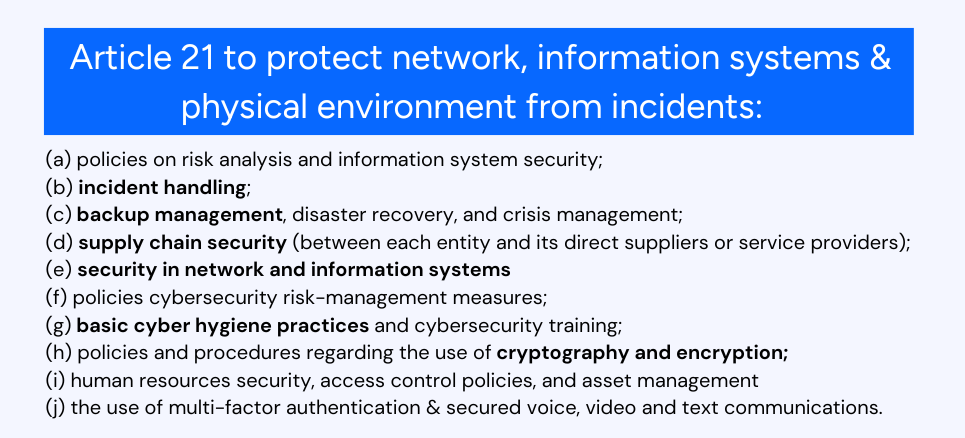
NIS2 Requirement 1: Have policies for analyzing risks and information security
Gart can find and evaluate all assets, systems, weaknesses, and cyber/operational risks in critical infrastructure environments. It uses this detailed visibility to automatically create and enforce network security policies that reduce exposure to those identified risks.
In simple terms, Gart's solution allows organizations to:
Discover all their critical assets, systems, and potential vulnerabilities
Assess the cyber and operational risks in their environments
Automatically define security policies to protect against those risks
Enforce those security policies across their networks
NIS2 Requirement 2: Dealing with Security Incidents
Gart Solutions constantly keeps watch over all critical infrastructure systems for any signs of potential threats, both known and new. It analyzes all security alerts in detail to prioritize the most important issues. Gart also integrates with existing security tools like SIEM and SOAR to extend an organization's security processes across all of its critical systems.
In simpler terms, Gart's solution allows organizations to:
Continuously monitor all their vital systems and networks
Quickly detect any potential cyber threats, even new unidentified ones
Understand the context and importance of every security alert
Work seamlessly with their existing security tools and workflows
Expand their incident response capabilities to cover all critical infrastructure
NIS2 Requirement 3: Managing Crises
Gart provides:
A complete, up-to-date list of all critical systems
Logging of all changes and unusual activity in assets and networks
Ability to create and enforce security policies to separate networks and control access
Ready integration with backup and recovery tools
All of these capabilities from Gart help organizations improve their overall crisis management and ensure the continuity of essential operations.
In simpler terms, Gart's solution allows organizations to:
Know exactly what critical assets they have at all times
Track all activity so they can investigate incidents
Lock down systems by enforcing strict security controls
Quickly backup and restore systems if needed
NIS2 Requirement 4: Security of Networks and Information Systems
By utilizing Gart's capabilities, customers can effectively:
Identify vulnerabilities and insecure configurations in their critical networks and systems
Assess and manage the cyber risks to their operational environments
Allow remote access for personnel to do their work securely
In simple terms, Gart helps organizations implement robust security measures for their networks and information systems as required by NIS2. This includes finding and fixing vulnerabilities, evaluating risks, and controlling access - all crucial for securing vital operational technology.
NIS2 Requirement 5: Basic Cybersecurity Practices and Training
Gart's solution helps organizations:
Identify areas where they need to improve their basic cybersecurity habits and procedures based on risk assessments.
Ensure all personnel, whether employees or vendors, follow proper access controls, password management, and other essential cybersecurity practices.
Use the recommendations to develop training programs to raise cybersecurity awareness and skills.
NIS2 Requirement 6: Policies and Procedures for Data Encryption
Gart provides:
1) Encryption of all user data, critical system data, and other sensitive information in compliance with NIS2, GDPR, and other regulations.
2) Alerts when sensitive data like personal health records is being processed in a way that violates security policies or could lead to a data breach.
Here's a rewording in simple language:
NIS2 Requirement 7: Using Multi-Factor Authentication and Secure Communications
Gart helps organizations:
- Enforce strong access controls like multi-factor authentication across their workforce and supply chain vendors/partners
- Allow only authorized and verified personnel to access critical systems remotely or on-site
- Ensure all communications to operational technology are fully secured
- Meet audit requirements by recording all access sessions
Get a sample of IT Audit
Sign up now
Get on email
Loading...
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Key Features:
Mapping of Critical Assets
We will create an overview of the various types of critical assets within your value chain and document their security levels.
Risk Assessment of Critical Assets, Systems, and Processes
We will conduct a risk assessment based on the current threat landscape, the assets' placement within the value chain, and their potential societal consequences.
GAP Analysis
We will obtain a clear overview of your current compliance level and implementation, identifying the essential control objectives required for NIS2.
Automated Processes
We will automate control follow-ups and communication with internal stakeholders to ensure all relevant tasks are carried out correctly and on time.
Compliance Control and Scope of SoA
We will begin with an initial compliance review, prioritize, and scope the Statement of Applicability (SoA) based on NIS2 requirements.
Create Awareness and Communicate Directly with Stakeholders
We will create awareness and directly communicate with stakeholders to keep everyone informed about policy and procedural changes, ensuring everyone understands their role.
Overview of Reporting to CSIRT
We will establish a process for reporting significant incidents and threats to the organization or its supply chain to CSIRT, protecting critical assets quickly and efficiently.
Ongoing Auditing
We will document internal compliance with NIS2 via dedicated management controls and functionality for auditing critical suppliers.
About the NIS2 Directive or NIS2 framework
The NIS 2 Directive, also referred to as the NIS2 framework, is a European Union regulation aimed at enhancing cybersecurity across the bloc. Here's a breakdown of the key points:
Goals:
Improve overall cybersecurity posture in the EU.
Strengthen existing cybersecurity measures in critical sectors.
Ensure a consistent approach to cybersecurity risk management across member states.
Key Features:
Broader Scope: NIS2 applies to a wider range of sectors compared to the previous NIS Directive. This includes essential services (energy, transport, water, etc.) and important entities in sectors like waste management, postal services, manufacturing, and more.
Enhanced Risk Management: Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures to manage risks to their network and information systems. This includes measures to prevent incidents, minimize their impact, and report them effectively.
Incident Reporting: Entities are required to report significant incidents to relevant authorities. This allows for faster response and improved coordination across member states.
Supply Chain Security: The directive emphasizes the importance of supply chain security. Organizations need to consider the cybersecurity risks associated with their suppliers and vendors.
Cooperation and Information Sharing: Increased cooperation and information sharing among member states and relevant authorities are crucial aspects of NIS2.
Current Status:
Adopted in December 2022 and came into effect in January 2023.
EU member states have until October 17, 2024 to transpose the NIS2 Directive into national law.
By April 17, 2025, member states need to establish a list of essential entities falling under the directive.
NIS2-Compliance-Checklist-A-Comprehensive-Guide-to-Audit_Free-PDFDownload
Conclusion
The European Union's Network and Information Security Directive, known as NIS2, sets stringent requirements for organizations to safeguard their critical assets and ensure the continuity of essential services.
Gart is here to guide you through every step of the process, providing the expertise, tools, and support you need to achieve and maintain compliance. With our systematic approach, you can focus on your core business operations, confident that your information security is in capable hands.
Are you ready to simplify your NIS2 compliance journey? Contact Gart today to learn more about how we can help you strengthen your information security and achieve regulatory compliance with ease.

The way businesses store and manage data is undergoing a significant shift. Traditionally, companies relied on on-premises infrastructure – physical servers and hardware located within their own facilities. However, the rise of cloud computing offers a compelling alternative. Let's delve into both options with facts and figures to help you decide which is best for your needs.
This article helps you decide when to use cloud computing, on‑premises hardware, or a hybrid strategy. Learn the advantages, costs, performance considerations, and compliance implications for each.
What Does Cloud Computing Mean and Why Most Enterprises Use It?
Cloud computing delivers IT services, including servers, databases, storage, networking, and analytics, over the internet. It supports scalability, rapid innovation, and cost flexibility.
As of 2019, 94% of enterprises used cloud services (Source: Flexera), and by 2025, 85% of IT strategies will be cloud-first (Source: Gartner). Why?
Cloud eliminates the upfront costs of buying and maintaining hardware. You only pay for the resources you use, leading to significant potential savings.
Cloud providers handle software updates and security patches, freeing up your IT staff for other tasks. Access your data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work and collaboration.
Key Cloud Benefits:
Elastic Resources: Scale up or down instantly.
Reduced Maintenance: Providers handle updates, patches, and uptime.
Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use (OpEx model).
Remote Access: Support distributed teams and collaboration.
Innovation Ready: Experiment faster with new tools and services.
A 2023 Flexera report found that cloud migration can cut infrastructure costs by up to 30%.
Why Choose On‑Premises Infrastructure Even Today?
Summary:
On‑premises infrastructure gives you full control, high customization, and total ownership of your environment—but also demands greater capital investment and ongoing maintenance.
What is On-Premises Infrastructure?
Also known as bare metal, it refers to computing resources physically located and managed within your organization’s facilities.
While cloud is trending, on-premises still holds relevance for:
Customization: Full control over hardware/software.
Data Security Preference: Some industries view on-prem as more secure.
Regulatory Pressure: Industries like finance or defense may require data to stay in-house.
The global bare metal cloud market was valued at $5.6B in 2021 and is expected to reach $56.6B by 2031 (CAGR of 26.1%).
On-Premises Infrastructure
On-premises or bare metal refers to a computing infrastructure that is installed and run on computers on the premises of the organization using the software, rather than at a remote facility or in the cloud. The global bare metal cloud market was valued at $5.6 billion in 2021, and is projected to reach $56.6 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 26.1% from 2022 to 2031. (Source: Verified Market Research).
On average, organizations using on-premises infrastructure spend 55% of their IT budgets on maintenance, compared to 45% for cloud users (Source: Deloitte).
While cloud computing is gaining traction, on-premises solutions still hold value for some businesses:
You have complete control over your hardware and software, allowing for high levels of customization.
Some businesses might prefer to keep sensitive data in-house, perceived to be more secure. However, with advanced security measures, reputable cloud providers offer robust data protection.
Certain industries may have strict data residency regulations that favor on-premises storage.
Cost Considerations: OpEx vs CapEx and Hidden Costs
Cloud services operate on an operational expenditure (OpEx) model, where you pay for resources and services as you use them. This eliminates the need for large upfront investments.
On-premises solutions require substantial capital expenditure (CapEx) for purchasing and setting up hardware, data centers, and related infrastructure. This includes costs for servers, storage, networking equipment, and facilities.
Starting with cloud services often requires minimal initial financial commitment. You can quickly provision resources without significant capital expenditure, making it accessible for startups and projects with limited budgets.
The hardware you buy will depreciate over time, which can affect long-term financial planning and capital allocation.
Cloud uses an OpEx model (pay-as-you-go), while on-premises requires CapEx (hardware + setup). However, the total cost includes hidden factors, such as maintenance, refresh cycles, and staff, which can make on-prem more expensive over time.
FeatureCloud ComputingOn-Premises (Bare Metal)Initial InvestmentLow (OpEx)High (CapEx)Hidden CostsFewer (no cooling, staffing)Higher (power, cooling, facilities, staff)Hardware RefreshHandled by providerRequires internal planning and expenseResource UtilizationPay only for what you useRisk of overprovisioning and idle hardwareScalabilityInstant, elastic, cost-efficientRequires physical scaling and long lead times
Key Insights:
On-prem may appear cheaper upfront, but over time, TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) can be significantly higher.
Many organizations overspend due to underused hardware and frequent refresh cycles.
Performance and Scalability: Cloud vs. Bare Metal
Cloud offers elastic scalability— ideal for dynamic workloads. Bare-metal provides raw power and consistency — ideal for latency-sensitive, compute-heavy tasks.
Cloud computing offers elasticity, allowing you to rapidly scale resources (processing power, storage) up or down based on real-time demand. This ensures optimal performance during peak loads without sacrificing resources during low usage periods. A 2023 study by Flexera found that 73% of businesses reported improved application performance after migrating to the cloud.
Examples:
▪️ You can choose from a range of instance types optimized for different workloads, such as compute-optimized, memory-optimized, and storage-optimized instances. For example, an m5.2xlarge instance provides 8 vCPUs and 32 GB of memory, suitable for high-performance computing tasks.
▪️ Azure offers virtual machine sizes tailored for specific scenarios, such as the D-series for general-purpose workloads and the H-series for high-performance computing.
Bare metal servers often provide superior performance for certain high-demand workloads due to their dedicated hardware. This can be critical for applications requiring high I/O throughput, low latency, or substantial computational power. With bare metal, you have the flexibility to configure hardware to meet specific performance requirements. This is particularly beneficial for specialized applications, such as machine learning models or high-frequency trading platforms.
Examples:
▪️ A bare metal server with Intel Xeon Platinum CPUs and NVMe SSDs can handle large-scale databases or data-intensive applications with minimal latency. For instance, benchmarks show that a single bare metal server can achieve up to 1 million IOPS (input/output operations per second) compared to 100,000 IOPS for a typical cloud SSD instance.
▪️ IBM offers customizable bare metal servers with up to 192 GB of RAM and 16 vCPUs, providing the raw performance needed for demanding workloads. These servers are often used for tasks that require consistent, high-speed performance without the overhead of virtualization.
Scaling on-premises infrastructure typically requires purchasing and installing additional hardware. This process involves significant planning, procurement, and installation time. For example, scaling from a small data center to a larger one may involve several months of lead time for new hardware and infrastructure.
Compliance, Data Sovereignty & Security: Cloud vs. On‑Premises
Cloud providers offer robust security and global compliance, but you must manage shared responsibilities. On-premises gives full control, but also full accountability.
Major cloud providers comply with a range of international and industry-specific standards. For example:
AWS Compliance: AWS holds certifications such as ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, GDPR compliance, and HIPAA compliance.
Azure Compliance: Microsoft Azure is compliant with standards including ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, GDPR, and HIPAA.
Google Cloud Compliance: Google Cloud complies with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, GDPR, and HIPAA.
Read more: Gart’s Expertise in ISO 27001 Compliance Empowers Spiral Technology for Seamless Audits and Cloud Migration
Cloud providers offer data residency options, allowing organizations to choose the geographical location where their data is stored. For instance, AWS provides data centers across various regions globally, and users can select the region that aligns with their data sovereignty requirements.
Cloud providers ensure compliance with local data protection laws, such as the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which mandates that data of EU citizens must be stored within the EU or in countries with adequate protection levels.
On‑Prem Compliance Pros and Cons:
Full control over data and infrastructure.
Ideal for strict regulations in finance, defense, or healthcare.
But: You’re fully responsible for audits, reporting, and security hardening.
A study by IAPP found that GDPR compliance costs average $1.5M per organization — cloud providers often absorb parts of this burden via shared responsibility.
On-premises environments require organizations to ensure compliance with local and industry regulations. This often involves implementing complex data protection measures and ensuring that all aspects of the infrastructure adhere to regulatory standards.
With on-premises infrastructure, organizations have complete control over their data and its location, which can be advantageous for meeting specific data sovereignty requirements. However, this also means that the organization is fully responsible for implementing and maintaining compliance measures.
Cloud Provider Security Measures vs. In-House Security
In cloud environments, security is a shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the customer. Providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure, including physical security, network security, and virtualization layers. Customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and configurations within the cloud.
On-premises security involves dedicated resources for managing physical security, network security, and data protection. This includes physical access controls, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
According to a Ponemon Institute study, organizations with in-house security teams spend an average of $3.6 million annually on security, compared to $2.6 million for organizations using managed security services. This highlights the potential cost advantage of cloud security solutions, where many security services are included as part of the subscription.
Use Cases and Considerations: Cloud vs. On-premises
Use CaseCloud ComputingOn-Premises InfrastructureStartups & Rapid DevIdeal – fast deployment, low CapEx, scalabilityLess suitable – high upfront costs, longer setup timeHigh-Traffic ApplicationsElastic scaling handles spikes effortlesslyRequires costly overprovisioning to match peak demandStable WorkloadsGood with cost-optimized reserved instancesSuitable, though scaling may be more complexVariable DemandBest – resources scale dynamicallyScaling up/down is time-consuming and hardware-boundSensitive Data ComplianceSupports with region selection + certificationsOffers full control for strict regulatory environments
The Future is Hybrid
Many businesses are adopting a hybrid approach, combining cloud and on-premises infrastructure. This allows them to leverage the benefits of both: cost-effectiveness, scalability, and control over sensitive data.
FeatureCloud ComputingOn-premises/Bare MetalDeployment ModelOff-site, delivered over the internetOn-site, within your data centerScalabilityEasy to scale up or down resourcesScaling can be slow and expensiveCostPay-as-you-go modelHigh upfront costs for hardware, software, and IT staffAccessibilityAccessible from anywhere with an internet connectionAccess might be restricted to the local networkSecurityRobust security features offered by cloud providersRequires strong internal security measuresMaintenanceManaged by the cloud providerRequires in-house IT staff for maintenanceControlLess control over hardware and softwareFull control over hardware and softwareCustomizationLimited customization optionsHighly customizable
Why Hybrid Works:
Critical apps or sensitive data stay on-premises.
Web apps, backups, and analytics move to the cloud.
You gain cost-efficiency, resilience, and agility.
Get a sample of IT Audit
Sign up now
Get on email
Loading...
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Additional Factors to Consider When Choosing Cloud or On-Premises
IT Expertise
Cloud simplifies infrastructure—no need for deep in-house IT skills.
On-premises requires hands-on experience for setup, maintenance, and compliance.
Industry Regulations
Healthcare, finance, and government may mandate data residency or on-premise data control.
Cloud providers increasingly meet these standards, but internal audits may still favor on-prem.
Business Stage
Startups or growing businesses benefit most from cloud flexibility.
Mature organizations with legacy systems may prefer to extend on-prem investments.
In Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses manage IT. With elastic scalability, global reach, and reduced CapEx, it fits most modern businesses.
However, on-premises remains valuable for highly regulated, security-conscious, or performance-driven environments.
For many, a hybrid approach offers the best balance — agility, control, and cost-efficiency combined.
Still unsure?Let’s discuss your infrastructure needs and tailor a solution that fits both your tech and your compliance goals.

Are you contemplating the shift to cloud computing? As businesses increasingly embrace the benefits of cloud technology, it's crucial to make an informed decision when selecting a cloud provider (AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud). With numerous options available, it can be overwhelming to determine the best fit for your specific needs.
[lwptoc]
But fear not! In this comprehensive blog post, we'll delve into various cloud providers and assist you in identifying the ideal choice for your organization.
CriteriaAmazon Web Services (AWS)Microsoft AzureGoogle Cloud Platform (GCP)PricingOffers various pricing models and options, including pay-as-you-go and reserved instances.Flexible pricing options, including pay-as-you-go and discounted reserved instances.Offers pay-as-you-go pricing and committed use discounts.Compute ServicesProvides a wide range of compute services, including EC2, Lambda, and Elastic Beanstalk.Offers compute services like Virtual Machines, App Service, and Azure Functions.Provides compute services such as Compute Engine, App Engine, and Kubernetes Engine.Storage OptionsProvides various storage services, including S3, EBS, and Glacier.Offers storage services like Blob Storage, File Storage, and Azure Disk Storage.Provides storage services such as Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, and Cloud Bigtable.Machine Learning and AI CapabilitiesOffers comprehensive AI and machine learning services with Amazon SageMaker, Rekognition, and more.Provides AI and ML capabilities through services like Azure Machine Learning, Cognitive Services, and more.Offers AI and ML services through Google Cloud AI, AutoML, and TensorFlow.Database ServicesProvides a wide range of database options, including Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, and Redshift.Offers database services like Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB, and Azure Database for MySQL.Provides database services such as Cloud SQL, Firestore, and BigQuery.NetworkingOffers extensive networking capabilities, including Amazon VPC, Route 53, and CloudFront.Provides networking services like Azure Virtual Network, Azure DNS, and Azure ExpressRoute.Offers networking services such as Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Cloud DNS, and Cloud Load Balancing.Global InfrastructureOperates in numerous regions worldwide with a large number of data centers.Has an extensive global presence with data centers located in many regions.Has a global network of data centers and regions to provide wide coverage.SupportProvides extensive documentation, support forums, and options for technical support.Offers comprehensive documentation, support options, and access to Azure support engineers.Provides documentation, community support, and access to Google Cloud support resources.A high-level overview of the different cloud providers
Pros and Cons: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Pros:
Extensive Service Offering: AWS has a vast range of services, including compute, storage, databases, AI/ML, networking, and more, providing comprehensive solutions for various business needs.
Market Leader: AWS is the leading cloud provider with a strong track record, extensive customer base, and a robust ecosystem of third-party integrations.
Global Infrastructure: AWS has a vast global infrastructure with multiple data centers worldwide, allowing businesses to have low-latency access and meet data sovereignty requirements.
Scalability and Flexibility: AWS offers auto-scaling features and flexible resource allocation, enabling businesses to easily scale up or down based on demand.
Strong Security Measures: AWS provides a wide range of security tools, encryption options, and compliance certifications to ensure the protection of data and meet regulatory requirements.
Cons:
Complex Pricing Structure: AWS pricing can be complex, especially when using a variety of services. Understanding the pricing models, estimating costs, and optimizing expenses may require careful planning and monitoring.
Steep Learning Curve: AWS has a rich set of services and features, which can make it challenging for beginners to navigate and fully utilize the platform. Learning resources and training may be necessary for effective usage.
Limited Support Options: While AWS provides documentation and support forums, some users have reported challenges with response times and the availability of personalized support.
Microsoft Azure
Pros:
Seamless Integration with Microsoft Products: Azure offers seamless integration with popular Microsoft tools and technologies, making it attractive for businesses already using the Microsoft ecosystem.
Hybrid Cloud Capabilities: Azure provides strong support for hybrid cloud scenarios, allowing businesses to seamlessly integrate on-premises infrastructure with the cloud.
Wide Range of Services: Azure offers a comprehensive set of services, including compute, storage, databases, analytics, and more, catering to diverse business needs.
Strong Enterprise Focus: Azure is well-suited for enterprise environments, with features like Active Directory integration, strong governance tools, and compliance certifications.
Global Presence: Azure has a wide global presence with data centers located in various regions, enabling businesses to have a global reach and meet local compliance requirements.
Cons:
Learning Curve for Non-Microsoft Users: Users not familiar with Microsoft technologies may face a learning curve when navigating Azure's services and features.
Some Services Still Maturing: While Azure offers a wide range of services, some may still be evolving and may not have the same maturity or feature set as those of AWS.
Limited Marketplace Offerings: The Azure Marketplace may have a smaller selection of third-party solutions compared to AWS, although it continues to grow.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Pros:
Strong AI and ML Capabilities: GCP is known for its advanced AI and ML services, offering pre-trained models, custom machine learning, and data analytics capabilities.
Cost-Effective Pricing: GCP's pricing structure is known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, with competitive pricing options and sustained usage discounts.
Scalable and Elastic Infrastructure: GCP provides flexible scaling options, allowing businesses to easily handle varying workloads and traffic spikes.
Global Network and Performance: GCP offers a high-performance global network, enabling businesses to deliver applications and services with low latency.
Developer-Friendly: GCP provides a range of developer tools and integration options, making it attractive for developers and DevOps teams.
Cons:
Smaller Market Share: GCP currently has a smaller market share compared to AWS and Azure, which may result in a comparatively smaller ecosystem and fewer third-party integrations.
Limited Enterprise Focus: GCP may be perceived as more focused on startups and developer-centric use cases, although it continues to expand its enterprise capabilities.
Learning Curve for Non-Google Users: Users who are not familiar with Google's technologies may need to invest time in learning and adapting to GCP's platform and services.
? Unable to choose a cloud provider? Seek expert guidance from Gart. Our experienced team can help you navigate the complexities of cloud computing and select the optimal provider for your business.
How to Choose a Cloud Service Provider
Choosing a cloud service provider requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are the key steps to guide you in selecting the right cloud service provider for your business:
Define Your Business Requirements:
Understand your business requirements and goals.
Evaluate services, performance, and security measures.
Consider global infrastructure and data centers.
Assess integration capabilities and ease of migration.
Evaluate disaster recovery options and pricing models.
Seek feedback and conduct trials to make an informed choice.
To begin the process of selecting the right cloud service provider for your business, it is crucial to gain a deep understanding of your organization's needs, objectives, and unique requirements in relation to cloud services. Take into account various factors, such as the types of workloads you handle, your storage and computing requirements, scalability expectations, compliance obligations, and any industry-specific regulations that apply.
Conduct a comprehensive workload analysis to assess the specific applications and workloads your business relies on. Consider the nature of these workloads, whether they involve web hosting, data analytics, AI/ML processing, e-commerce, or other operations. Identify the computing resources, storage needs, and network prerequisites associated with each workload.
This table provides a brief overview of the compute services offered by each cloud provider:
Cloud ProviderCompute ServicesAWSAmazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)AWS Lambda (Serverless Computing)Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service)AWS Batch (Batch Computing)AWS Elastic Beanstalk (Platform-as-a-Service)AzureAzure Virtual MachinesAzure Functions (Serverless Computing)Azure Container InstancesAzure Batch (Batch Computing)Azure App Service (Platform-as-a-Service)GCPGoogle Compute EngineGoogle Cloud Functions (Serverless Computing)Google Kubernetes Engine (Managed Kubernetes)Google Cloud Run (Container Instances)Google App Engine (Platform-as-a-Service)A table comparing the compute services offered by AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
Determine the scalability and flexibility your business demands. Evaluate whether you require the capability to quickly scale resources up or down in response to fluctuating demands. Consider whether potential cloud providers offer features like auto-scaling, elastic load balancing, and flexible resource allocation to meet your scalability requirements effectively.
Evaluate your data storage and database needs. Analyze the volume of data your business needs to store and process, as well as the specific data access patterns (real-time, batch processing) that are crucial to your operations. Consider the level of data durability, redundancy, and availability required. Assess the availability of different storage options (such as object storage or block storage) and the variety of database solutions (relational or NoSQL) offered by each cloud service provider.
Here's a table comparing the database and storage services offered by AWS, Azure, and GCP
Cloud ProviderDatabase ServicesStorage ServicesAWSAmazon RDS (Relational Database Service)Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL Database)Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store)Amazon Aurora (Managed Relational Database)Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)Amazon DocumentDB (MongoDB-compatible Document Database)Amazon FSx (File Storage)Amazon Neptune (Graph Database)Amazon Glacier (Long-term Archive Storage)AzureAzure SQL DatabaseAzure Blob StorageAzure Cosmos DB (NoSQL Database)Azure Files (Managed File Storage)Azure Database for MySQLAzure Disk StorageAzure Database for PostgreSQLAzure Archive Storage (Long-term Archive Storage)Azure Synapse Analytics (Data Warehousing)Azure Data Lake StorageGCPGoogle Cloud SQL (Managed Relational Database Service)Google Cloud StorageGoogle Cloud Firestore (NoSQL Document Database)Google Cloud Persistent DiskGoogle Cloud Spanner (Horizontally Scalable Relational Database)Google Cloud FilestoreGoogle Cloud Bigtable (Wide-column NoSQL Database)Google Cloud Storage Nearline (Long-term Archive Storage)Google Cloud Datastore (NoSQL Database)Google Cloud Archive Storage (Long-term Archive Storage)AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud: database and storage services
Assess the security and compliance features provided by each cloud service provider, especially if your business operates in an industry with specific regulatory requirements such as healthcare (HIPAA) or financial services (PCI DSS). Pay attention to aspects like data encryption, access controls, compliance certifications, and auditing capabilities offered by potential providers.
Take into account your business's geographic presence and any data sovereignty obligations you may have. Determine whether the cloud provider has data centers located in regions that align with your operations or customer base. Ensure that the provider can meet local data residency requirements and provide low-latency access for optimal performance.
Evaluate the compatibility and integration capabilities of the cloud provider with your existing systems, applications, and IT infrastructure. Look for pre-built integrations, APIs, and software development kits (SDKs) that facilitate seamless connectivity and data exchange. Consider the ease of migrating your current applications and data to the platform of the cloud service provider under consideration.
Assess your disaster recovery and business continuity needs. Determine whether the cloud provider offers robust backup and disaster recovery solutions, including data replication across multiple regions, automated backup processes, and options for high availability and fault tolerance. These features are critical to ensure the uninterrupted operation of your business.
Consider your budget and cost expectations for cloud services. Evaluate the pricing models, cost structures, and billing options provided by each cloud service provider. Take into account factors such as compute and storage costs, data transfer fees, and potential discounts or cost optimization tools offered by the provider.
By conducting a thorough analysis and defining your business requirements across these dimensions, you will be better equipped to evaluate different cloud service providers and select the one that aligns most effectively with your organization's needs, goals, and constraints.
Still undecided on the right cloud provider? Get in touch with us now and embark on your cloud transformation journey!
Consider Performance and Reliability
Performance and reliability are crucial for smooth operations. Evaluate the uptime guarantees and service level agreements (SLAs) provided by cloud providers. Look for low-latency connections, robust network infrastructure, and features like content delivery networks (CDNs) and load balancing that can enhance performance and improve user experience.
AWS Networking Services
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
Amazon CloudFront (Content Delivery Network)
Amazon Route 53 (Domain Name System)
AWS Direct Connect (Dedicated Network Connection)
AWS Elastic Load Balancer (Application Load Balancer, Network Load Balancer)
Azure Networking Services
Azure Virtual Network
Azure CDN (Content Delivery Network)
Azure DNS (Domain Name System)
Azure ExpressRoute (Dedicated Network Connection)
Azure Load Balancer (Application Gateway, Traffic Manager)
GCP Networking Services
Google VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
Cloud CDN (Content Delivery Network)
Cloud DNS (Domain Name System)
Cloud Interconnect (Dedicated Network Connection)
Load Balancing (HTTP/HTTPS, TCP/SSL)
Assess Security and Compliance
It is essential to carefully evaluate the security measures and certifications provided by each cloud provider. This evaluation should encompass considerations such as encryption options, access controls, identity and access management (IAM) capabilities, and the provider's compliance with industry regulations that are relevant to your business. Ensuring that the chosen cloud provider meets your specific security and compliance requirements is crucial for safeguarding your data and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Review Pricing and Cost Structures
When reviewing the pricing and cost structures of various cloud providers, it is important to gain a comprehensive understanding of their pricing models, cost structures, and billing options. Evaluate key factors such as pay-as-you-go pricing, the availability of reserved instances, costs associated with data storage, and fees for data transfers. It is crucial to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) over time and compare it with your budget and cost expectations. To effectively manage expenses, look for cost optimization tools and explore available options that can assist in optimizing and controlling your cloud-related costs. By conducting a thorough evaluation of pricing and cost structures, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial objectives while maximizing the value derived from your chosen cloud provider.
Read more: Azure Cost Optimization for a Software Development Company
This case study highlights how Gart assisted Appsurify.com, a software development and testing company, in optimizing their Microsoft Azure infrastructure costs. By conducting a thorough analysis of the client's cloud infrastructure and identifying cost drivers, our team implemented strategic changes to reduce network costs by 90%. Additionally, the solution improved performance, security, and reliability while saving the client up to $400 per day in network and infrastructure expenses. The case study demonstrates the effectiveness of Azure cost optimization in achieving significant savings and enhancing overall infrastructure performance.
Consider Global Infrastructure and Data Centers
The proximity of data centers to your target audience can play a vital role in minimizing latency and ensuring optimal performance. Additionally, it is crucial to consider data sovereignty requirements and choose a provider that can comply with the regulations specific to the regions where you operate. Evaluating the cloud provider's content delivery network (CDN) capabilities is also important, as it can enhance performance by delivering content efficiently to end users across various locations. By carefully considering global infrastructure and data center availability, you can ensure a seamless and responsive user experience while meeting regulatory obligations.
The three major cloud providers each have an extensive global presence:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) operates in 25 geographic regions, which are further divided into 81 availability zones. They have a vast network of 218+ edge locations and 12 Regional Edge Caches.
Microsoft Azure has a footprint in over 60 regions worldwide. Each region is equipped with a minimum of three availability zones, ensuring high availability. Additionally, they have established more than 116 edge locations, also known as Points of Presence (PoPs).
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is available in 27 cloud regions, and within these regions, there are a total of 82 zones. GCP further extends its network reach through 146 edge locations across the globe.
Evaluate Support and Documentation
Consider the level of support and customer service provided by each cloud provider. Look for availability of support channels, response times, and the quality of documentation, tutorials, and knowledge base resources. A responsive and knowledgeable support team can be crucial in resolving issues promptly.
Consider Vendor Lock-in and Portability
Assess the level of vendor lock-in associated with each provider. Evaluate the ease of migrating to and from the cloud provider, as well as the compatibility and portability of your applications and data. Consider strategies to mitigate vendor lock-in risks and ensure future flexibility.
Seek Feedback and References
Look for feedback from other businesses or industry peers who have experience with the cloud providers you are considering. Research case studies and success stories to understand how well the providers have supported similar organizations in achieving their goals.
Conduct Proof-of-Concept (PoC) or Trial Periods
Before making a final decision, consider conducting a proof-of-concept or taking advantage of trial periods offered by cloud providers. This allows you to test the provider's services, performance, and compatibility with your applications and workloads before committing fully.
By following these steps and thoroughly evaluating each cloud service provider based on your specific business requirements, you can make an informed decision and choose the cloud service provider that best fits your needs and goals.
Don't let the cloud provider decision overwhelm you. Gart is here to help.
Exploring Other Cloud Providers: Beyond AWS, Azure, and GCP
In addition to AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud, there are several other notable cloud providers in the market. Here are a few examples:
IBM Cloud
IBM's cloud platform that offers a range of services including compute, storage, AI, and blockchain. It emphasizes enterprise-grade security and hybrid cloud capabilities.
Oracle Cloud
Oracle's cloud platform provides services for infrastructure, databases, applications, AI, and data analytics. It focuses on integrating with existing Oracle software and technologies.
Alibaba Cloud
Alibaba's cloud platform offers a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including compute, storage, networking, AI, and big data analytics. It has a strong presence in the Asia-Pacific region.
DigitalOcean
DigitalOcean is a developer-focused cloud provider that specializes in providing simple and cost-effective infrastructure services such as virtual machines, storage, and Kubernetes clusters.
Vultr
Vultr is a cloud provider known for its high-performance and affordable infrastructure services. It offers scalable compute, storage, and networking resources across multiple data centers worldwide.
Rackspace
Rackspace provides managed cloud services and expertise across various cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and GCP. It offers support, migration, and optimization services to help businesses leverage the benefits of the cloud.
Salesforce Cloud
Salesforce offers a suite of cloud-based applications for customer relationship management (CRM), sales, marketing, and service management. Its platform-as-a-service (PaaS), known as Salesforce Platform, allows businesses to build and deploy custom applications.
Tencent Cloud
Tencent Cloud is a leading cloud provider in China, offering a wide range of cloud services including computing, storage, databases, AI, and IoT. It focuses on serving businesses in the Chinese market.
OVHcloud
OVHcloud is a European cloud provider offering a broad portfolio of services, including virtual private servers, dedicated servers, storage, and network solutions. It emphasizes data privacy and compliance with European regulations.
Hetzner Cloud
Hetzner Cloud is a German cloud provider offering a range of infrastructure services, including virtual machines, storage, and networking. It is known for its competitive pricing and reliable performance.
Conclusion: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
When comparing AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud, it's clear that each cloud provider offers a robust set of services and features. AWS excels in its expansive service offerings and market dominance. Azure stands out with its seamless integration with Microsoft technologies and comprehensive enterprise solutions. Google Cloud impresses with its cutting-edge technology and strong focus on data analytics and machine learning. Ultimately, the right choice depends on your specific business requirements, budget, and preferences. We hope that our assistance has been valuable in guiding you on how to choose a cloud provider.