The healthcare sector is gearing up for big changes, and cloud technology is quickly becoming a vital part of its IT backbone. As data demands grow and patient care and security needs become more complex, the cloud offers a scalable, efficient solution to improve healthcare operations.
In this article, we’ll dive into how cloud computing is reshaping healthcare IT—covering what it is, the main challenges, practical applications, and the game-changing potential.
Defining Cloud for Healthcare
“A cloud-based architecture can help overcome many of these challenges, turning IT from a backend support function into a strategic enabler of healthcare.”
Jason Jones
The term “cloud” is often associated with innovation but also confusion, as various industries interpret it differently. In healthcare, cloud computing refers to delivering IT services—storage, applications, and networking—through remote servers rather than traditional on-premise systems.
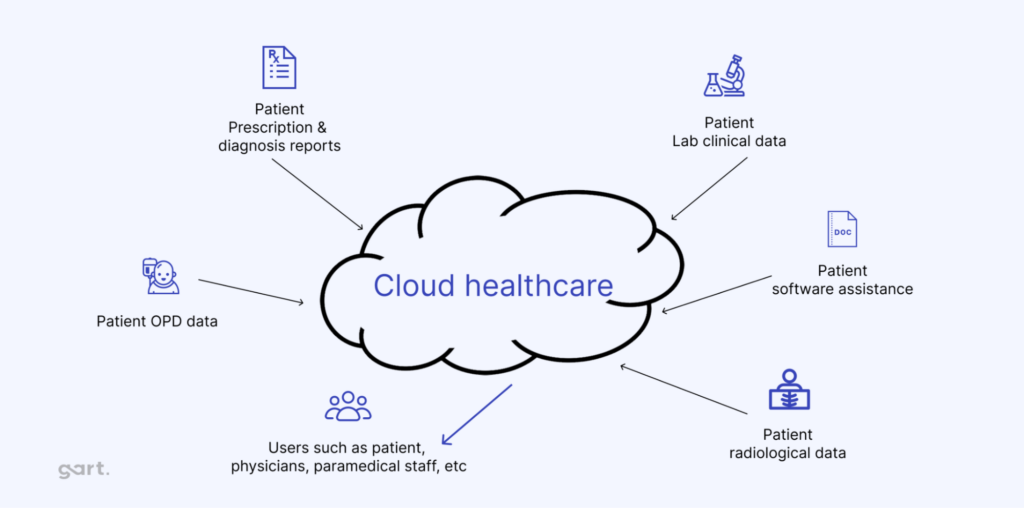
- Private Cloud: internal infrastructure managed by an organization.
- Public Cloud: external services, e.g., AWS, Azure, offering flexible, on-demand resources but with security considerations.
- Hybrid Cloud: combination of private and public, enabling flexible use for storage, scalability, and backup.
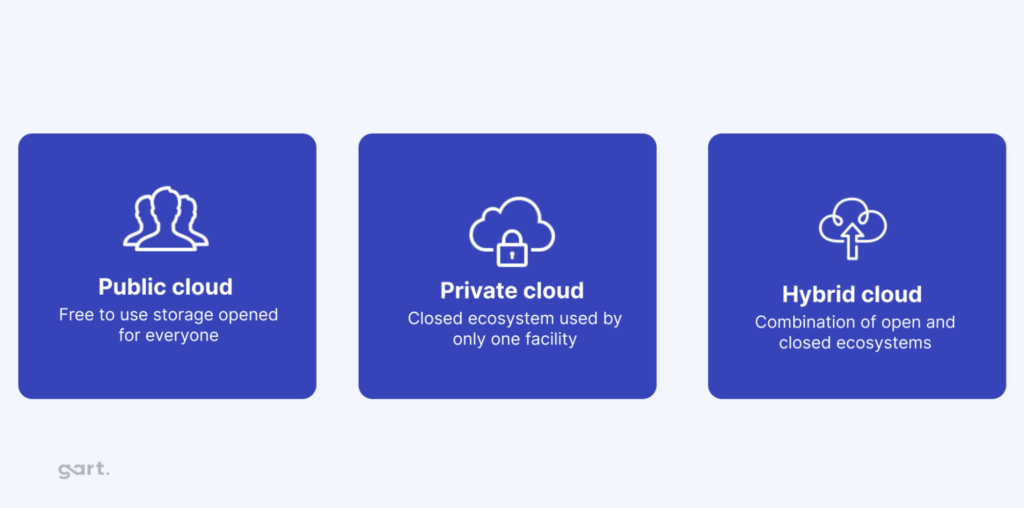
Cloud technology can be configured in several ways to meet the specific needs of healthcare providers:
Private Cloud
Managed internally within the organization, a private cloud offers control and security for sensitive healthcare data, ensuring that resources are exclusively used by the organization.
Public Cloud
“In healthcare, especially, we need systems that are horizontally and infinitely scalable based on organizational needs.”
Tony Nunes, Pharmacoepidemiologist, Assistant Professor
Hosted by third-party providers like AWS or Microsoft Azure, public clouds offer scalable resources on demand, though concerns about data privacy and security often restrict their use for healthcare’s most sensitive information.
Hybrid Cloud
“The hybrid cloud approach really has become something that’s evolving to a point where today, a majority of healthcare providers…are looking to balance between an on-prem private cloud solution and a hybrid cloud public workload solution.”
Chris Mohen
Combining private and public cloud, a hybrid model provides flexibility by allowing healthcare providers to scale with external resources while maintaining strict control over critical data.
For healthcare, the hybrid cloud often represents an ideal balance, offering an adaptable infrastructure that aligns with data privacy regulations while providing scalability. Steven Lazer, CTO of Healthcare at Dell EMC, suggests that healthcare has essentially been engaging in cloud practices for years under different labels, such as affiliate services, where remote access was given to necessary services
Lazer advocates for a “cloud-smart” approach, where healthcare organizations strategically place applications in the cloud or on-premises based on each application’s unique needs. This model enhances flexibility, scalability, and data security while supporting both traditional and emerging healthcare needs.
Key Challenges in Cloud Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, healthcare’s journey to the cloud is marked by challenges that require careful planning and robust solutions:
Data Privacy and Security
Healthcare data is a prime target for cyberattacks, so security is essential. Although cloud providers offer strong protections, healthcare organizations must ensure strict access controls and encryption to comply with regulations like HIPAA.

Legislations related to Cloud security and healthcare:
| Legal Requirements | Privacy & Data Protection | Cybersecurity | Cloud Security | Health |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | – General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | – Network and Information Security Directive (NIS Directive) | – None | – Medical Device Regulation (MDR) |
| – European Union Cybersecurity Act | – Electronic Cross-Border Health Services Directive | |||
| – Medical Device Directive (MDD) | ||||
| National | – National data protection or privacy laws | – National information and data security laws | – National cloud security laws | – National healthcare-related laws for data protection and cybersecurity |
Security remains a paramount concern as healthcare organizations adopt cloud technologies:
- Data Encryption: Both symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods are essential to secure data at rest and in transit.
- Access Controls: Multi-factor authentication and role-based access control ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive patient information.
- Compliance with Regulations: Healthcare organizations must comply with frameworks such as HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in Europe, and local privacy laws. Ensuring compliance helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
- Continuous Monitoring: Tools such as Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms are vital for identifying and responding to threats in real-time.
Costs
Setting up and managing a cloud environment can be expensive, especially for hybrid models. But as bandwidth costs drop and security improves, the long-term gains in efficiency and scalability are making cloud solutions more affordable.
“As a CFO, I no longer am over-investing in our IT environments… Cloud has allowed us to consolidate and use only what is needed, without pools of unused storage or compute capacity.”
Tony Nunes
Resistance to Change
Switching to cloud disrupts traditional IT roles, needing collaboration between IT and clinical teams. This shift requires cultural adjustments to align data access with security needs.
The bigger challenge isn’t technology—we can solve a lot of problems with technology—but rather, it’s the people and the process.
Jason Jones
Knowledge Gaps
Some organizations hesitate to adopt cloud tech due to limited understanding of how it integrates or improves their current systems. Demonstrating real-world successes can help show the cloud’s potential.
Dan Trott, a healthcare strategist with Dell EMC, highlights that while security used to be the foremost concern, now the greatest obstacle is educating stakeholders on how cloud solutions healthcare can work for them and how they can maximize cloud-based resources for better outcomes.
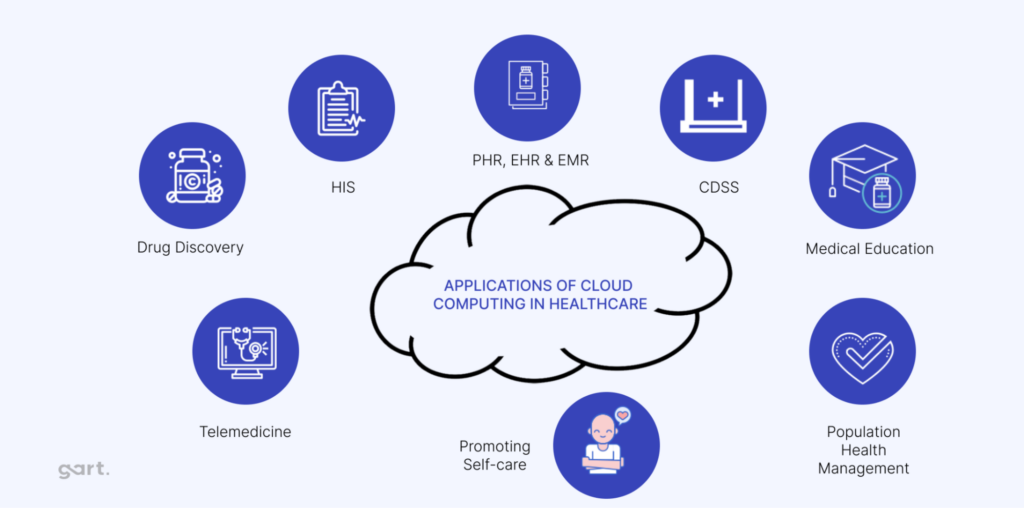
Healthcare Cloud Use Cases
The potential applications for cloud in healthcare are vast, ranging from managing data-heavy imaging systems to electronic health records (EHRs) and research initiatives.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Cloud-based EHRs enable seamless sharing of patient data among healthcare providers. Advanced encryption and access controls ensure data privacy and security.
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: Cloud technologies facilitate remote consultations and monitoring, expanding healthcare access in underserved regions. For instance, blockchain-based models enhance secure data sharing in telemedicine platforms.
- Health Management and Predictions: Predictive analytics powered by cloud computing aids in identifying health trends and managing chronic diseases. Machine learning algorithms on cloud platforms have been used for mortality predictions and early disease detection.
- Medical Imaging and Diagnostics: Cloud platforms allow the storage and analysis of high-resolution imaging data, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses.
- Collaboration and Research: Cloud services enable collaboration across healthcare providers, enhancing clinical research and innovation. Centralized platforms support multi-disciplinary teams in analyzing data efficiently.
Patient Population Analysis with Cloud Computing
Cloud computing revolutionizes patient population analysis by providing robust tools for aggregating, processing, and analyzing vast datasets from diverse demographics. Through centralized storage of electronic health records (EHRs), patient demographics, and social determinants of health, cloud platforms enable healthcare providers to identify disease patterns, predict outbreaks, and design targeted public health interventions. Advanced analytics tools hosted on cloud platforms, combined with real-time data from Internet of Things (IoT) devices, allow healthcare systems to monitor patient vitals and derive insights at scale.
The integration of Container as a Service (CaaS) and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines further enhances population health analytics. CaaS enables the deployment and scaling of containerized applications, allowing healthcare organizations to run complex analytics tools and machine learning models efficiently. CI/CD ensures these applications are continuously updated and refined, fostering innovation and reducing downtime for critical services. For instance, a population health model can seamlessly incorporate new data sources or algorithm improvements without disrupting operations.
Moreover, cloud platforms promote interoperability, consolidating data from clinics, laboratories, and pharmacies into a unified system. This integrated approach helps address disparities in healthcare delivery by enabling targeted interventions in underserved populations. Security measures, such as encryption and pseudonymization, ensure patient privacy while permitting researchers and policymakers to access de-identified datasets for broader health studies. By leveraging CaaS and CI/CD alongside cloud computing, healthcare systems can transition from reactive to proactive care strategies, improving public health outcomes with greater agility and efficiency.
Medical Imaging
“Medical imaging represents 80-85% of the total amount of data any one hospital has to manage and store.”
Dan Trott
Medical imaging is essential in healthcare, helping doctors diagnose, plan treatments, and monitor progress. As imaging tech has advanced, so has the size and complexity of imaging data, creating new challenges around storage, access, and security.
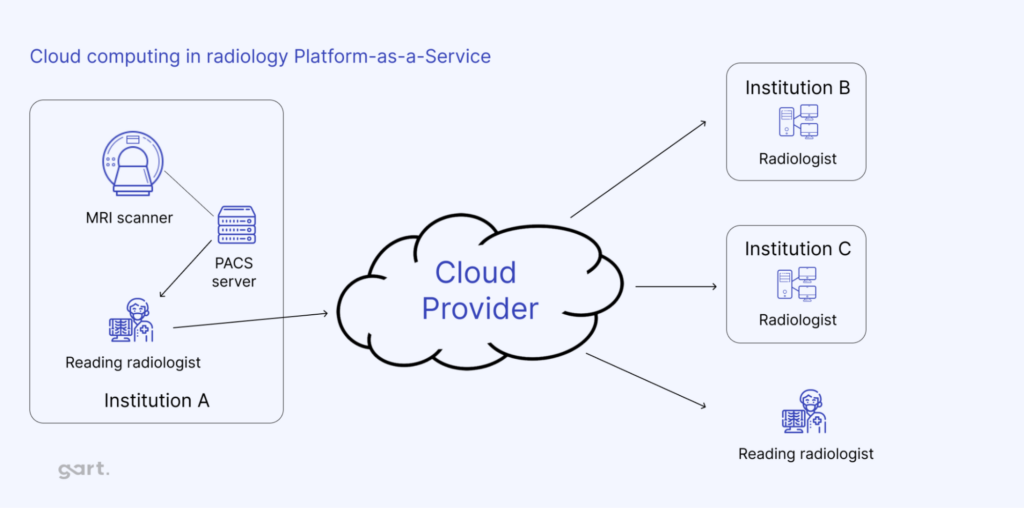
Here’s how cloud storage is transforming medical imaging:
Easier Storage & Scalability
Cloud storage handles large amounts of imaging data without the need for physical hardware. This scalability is especially helpful for smaller facilities that don’t want to invest in new servers as data needs grow.
Better Security & Compliance
Leading cloud providers offer strong security, like encryption and multi-factor authentication, often surpassing what on-site systems can do. These solutions are designed to meet healthcare regulations, making compliance easier.
Improved Data Sharing & Collaboration
Cloud-based imaging supports easy data sharing across healthcare facilities, which is crucial for patients seeing multiple providers. This ensures every provider has access to the same, up-to-date images.
Disaster Recovery & Backup
Cloud solutions automatically back up imaging data across locations, protecting against data loss from hardware failures or natural disasters.
Fast Image Access
Storing images in the cloud allows providers to access them instantly from anywhere, which is especially valuable in emergencies when quick access can impact patient outcomes.
Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are digital versions of patient charts and are a key part of modern healthcare. Unlike paper records, EHRs provide a complete, real-time, and secure way to manage patient information across different healthcare settings.
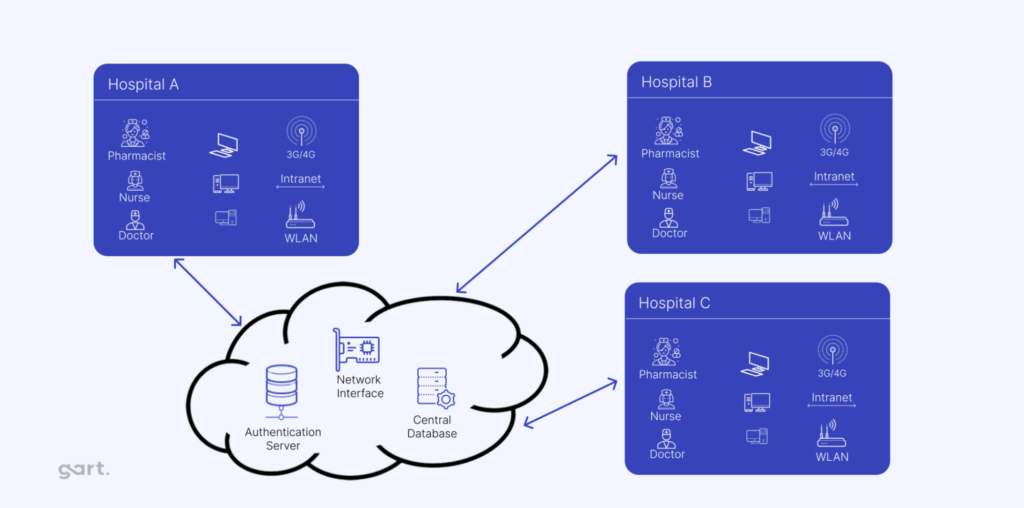
Using the cloud to store and manage EHRs is a big step forward, though it’s complicated by strict privacy laws and the need for strong security. While some providers offer hosted models, fully cloud-based EHR solutions are still a challenge due to the sensitivity of patient data. Here’s how cloud technology is helping to advance EHRs:
Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
Cloud-based EHRs are more affordable and scalable, making them ideal for smaller practices and rural healthcare providers. By storing data in the cloud, organizations can reduce physical storage needs and avoid the high costs of running their own servers and data centers.
Improved Data Sharing and Interoperability
Cloud systems allow data to be accessed from anywhere, supporting better interoperability across healthcare facilities. This enables patient data to follow the patient through different providers, ensuring consistent care no matter the location.
“What the cloud provides is a way of outsourcing that information… putting it into a very large data center that has significant cost efficiency and volume efficiency.”
Dan Trott
Enhanced Data Security
Many cloud providers offer top-level security features like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time monitoring. These protections often go beyond what traditional on-site systems provide, addressing security concerns while meeting healthcare regulations.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud-based EHR providers handle system updates and maintenance, so healthcare providers always have the latest security and functionality enhancements without disrupting their workflow. This is especially helpful for organizations without dedicated IT resources.
Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
Cloud storage includes built-in data backup and disaster recovery options, meaning patient information stays safe even if there’s a hardware failure or natural disaster. This added redundancy is essential for protecting patient data and keeping services running smoothly.
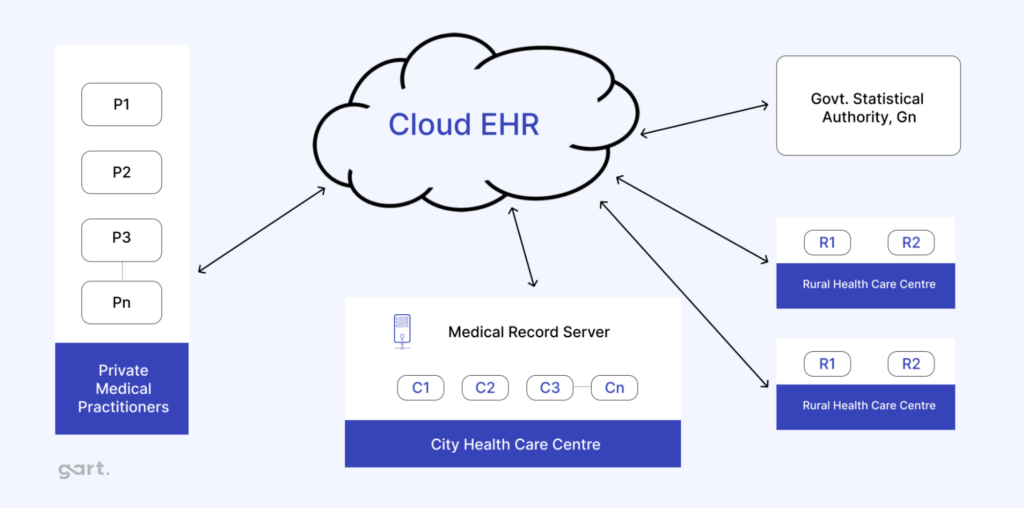
Clinical Research and Development
A cloud-based infrastructure is valuable for research-intensive organizations as it allows researchers to quickly scale resources for data processing. Data silos can be eliminated, providing a more seamless research process and helping projects launch faster. For instance, grants often require complex data environments, which can be set up more efficiently in a cloud environment.
These use cases demonstrate how the cloud supports efficiency and innovation by reducing physical storage needs and enhancing data security.
Cloud as a Disruptor in Healthcare IT
The move to cloud computing is shaking up healthcare IT and redefining traditional roles. With the cloud, healthcare providers can use “bimodal IT,” where stable systems work alongside fast, DevOps-driven setups. This approach meets both steady operational needs and the quick-paced demands of data-driven patient care.
“This concept of ‘bimodal IT’—where you can use infrastructure in a consolidated way while still delivering essential services—really enables healthcare to enhance the quality and value of the care system.”
Steven Lazer
Changing IT Roles
Cloud computing in healthcare pushes IT teams to move from specialized, separate roles (like storage or security) to a more service-oriented and collaborative approach. This shift brings IT closer to clinical workflows, enabling faster data sharing and quicker response times for patient care.
Cost Savings
Consolidating IT into unified cloud platforms cuts down on “maintenance-only” spending. For example, Dell EMC estimates significant cost reductions when switching to cloud systems, allowing more resources to go toward innovative patient care solutions.
Delivering Higher Value
With cloud solutions, healthcare IT can focus on real impact rather than routine tasks. For example, a developer environment can be set up and taken down in just 48 hours, allowing rapid innovation while keeping resources directed at high-impact areas.
“The next step of evolution we’re going to see in cloud is around the concept of a virtual private cloud—using shared infrastructure but isolated resources.“
Steven Lazer
Мirtual private clouds are the next phase, where organizations can gain the scalability benefits of public cloud while maintaining the security of private cloud through isolated resources on shared infrastructure.
Cloud computing in healthcare is rapidly evolving, with emerging technologies enhancing its capabilities:
- Zero Trust Architecture: Adopting a Zero Trust model ensures no implicit trust for any user or system, enhancing security in cloud environments.
- AI and Machine Learning: Real-time threat detection and advanced predictive models are becoming integral to healthcare cloud solutions.
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain provides decentralized and immutable data storage, enhancing trust and transparency in healthcare operations.
- Confidential Computing: Techniques to secure data during processing are gaining traction, enabling sensitive operations without exposing data to risks.
Cloud is disrupting the old IT model, building a fast, scalable, and integrated infrastructure that directly supports better care delivery.
Conclusion: The Future of Cloud in Healthcare
“Cloud really becomes a disruptor of the status quo within IT.“
Tony Nunes
As healthcare organizations continue adopting cloud solutions, they are poised to deliver more reliable, efficient, and scalable services to patients. The cloud enables them to break free from traditional IT limitations, reduce costs, enhance data security, and improve operational resilience. As demonstrated by the success at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center and other institutions, healthcare is ready to move into a new era where the cloud not only supports IT but also becomes integral to patient-centered care and operational excellence.
Through a thoughtful approach to cloud adoption, healthcare organizations can unlock new potential for innovation, efficiency, and patient satisfaction, transforming how care is delivered in a digitally connected world.
The following experts contributed valuable insights and perspectives, which were instrumental in the creation of this article:
- Tony Nunes: 22+ years in healthcare IT.
- Chris Mohen: Experience in clinical areas and transformative IT solutions.
- Steven Lazer: Global Healthcare & Life Sciences CTO – Dell Technologies at Dell Technologies
- Jason Jones: 15+ years, focusing on cloud strategies for healthcare.
- Dan Trott: Extensive experience since 2010, working with clinical and IT solutions.
See how we can help to overcome your challenges