Moving to the cloud is no longer just a trend; it’s a crucial strategic decision. Businesses now understand that adopting cloud solutions is not a choice but a necessity to stay competitive, resilient, and adaptable in today’s dynamic world.
The reasons for this increasing use of cloud services are practical and varied. They focus on four main goals: saving costs, scaling easily, being agile, and improving security.
Starting a cloud migration without a clear strategy can be overwhelming and expensive. This guide will help you create a successful plan for your cloud migration journey.
What is cloud migration?
Cloud migration involves transferring an organization’s data, applications, and workloads from on-premises infrastructure to cloud platforms. Businesses adopt cloud solutions to achieve flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. According to the study, 93% of organizations cite scalability and cost savings as their primary motivations for migration. The shift reduces dependence on traditional IT investments, allowing companies to allocate resources more strategically.
Cloud migration lifecycle
The cloud migration lifecycle encompasses a series of phases, from assessment and planning to execution, monitoring, and optimization.
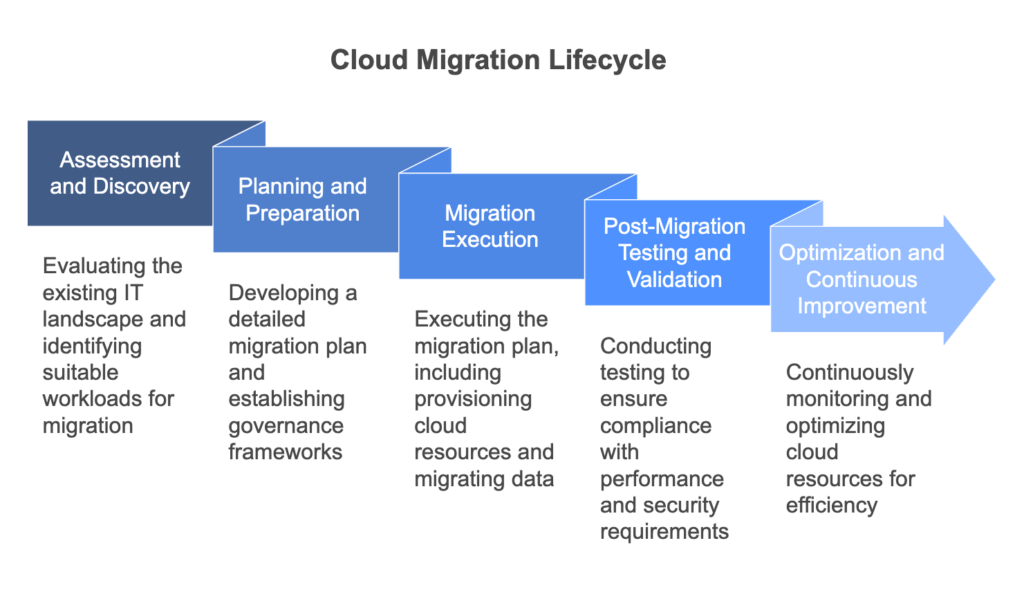
Common stages in the cloud migration lifecycle include:
1) Assessment and Discovery:
Assessing the existing IT landscape, identifying workloads and applications suitable for migration, and conducting a comprehensive analysis of dependencies, performance requirements, and compliance considerations.
2) Planning and Preparation:
Developing a detailed migration plan, defining migration strategies and priorities, estimating costs and resource requirements, and establishing governance and security frameworks to ensure a smooth migration process.
3) Migration Execution:
Executing the migration plan, including provisioning cloud resources, migrating data and applications, configuring networking and security policies, and validating functionality and performance in the cloud environment.
4) Post-Migration Testing and Validation:
Conducting thorough testing and validation to ensure that migrated workloads and applications meet performance, security, and compliance requirements in the cloud environment.
5) Optimization and Continuous Improvement:
Continuously monitoring and optimizing cloud resources, refining governance and security policies, and leveraging cloud-native services and automation tools to drive efficiency and innovation.
Here is a table outlining the steps involved in a cloud migration strategy
| Step | Description |
| 1. Define Objectives | Clearly state the goals and reasons for migrating to the cloud. |
| 2. Assessment and Inventory | Analyze current IT infrastructure, applications, and data. Categorize based on suitability. |
| 3. Choose Cloud Model | Decide on public, private, or hybrid cloud deployment based on your needs. |
| 4. Select Migration Approach | Determine the approach for each application (e.g., rehost, refactor, rearchitect). |
| 5. Estimate Costs | Calculate migration and ongoing operation costs, including data transfer, storage, and compute. |
| 6. Security and Compliance | Identify security requirements and ensure compliance with regulations. |
| 7. Data Migration | Develop a plan for moving data, including cleansing, transformation, and validation. |
| 8. Application Migration | Plan and execute the migration of each application, considering dependencies and testing. |
| 9. Monitoring and Optimization | Implement cloud monitoring and optimize resources for cost-effectiveness. |
| 10. Training and Change Management | Train your team and prepare for organizational changes. |
| 11. Testing and Validation | Conduct extensive testing and validation in the cloud environment. |
| 12. Deployment and Go-Live | Deploy applications, monitor, and transition users to the cloud services. |
| 13. Post-Migration Review | Review the migration process for lessons learned and improvements. |
| 14. Documentation | Maintain documentation for configurations, security policies, and procedures. |
| 15. Governance and Cost Control | Establish governance for cost control and resource management. |
| 16. Backup and Disaster Recovery | Implement backup and recovery strategies for data and applications. |
| 17. Continuous Optimization | Continuously review and optimize the cloud environment for efficiency. |
| 18. Scaling and Growth | Plan for future scalability and growth to accommodate evolving needs. |
| 19. Compliance and Auditing | Regularly audit and ensure compliance with security and regulatory standards. |
| 20. Feedback and Iteration | Gather feedback and make continuous improvements to your strategy. |
Pre-migration preparation: analyzing your current IT landscape
Before your cloud migration journey begins, gaining a deep understanding of your current IT setup is crucial. This phase sets the stage for a successful migration by helping you make informed decisions about what, how, and where to migrate.
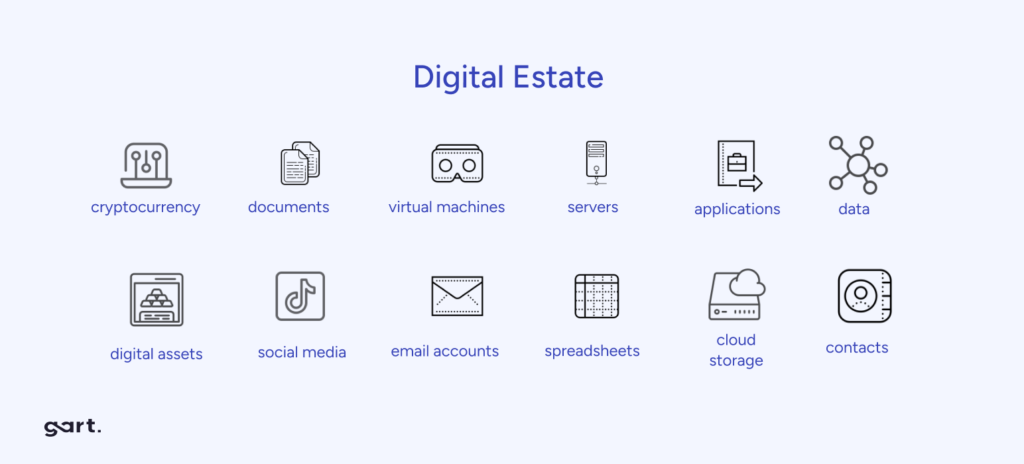
Assessing Your IT Infrastructure:
- Inventory existing IT assets: List servers, storage, networking equipment, and data centers.
- Identify migration candidates: Note their specs, dependencies, and usage rates.
- Evaluate hardware condition: Decide if migration or cloud replacement is more cost-effective.
- Consider lease expirations and legacy system support.
Application Assessment:
- Catalog all applications: Custom-built and third-party.
- Categorize by criticality: Identify mission-critical, business-critical, and non-critical apps.
- Check cloud compatibility: Some may need modifications for optimal cloud performance.
- Note dependencies, integrations, and data ties.
Data Inventory and Classification:
- List all data assets: Databases, files, and unstructured data.
- Classify data: Based on sensitivity, compliance, and business importance.
- Set data retention policies: Avoid transferring unnecessary data to cut costs.
- Implement encryption and data protection for sensitive data.
Based on assessments, categorize assets, apps, and data into:
- Ready for Cloud: Suited for migration with minimal changes.
- Needs Optimization: Benefit from pre-migration optimization.
- Not Suitable for Cloud: Better kept on-premises due to limitations or costs.
These preparations ensure a smoother and cost-effective migration process.
Choose a cloud model
After understanding cloud deployment types, it’s time to shape your strategy. Decide on the right deployment model:
- Public Cloud: For scalability and accessibility, use providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Private Cloud: Ensure control and security for data privacy and compliance, either on-premises or with a dedicated provider.
- Hybrid Cloud: Opt for flexibility and workload portability by combining on-premises, private, and public cloud resources.
- Multi-Cloud: Multi-cloud refers to the use of multiple cloud providers to host different workloads and applications. Organizations adopt a multi-cloud strategy to mitigate vendor lock-in, enhance redundancy and fault tolerance, and optimize costs by leveraging the
Choose from major providers like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and others.
Read more: Choosing the Right Cloud Provider: How to Select the Perfect Fit for Your Business
Your choices impact migration success and outcomes, so assess needs, explore options, and consider long-term scalability when deciding. Your selected cloud model and provider shape your migration strategy execution and results.
Key cloud migration strategies
With your cloud model and provider(s) in place, the next critical step in your cloud migration strategy is to determine the appropriate migration approach for each application in your portfolio. Not all applications are the same, and selecting the right approach can significantly impact the success of your migration.
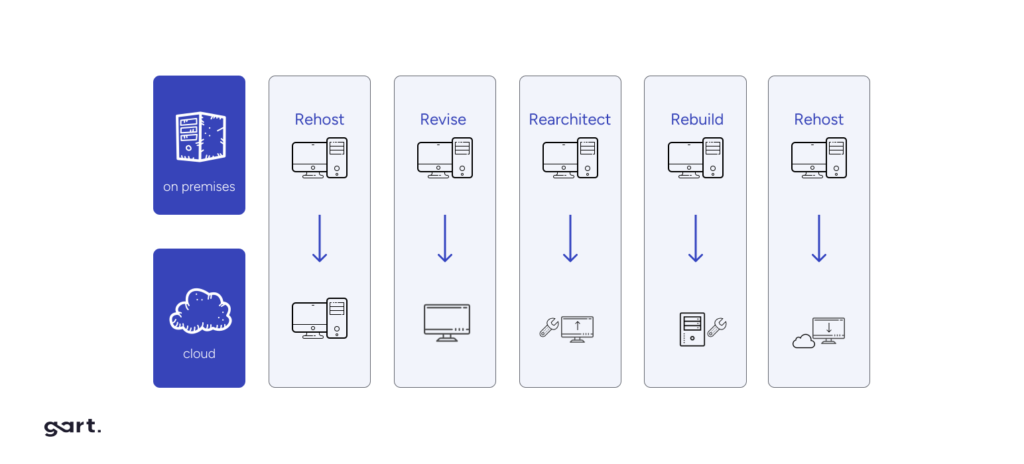
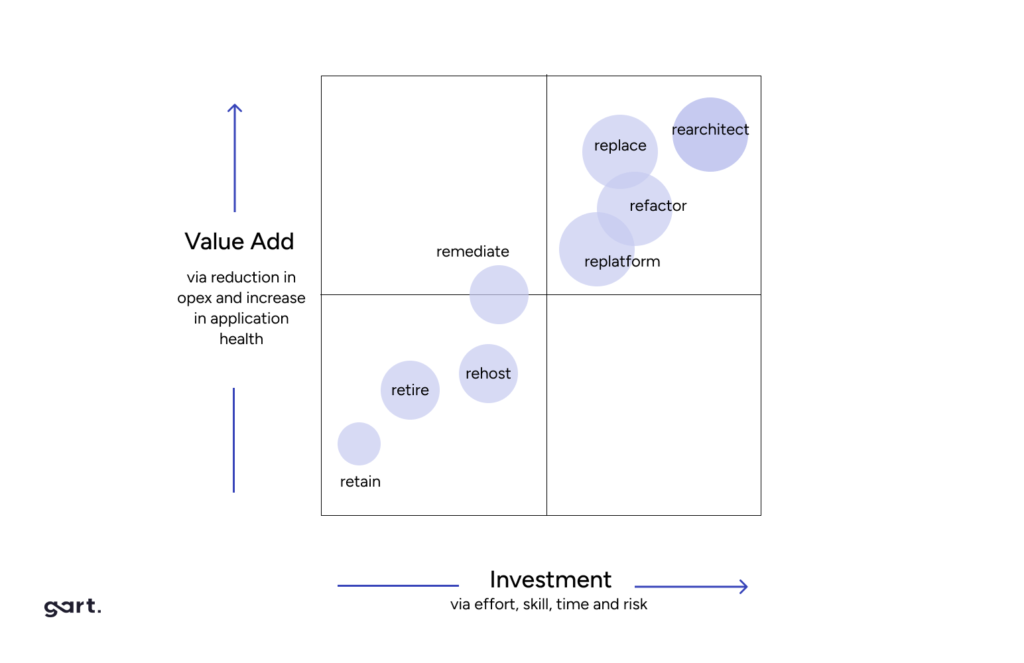
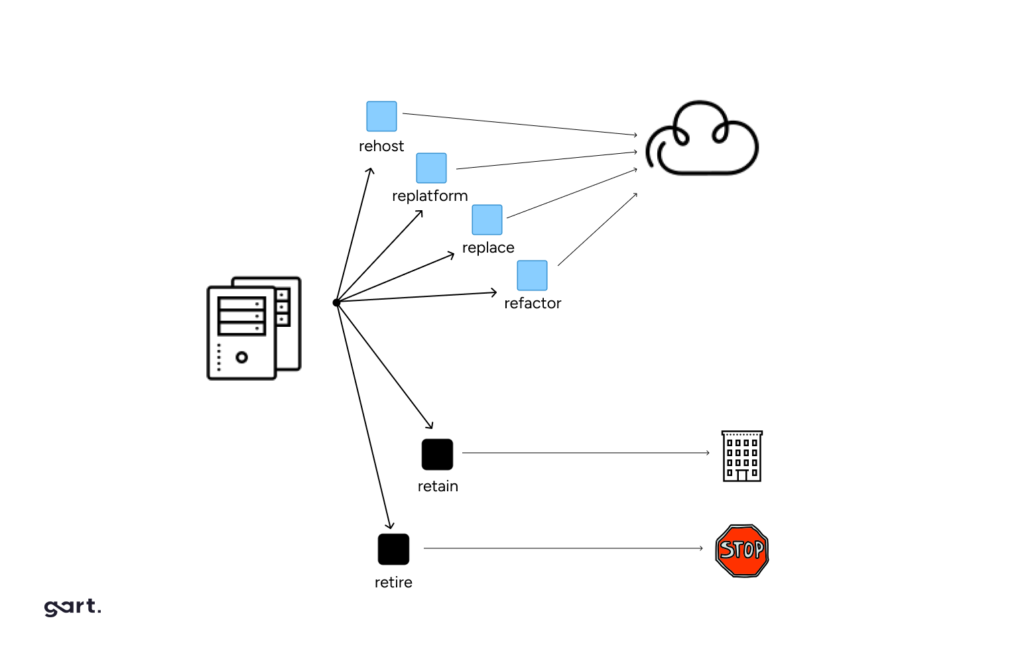
Here are the five common migration approaches and how to choose the appropriate one based on application characteristics:
Lift and Shift (Rehost)
Also known as rehosting, this is the simplest migration approach. Applications and workloads are moved to the cloud without modifications to their architecture. While cost-effective, it often requires post-migration optimization to harness the full benefits of the cloud. For example:
Rehosting involves moving an application to the cloud with minimal changes. It’s typically the quickest and least disruptive migration approach. This approach is suitable for applications with low complexity, legacy systems, and tight timelines.
- Cost Savings: Organizations pay only for what they use, reducing idle resources.
- Time Efficiency: Applications can be migrated quickly, enabling businesses to explore cloud capabilities with minimal disruption.
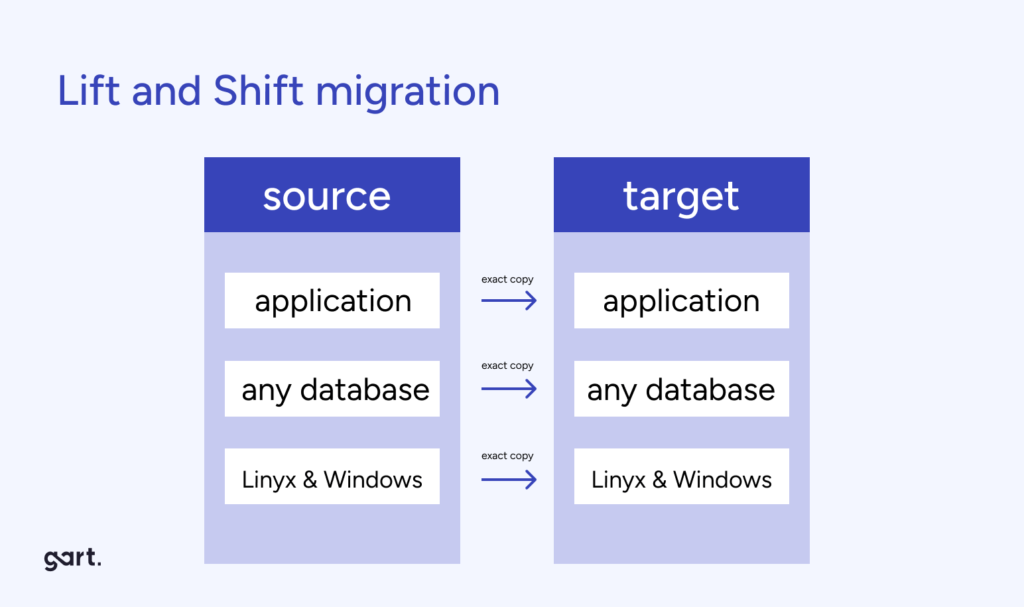
When to Choose: Opt for rehosting when your application doesn’t require significant changes or when you need a quick migration to take advantage of cloud infrastructure benefits.
Refactor (Lift Tinker and Shift)
Refactoring involves making significant changes to an application’s architecture to optimize it for the cloud. This approach is suitable for applications that can benefit from cloud-native features and scalability, such as microservices or containerization.
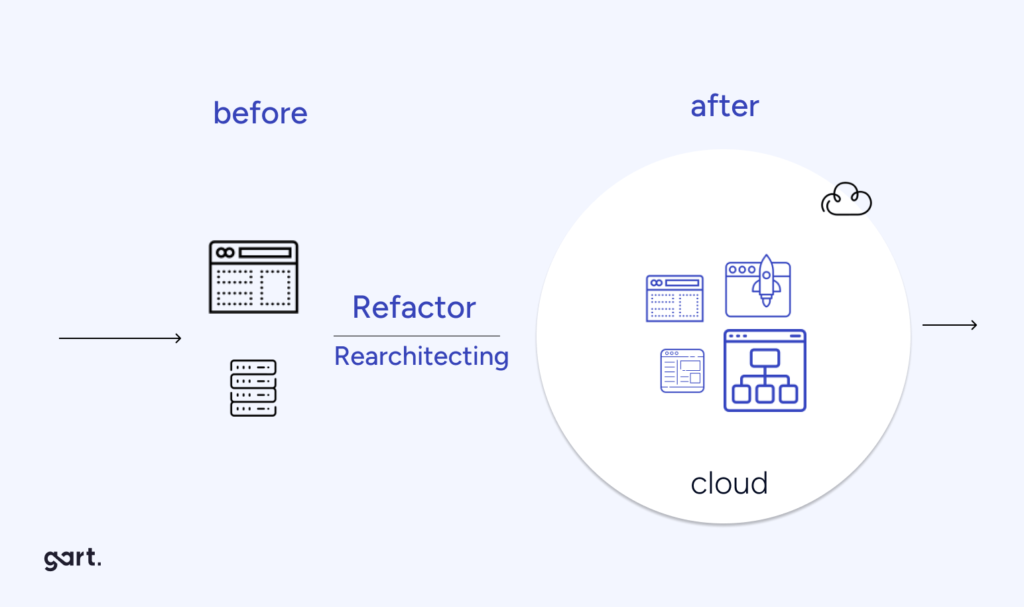
When to Choose: Choose refactoring when you want to modernize your application, improve performance, and take full advantage of cloud-native capabilities.
Rearchitect (Rebuild)
Re-architecting involves rebuilding applications to exploit cloud-native features fully. It is ideal for:
- Applications reliant on legacy technologies.
- Organizations aiming for significant agility and innovation.
- Handling data-intensive tasks through scalable hybrid cloud architectures.
Rearchitecting is a complete overhaul of an application, often involving a rewrite from scratch. This approach is suitable for applications that are outdated, monolithic, or require a fundamental transformation.
When to Choose: Opt for rearchitecting when your application is no longer viable in its current form, and you want to build a more scalable, resilient, and cost-effective solution in the cloud.
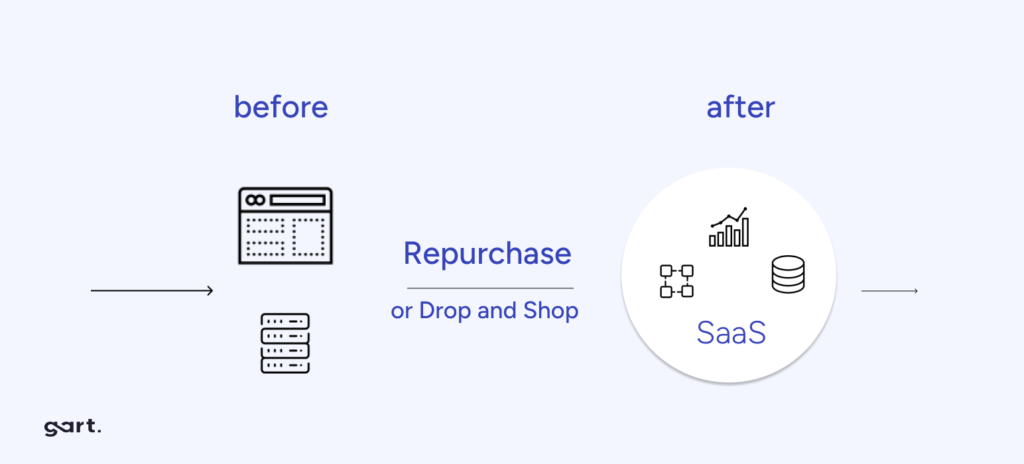
Replace or Repurchase (Drop and Shop)
Typically, solutions are implemented using the best available technology. SaaS applications may offer all needed functionality, allowing for future replacement and easing the transformation process.
Replatform (Lift, Tinker, and Shift)
This strategy involves making minimal changes to optimize the application for cloud environments. It enables organizations to:
- Leverage managed services.
- Scale resources dynamically, such as adjusting CPU throughput or reserving instances.
- Discard legacy components while modernizing infrastructure.
Replatforming involves making minor adjustments to an application to make it compatible with the cloud environment. This approach is suitable for applications that need slight modifications to operate efficiently in the cloud.
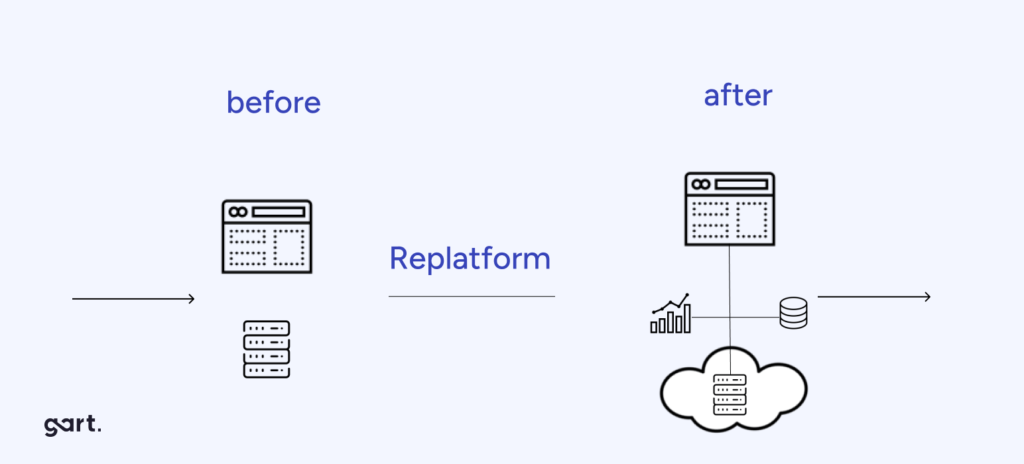
When to Choose: Choose replatforming when your application is almost cloud-ready but requires a few tweaks to take full advantage of cloud capabilities.
Retire (Eliminate)
Retiring involves decommissioning or eliminating applications that are no longer needed. This approach helps streamline your portfolio and reduce unnecessary costs.
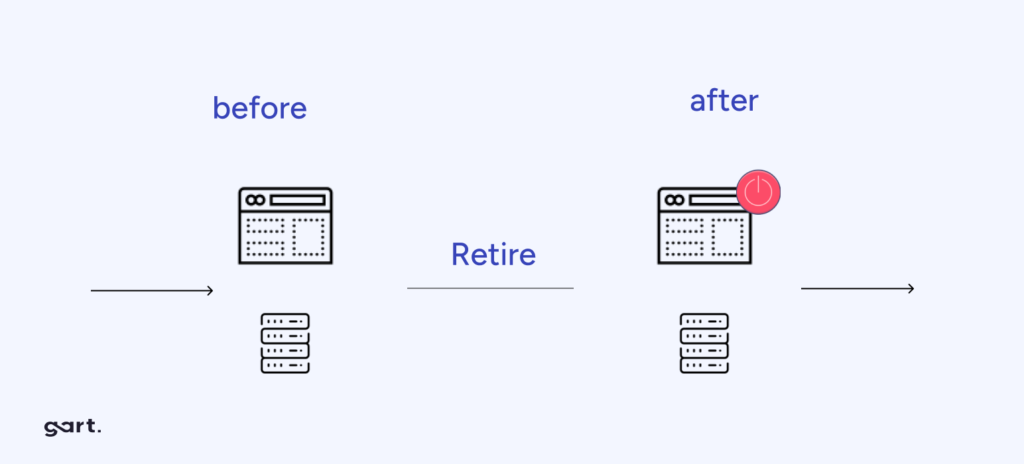
When to Choose: Opt for retirement when you have applications that are redundant, obsolete, or no longer serve a purpose in your organization.
Retain
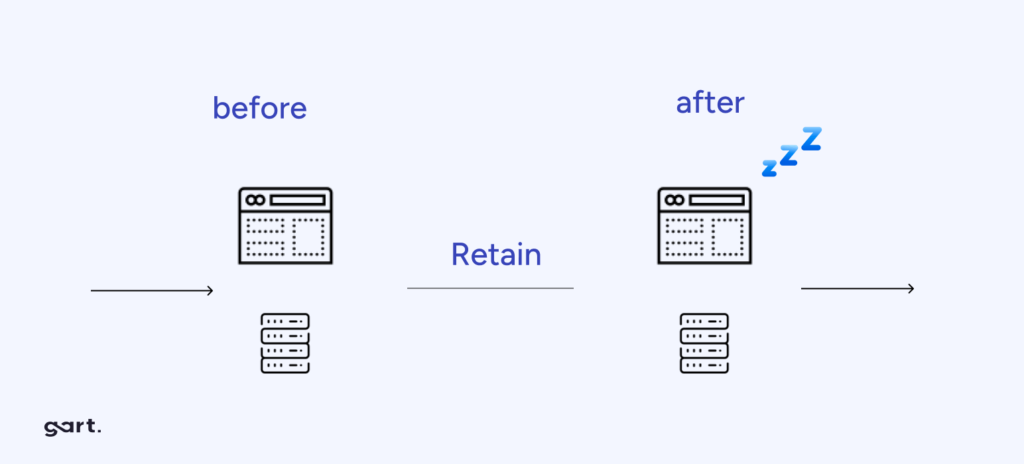
To select the right migration approach for each application, follow these steps:
Assess each application’s complexity, dependencies, and business criticality. Consider factors like performance, scalability, and regulatory requirements.
Ensure the chosen approach aligns with your overall migration goals, such as cost savings, improved performance, or innovation.
Assess the availability of skilled resources for each migration approach. Some approaches may require specialized expertise.
Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the expected return on investment (ROI) for each migration approach.
Consider the risks associated with each approach, including potential disruptions to operations and data security.
Ready to harness the potential of the cloud? Let us take the complexity out of your migration journey, ensuring a smooth and successful transition.
Challenges in cloud migration
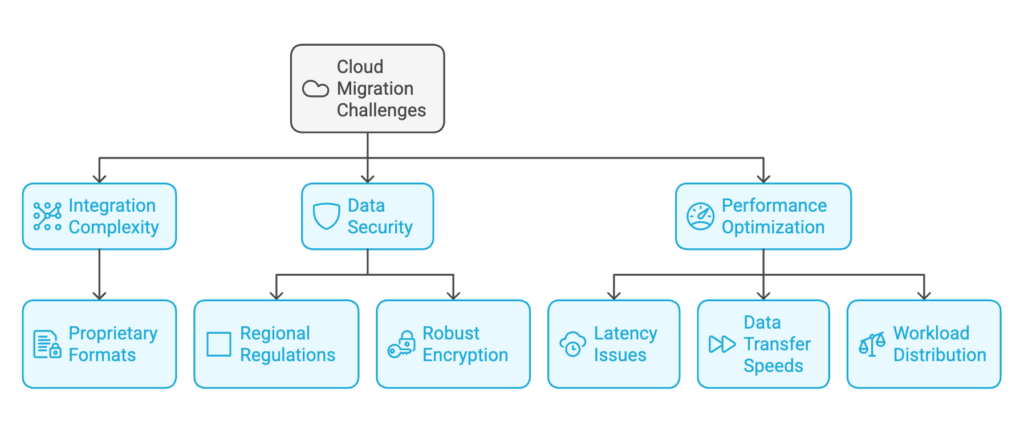
Despite its advantages, cloud migration comes with challenges:
- Integration Complexity: Legacy systems often rely on proprietary formats, making seamless integration with cloud platforms challenging.
- Data Security: Ensuring compliance with regional regulations and implementing robust encryption is critical.
- Performance Optimization: Addressing latency, data transfer speeds, and workload distribution is essential for a successful migration.
For instance, businesses leveraging Platform as a Service (PaaS) benefit from streamlined operations but must manage compatibility issues with legacy systems.
Security and compliance in cloud migration
When you’re thinking about moving to the cloud, security should be at the top of your mind. Think about it – you’re dealing with massive amounts of data, and some of it might be pretty sensitive stuff. If something goes wrong and there’s a security breach, it’s not just about losing data – your organization’s reputation could take a serious hit, and you might find yourself in hot water legally.
One of the biggest challenges is making sure only the right people can get their hands on your cloud resources. You definitely don’t want unauthorized users poking around in there, as that’s basically leaving the door open for data leaks and security nightmares.
And here’s something you can’t afford to overlook – compliance. Whether you’re in healthcare dealing with HIPAA, handling credit card data under PCI DSS, or working with European customers under GDPR, there are some serious rules you need to follow. Skip these requirements, and you could be looking at hefty fines and legal troubles. Trust me, that’s not a headache anyone wants to deal with.
Here’s a short case study for HIPAA compliance – CI/CD Pipelines and Infrastructure for an E-Health Platform
Cloud migration success stories
When considering cloud migration, success stories often serve as beacons of inspiration and guidance. Here, we delve into three real-life case studies from Gart’s portfolio, showcasing how our tailored cloud migration strategies led to remarkable outcomes for organizations of varying sizes and industries.
Case Study 1: Migration from On-Premise to AWS for a Financial Company
Industry: Finances
Our client, a major player in the payment industry, sought Gart’s expertise for migrating their Visa Mastercard processing application from On-Premise to AWS, aiming for a “lift and shift” approach. This move, while complex, offered significant benefits.
Key Outcomes:
- Cost Savings: AWS’s pay-as-you-go model eliminated upfront investments, optimizing long-term costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Elastic infrastructure allowed resource scaling, ensuring uninterrupted services during peak periods.
- Enhanced Performance: AWS’s global network reduced latency, improving user experience.
- Security and Compliance: Robust security features and certifications ensured data protection and compliance.
- Reliability: High availability design minimized downtime, promoting continuous operations.
- Global Reach: AWS’s global network facilitated expansion to new markets and regions.
- Automated Backups and Disaster Recovery: Automated solutions ensured data protection and business continuity.
This migration empowered the financial company to optimize operations, reduce costs, and deliver enhanced services, setting the stage for future growth and scalability.
Case Study 2: Implementing Nomad Cluster for Massively Parallel Computing
Industry: e-Commerce
Our client, a software company specializing in Earth modeling, faced challenges in managing parallel processing on AWS instances. They sought a solution to separate software from infrastructure, support multi-tenancy, and enhance efficiency.
Key Outcomes:
- Infrastructure Efficiency: Infrastructure-as-Code and containerization simplified management.
- High-Performance Computing: HashiCorp Nomad orchestrates high-performance computing, addressing spot instance issues.
- Vendor Flexibility: Avoided vendor lock-in with third-party integrations.
This implementation elevated infrastructure management, ensuring scalability and efficiency while preserving vendor flexibility
Future trends of cloud migration
The evolution of cloud computing will continue to redefine business strategies. Emerging trends include:
- Green IT: Sustainable cloud solutions aim to balance scalability with energy efficiency.
- AI Integration: Leveraging artificial intelligence in cloud platforms enhances automation and decision-making processes.

At Gart, we stand ready to help your organization embark on its cloud migration journey, no matter the scale or complexity. Your success story in the cloud awaits – contact us today to turn your vision into reality.
See how we can help to overcome your challenges








