The HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health) Act has changed how healthcare providers handle patient information by promoting the use of Electronic Health Records (EHR) and creating a strong compliance framework.
A key part of this framework is the audit process, which ensures that healthcare organizations follow HIPAA’s rules on privacy, security, and notifying patients in case of a breach.
One important aspect is the possibility of an audit by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR), which checks for compliance and can impose serious penalties for violations.
In this article, we’ll break down the HITECH audit process and share practical steps that healthcare providers can take to get ready, with helpful insights from healthcare IT expert Anupam Sahai.
Quick summary:
📍 HITECH Act audits typically take several weeks to a few months to complete, depending on the complexity of the organization and the scope of the audit.
📍 The HITECH Act increased the potential penalties for HIPAA violations significantly. Fines can range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million for repeated violations.
📍 The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) conducts audits on a random sample of covered entities and business associates. While there is no set schedule, the OCR aims to audit about 200 organizations each year as part of its compliance initiative.
📍 The OCR has established a detailed audit protocol that includes 125 audit steps, covering areas such as administrative safeguards, physical safeguards, technical safeguards, and policies and procedures.
📍 Gart Solutions can help your business with HITECH Act and HIPAA Audits
Understanding the HITECH Act and HIPAA Audits
The HITECH Act, passed in 2009, built on the privacy and security rules set by HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). Its main goal is to encourage healthcare providers to adopt health information technology, especially Electronic Health Records (EHRs), to improve patient care. To make sure these rules are followed, the HITECH Act introduced stricter data protection measures and required audits.
HIPAA audits are carried out by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR), which is part of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). These audits are important because they check that healthcare providers and their partners are following the necessary privacy, security, and breach notification rules. Depending on the organization’s risk level, these audits can be done remotely (desk audits) or in person (on-site audits).
Together, the HITECH Act and HIPAA aim to make healthcare better by improving how patient information is managed and reducing costs. HIPAA specifically focuses on protecting patient information and requires that all healthcare providers, insurers, and other organizations that handle this data put strong safeguards in place to keep electronic patient information safe.
These audits cover both covered entities (CEs) and business associates (BAs), raising the stakes for organizations that don’t comply:
▪️ Fines: The maximum fine for a HIPAA violation has jumped to $1.5 million for each incident, and there’s no limit to how many times fines can be imposed.
▪️ Whistleblower Incentives: The HITECH Act encourages people to report non-compliance by offering them a share of the penalties collected.
▪️ Liability Expansion: Business associates and subcontractors are now held to the same standards as covered entities. This creates a “liability chain,” meaning everyone involved in handling patient information is responsible for following the rules.
OCR Audits: Key Elements and Findings
Pilot Audit Program (2012)
In 2012, the OCR started a pilot audit program to check how well covered entities were following HIPAA privacy and security rules. They found that smaller organizations had a tougher time meeting these requirements. Some of the key issues included:
- Many organizations didn’t do proper security risk analyses.
- There were weak controls over who could access Protected Health Information (PHI).
- Few organizations had plans to deal with data breaches or system failures.
Ongoing and Future Audits
Since then, the OCR has made the audit program permanent and expanded it to include business associates (BAs)—the vendors or contractors that provide services to healthcare providers and have access to PHI.
Starting in 2015, the OCR began sending out pre-audit surveys to about 1,200 covered entities to collect information about them. From those, 200 entities were chosen for desk audits. The OCR is using these audits not only to find common compliance problems but also to offer guidance to healthcare providers on how to improve their practices.
Preparing for an OCR Audit
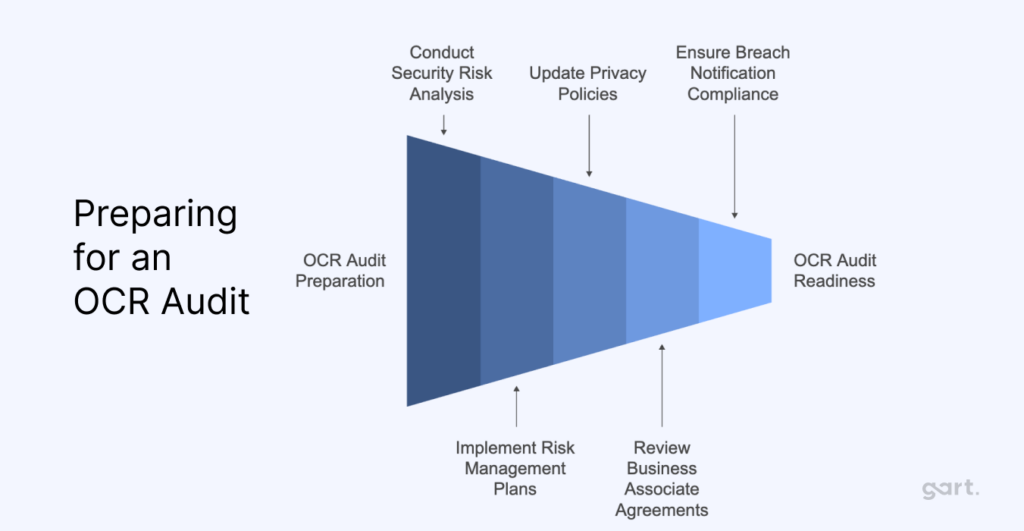
Getting ready for an OCR audit means being proactive and showing you have the right policies and procedures in place for HIPAA and HITECH compliance. Here’s how healthcare providers can prepare:
Step 1: Conduct a Security Risk Analysis
The HIPAA Security Rule requires covered entities and business associates to perform a risk analysis to find weaknesses in handling Protected Health Information (PHI). This analysis should cover:
- How PHI is stored, shared, and accessed.
- Potential risks to PHI security.
- Steps to reduce these risks.
This is especially important for those in the Meaningful Use program, which requires an annual risk analysis. Make sure PHI is encrypted when stored and sent, using tools like firewalls and VPNs to block unauthorized access.
Step 2: Implement Risk Management Plans
After the risk analysis, create a risk management plan to address vulnerabilities. Have a contingency plan ready to respond to data breaches, natural disasters, or system failures that could impact PHI.
Step 3: Update Privacy Policies
Keep your Privacy Rule policies current, including:
- Procedures for patient access to their health information.
- Rules for using and sharing PHI.
- An updated Notice of Privacy Practices (NPP) to inform patients of their rights.
Step 4: Review Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
If a contractor or vendor handles PHI, ensure there’s a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) in place. This holds them accountable for protecting PHI and outlines their responsibilities in case of a breach.
Step 5: Ensure Breach Notification Compliance
The Breach Notification Rule requires notifying affected individuals, HHS, and sometimes the media if a data breach affects 500 or more people. For smaller breaches, notifications can be delayed but must still be reported annually. Make sure your breach notification procedures meet these standards.
Specific Areas of Focus for 2024 Audits
In 2024, OCR audits will continue to emphasize important compliance areas, including:
- HIPAA Security Rule: There will be a focus on risk analysis, how devices and media are controlled, encryption, and securing data during transmission.
- HIPAA Privacy Rule: Auditors will look at policies related to access to Protected Health Information (PHI), workforce training, and administrative safeguards.
- Business Associate Audits: The OCR will keep auditing business associates (BAs), especially regarding the Breach Notification Rule and their adherence to security requirements.
Preparing for CMS Meaningful Use Audits
Along with OCR audits, healthcare providers involved in the CMS Meaningful Use program will also face audits to confirm they are meeting the program’s core measures. Providers must show:
- They have adopted certified EHR technology.
- They can provide documentation that supports their claims of meeting core measures, such as giving patients electronic access to their health records.
A significant part of these audits will focus on the security risk analysis, which is a key requirement under both Stage 1 and Stage 2 of Meaningful Use.
How Gart Solutions Can Help Businesses with HITECH Act Audits
Gart Solutions offers a comprehensive suite of services designed to streamline and enhance the compliance readiness of healthcare organizations, ensuring they are fully prepared for HITECH Act audits.
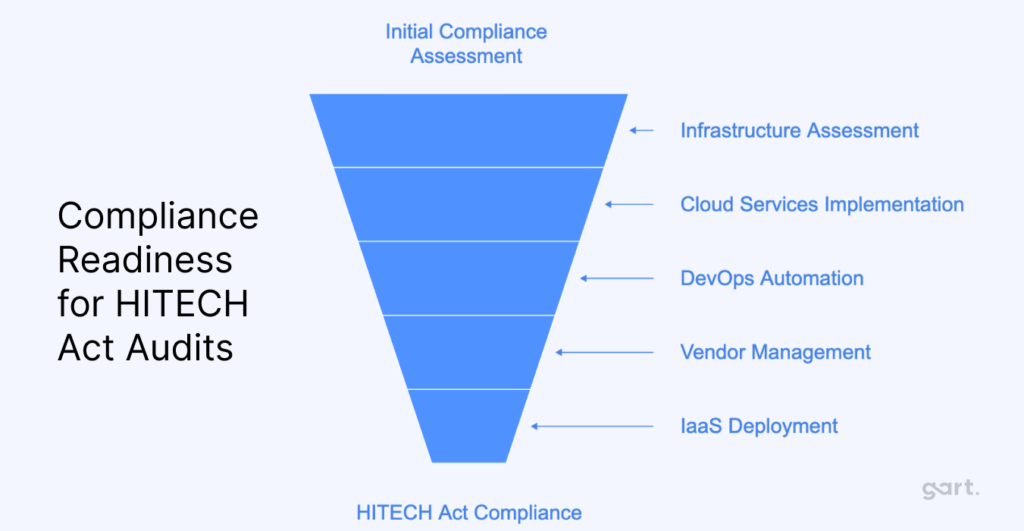
1. Infrastructure Assessment and Risk Analysis
One of the key requirements of the HITECH Act is conducting a comprehensive security risk analysis, a critical component of the HIPAA Security Rule. Gart Solutions specializes in evaluating IT infrastructure to identify vulnerabilities, gaps, and security risks related to PHI storage, transmission, and access.
Comprehensive Risk Assessments
Gart Solutions conducts detailed assessments to identify potential weaknesses in your IT systems. These assessments cover areas such as network security, endpoint protection, data encryption, and access control mechanisms.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
After identifying vulnerabilities, Gart Solutions helps you develop a risk management plan to address and mitigate these risks. This ensures that your organization is prepared to meet the audit’s security and compliance requirements.
2. Cloud Services and Data Encryption
Healthcare organizations increasingly rely on cloud-based solutions for EHR management and storage. However, maintaining HIPAA-compliant security in the cloud can be challenging. Gart Solutions offers cloud infrastructure services tailored to meet the HITECH Act’s strict data protection guidelines.
HIPAA-Compliant Cloud Solutions
Gart Solutions helps businesses implement secure, HIPAA-compliant cloud environments that ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI (electronic protected health information). By leveraging secure cloud infrastructure, your organization can securely store, manage, and process sensitive health data.
Data Encryption
Encryption is a key safeguard required by HIPAA. Gart Solutions ensures that your data is encrypted both at rest and in transit, protecting it from unauthorized access during storage or transmission. This reduces the risk of data breaches and helps your organization meet audit requirements.
3. DevOps for Compliance Automation
Preparing for HITECH Act audits can be resource-intensive, requiring constant monitoring and documentation of compliance measures. Gart Solutions’ DevOps services automate many of the tasks associated with maintaining HIPAA and HITECH compliance.
Automated Compliance Monitoring
Through DevOps automation, Gart Solutions enables continuous monitoring of your systems and networks for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and non-compliant activities. Automated alerts and reports ensure your organization can quickly address issues before they escalate.
Policy Enforcement and Logging
Gart Solutions integrates tools that enforce compliance policies in real-time, ensuring that every system change or user access is logged and documented for audit purposes. This continuous auditing capability ensures that your business is always prepared for an OCR audit.
4. Business Associate Agreements (BAA) and Vendor Management
The HITECH Act expands liability to include business associates (BAs), such as vendors and service providers who handle PHI on behalf of healthcare organizations. Gart Solutions can assist in managing your BA agreements and ensuring your vendors are HIPAA-compliant.
Vendor Risk Management
Gart Solutions helps you assess the compliance readiness of your business associates, ensuring they adhere to the same security standards as your organization. By reviewing vendor policies and procedures, you can reduce risks related to third-party breaches.
BAA Support
Gart Solutions assists with the creation, review, and management of BAAs, ensuring that all legal agreements are in place and comply with HIPAA’s requirements. This helps mitigate risk during HITECH audits and ensures that third-party vendors are accountable for PHI security.
5. HIPAA-Compliant Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
For businesses that require scalable and flexible infrastructure, Gart Solutions offers HIPAA-compliant IaaS solutions that are fully tailored to healthcare industry needs. Gart Solutions designs and deploys infrastructure environments that meet HIPAA’s physical, administrative, and technical safeguards. This includes access control, physical security, and secure backups
Conclusion: Why Choose Gart Solutions?
As the regulatory environment around healthcare data continues to evolve, being prepared for a HITECH Act audit is crucial for protecting your business and your patients. Gart Solutions provides expert guidance and technological solutions to help healthcare organizations stay compliant, secure their IT infrastructure, and confidently manage the audit process.
By leveraging our expertise in DevOps, cloud, and infrastructure services, your business can enhance its compliance posture, minimize risks, and ensure you are fully prepared for any HITECH or HIPAA audit.
Let Gart Solutions handle the technical complexities of compliance so you can focus on delivering exceptional healthcare services to your patients.
See how we can help to overcome your challenges









