The strategic landscape for healthcare technology organizations in 2026 is defined by a In 2026, healthcare technology organizations are reassessing long-standing infrastructure decisions, particularly around PostgreSQL HIPAA compliance and the sustainability of managed cloud databases. For over a decade, managed services—most notably AWS Relational Database Service (RDS)—have been positioned as the default option for safeguarding Protected Health Information (PHI). The value proposition was clear: reduced operational complexity, inherited compliance controls, and lower perceived regulatory exposure.
That model is now under scrutiny.
Escalating cloud costs, higher performance expectations, increasingly rigorous audits, and a far more capable DevOps landscape are prompting healthtech leaders to reevaluate whether managed databases remain the most effective solution for long-term, steady-state workloads. As a result, cloud repatriation—the strategic shift of core systems from hyperscale cloud platforms to dedicated or private infrastructure—has moved from a fringe consideration to a credible indicator of infrastructure maturity.
For organizations operating under HIPAA, the discussion has evolved. The key question is no longer whether compliance is possible outside AWS, but whether greater control, clearer auditability, and materially lower costs can be achieved through alternative architectures.
This article addresses that question by comparing AWS RDS with a hardened, self-managed PostgreSQL deployment on dedicated infrastructure, using Gart Solutions’ Compliance Wrapper as the reference model for achieving secure, auditable, and cost-efficient HIPAA compliance.
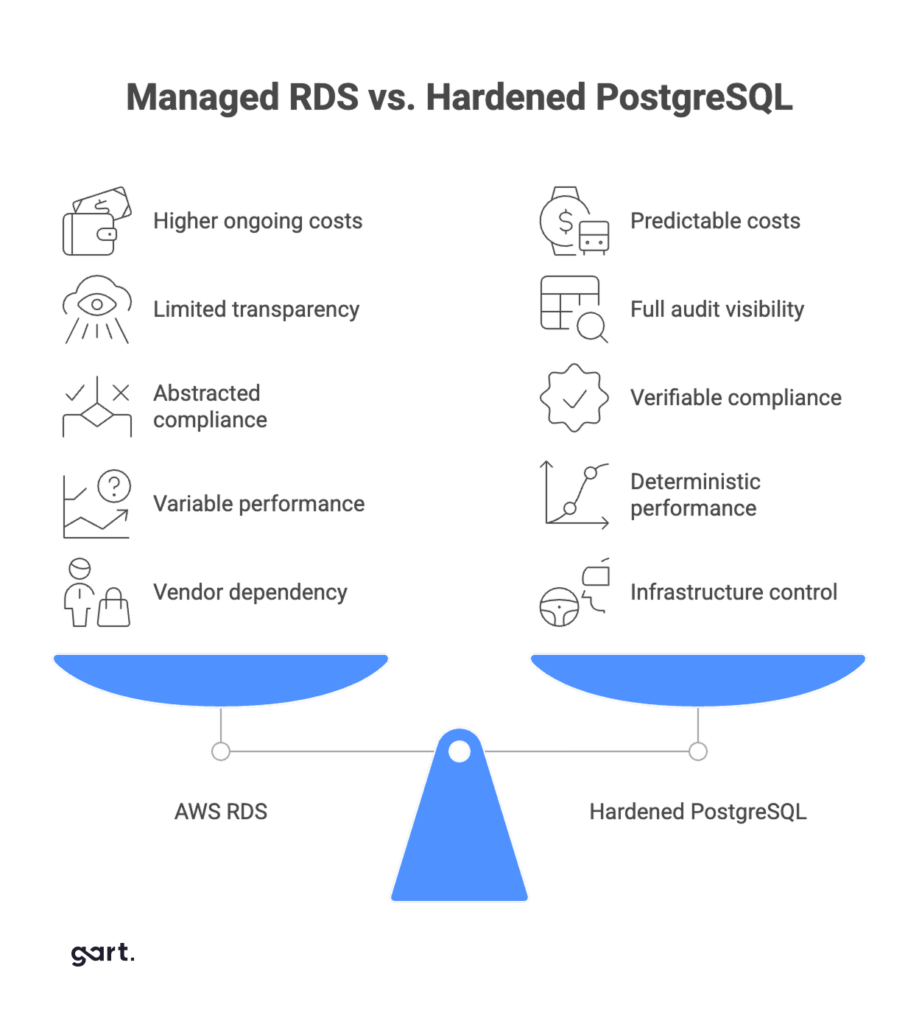
AWS RDS and PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance: The Promise and the Tradeoffs
Why AWS RDS Became the Default for PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance
AWS RDS gained dominance in healthcare and life sciences for three primary reasons:
- Shared Responsibility Model – AWS assumes responsibility for physical data centers, hardware, and underlying virtualization.
- Business Associate Addendum (BAA) – Signing a BAA transfers part of the compliance burden to AWS, reducing perceived regulatory risk.
- Integrated Security Services – Native integration with AWS KMS, CloudTrail, IAM, and VPC networking enables relatively fast HIPAA-aligned deployments.
For early-stage healthtech companies, this model provides compliance velocity: teams can focus on product-market fit instead of infrastructure engineering.
The PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance Illusion in Managed Cloud Services
However, managed services often create a false sense of security.
While AWS secures the infrastructure below the database, customers remain fully responsible for:
- IAM role design
- Network exposure and security groups
- Encryption configuration
- Database-level access control
- Application-layer authorization
Industry breach data consistently shows that misconfiguration, not hardware compromise, is the dominant cause of healthcare data leaks. In practice, RDS does not eliminate compliance risk—it merely obscures it behind abstractions.
The Cost of Abstraction
RDS introduces several structural inefficiencies:
- Virtualized storage latency via EBS
- IOPS-based billing models that penalize high-throughput workloads
- Data egress charges that silently grow with analytics, integrations, and backups
- Opaque pricing for snapshots, exports, and cross-AZ replication
As healthtech platforms scale, these inefficiencies compound into what many CFOs now call the cloud tax.
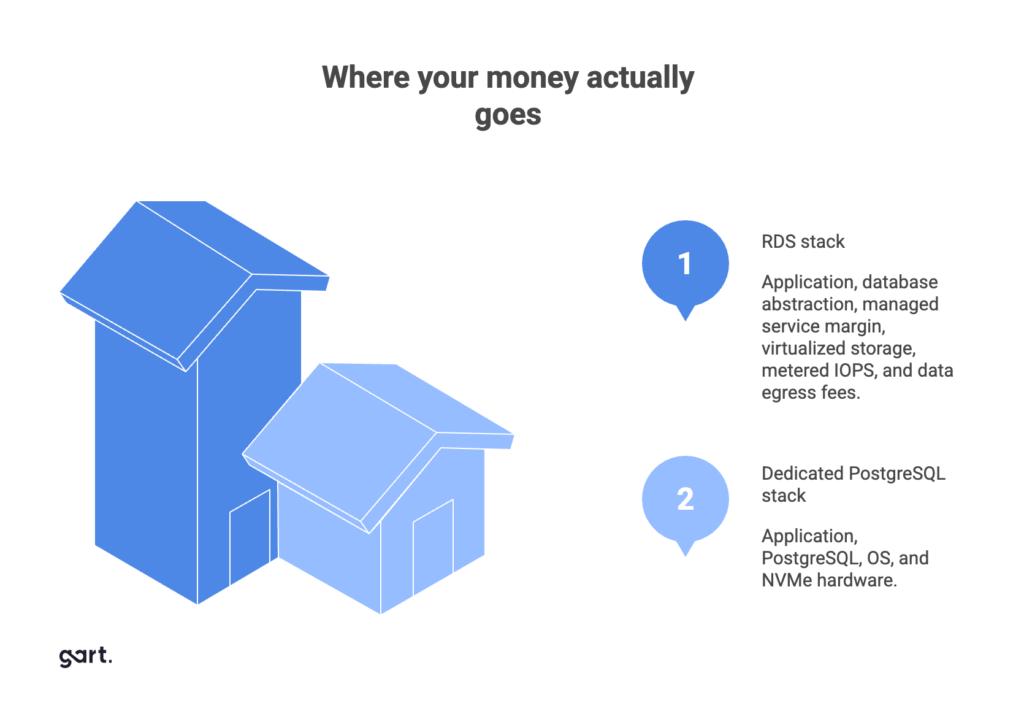
The Cost Math of PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance and Cloud Repatriation
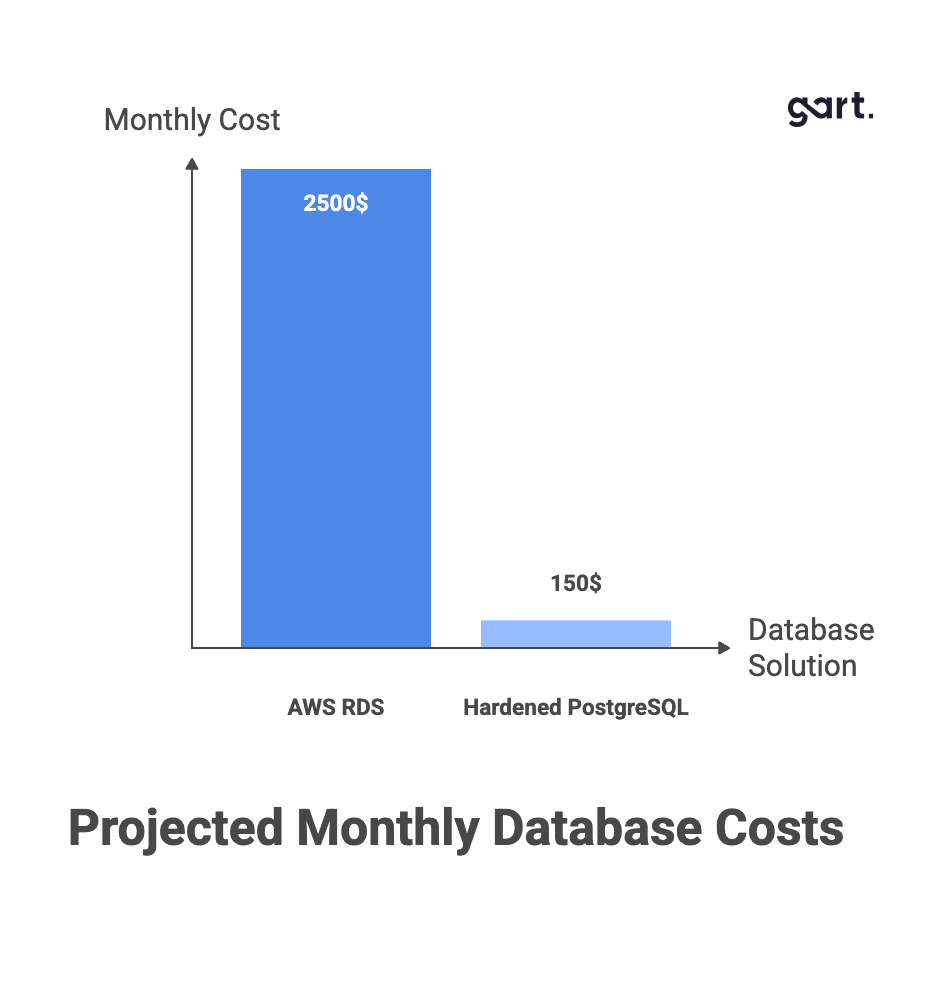
Direct Cost Comparison (Projected 2026)
| Component | AWS RDS (db.r6g.4xlarge) | Hardened Dedicated Server |
| Compute | 16 vCPU / 128 GB RAM | 16 cores / 128 GB ECC DDR5 |
| Base Cost | ~$1,518 / month | ~$66–221 / month |
| Storage (1 TB SSD) | ~$115 (gp3) | ~$10 or included |
| Data Egress (10 TB) | ~$900 | ~$10 |
| IOPS | Metered | Included (NVMe) |
| Total MRC | ~$2,533 | ~$76–232 |
| Savings | — | 90–97% |
Beyond headline pricing, RDS imposes additional costs for backup retention, snapshot exports, and cross-region replication. In a self-managed environment, these functions are implemented using open-source tools such as pgBackRest or Barman, storing backups on low-cost S3-compatible object storage or secondary disks.
The result: predictable costs with no management premium.
Performance Determinism: A Hidden Risk to PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance
Performance is not just an engineering concern—it is a clinical risk.
Healthcare systems increasingly rely on:
- Real-time patient monitoring
- Medical imaging pipelines
- AI-assisted diagnostics
- Time-sensitive clinical workflows
RDS Latency Ceiling
RDS is bound to EBS latency characteristics, typically ranging from 1–2 ms, even on provisioned IOPS volumes.
Bare Metal Reality
Dedicated servers with local NVMe storage routinely deliver:
- <200 microseconds latency
- 200,000+ IOPS per volume
This is an order-of-magnitude performance improvement—at a fraction of the cost.
For HIPAA workloads, deterministic performance reduces timeout failures, incomplete writes, and cascading application errors that can indirectly affect data integrity.
Gart Solutions’ Approach to PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance on Dedicated Infrastructure
Cloud repatriation is not a lift-and-shift exercise. Gart Solutions approaches it as a systematic reconstruction of trust, replacing managed abstractions with verifiable controls.
The Compliance Wrapper is built on three pillars.
Pillar 1: Infrastructure as Code (Terraform)
Terraform defines every infrastructure component—servers, networks, firewalls, storage—using version-controlled code. This provides:
- Immutable infrastructure
- Repeatable, auditable deployments
- Complete traceability for HIPAA audits
For healthcare platforms such as EMRS systems, Terraform enables private hardware deployments with cloud-like automation while preserving data sovereignty.
Pillar 2: Configuration Management (Ansible)
Ansible enforces a hardened baseline across OS and PostgreSQL layers:
- Disabled unnecessary services
- Mandatory Access Control (SELinux/AppArmor)
- Kernel-level filtering and eBPF controls
- PostgreSQL hardening (SCRAM-SHA-256, restricted listen addresses)
- pg_audit-based database activity logging
Every configuration is reproducible, reviewable, and continuously enforced.
Pillar 3: Secrets Management (HashiCorp Vault)
Vault replaces AWS KMS with:
- Centralized secret storage
- Encryption-as-a-service
- Fine-grained access control
- Full audit trails for every key operation
Unlike cloud KMS services, Vault offers complete transparency, a critical advantage during regulatory reviews.
Mapping Hardened PostgreSQL to HIPAA Technical Safeguards (PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance in Practice)
HIPAA §164.312 defines five technical safeguard categories. A hardened PostgreSQL deployment addresses each with precision.
Access & Authentication Controls
- Unique user roles (no shared accounts)
- LDAP/Kerberos integration
- SCRAM-SHA-256 authentication
- Idle session timeouts
- Row-Level Security (RLS) for tenant isolation
RLS is particularly important for multi-tenant healthtech platforms, acting as an internal firewall against cross-tenant data exposure.
Audit Controls
Using pg_audit with real-time streaming into a SIEM provides granular visibility into:
- Every DDL change
- Every data access event
- Role and permission modifications
Unlike CloudTrail, which can introduce minutes of delay, this approach enables near-instant detection.
SIEM Transparency for PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance: Wazuh vs. GuardDuty
AWS GuardDuty is powerful—but opaque and traffic-priced.
Wazuh, used by Gart Solutions, offers:
- File Integrity Monitoring (FIM)
- Security Configuration Assessment (SCA)
- Kernel, OS, application, and database visibility
- Pre-mapped HIPAA controls
- Predictable, infrastructure-only cost
| HIPAA Safeguard | AWS RDS | Hardened PostgreSQL |
|---|---|---|
| Access control | Partial | Full |
| Audit logging | Delayed | Real-time |
| Encryption evidence | Abstracted | Verifiable |
| Tenant isolation | Limited | Row-Level Security |
| Forensic readiness | Vendor-dependent | Native |
For SMEs, this transparency is often more valuable than vendor-managed intelligence.
Encryption for PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance: From Opaque to Verifiable
Encryption at Rest
Instead of EBS encryption, Gart implements LUKS2 (AES-256) with:
- TPM 2.0 hardware binding
- Argon2id key derivation
- Tamper-evident audit logs
This produces verifiable evidence of encryption—critical during HIPAA audits.
Encryption in Transit
- TLS 1.3 enforced for all database connections
- Private networking via WireGuard or IPSec
- Zero public internet exposure for inter-system traffic
Confidential Computing and PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance Beyond the Cloud
AWS Nitro Enclaves are often cited as a blocker for repatriation. In practice, modern hardware offers equivalents.
Why AMD SEV-SNP Matters
AMD SEV-SNP encrypts the entire VM memory, enabling:
- Full PostgreSQL encryption-in-use
- No code changes
- Near-native performance
For database-heavy healthcare workloads, SEV-SNP provides stronger guarantees than enclave-based approaches that require architectural refactoring.
Operational Reality of PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance: Automation vs. Myth
The belief that self-managed databases require significantly more labor is outdated.
With GitOps, Terraform, Ansible, Patroni, and HAProxy:
- Provisioning is automated
- Patching is automated
- Backups exceed RDS retention limits
- High availability mirrors Multi-AZ behavior
- Compliance reporting is continuous
The operational delta between RDS and a fully automated bare-metal stack is far smaller than most teams expect.
Case Study: PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance and Cloud Repatriation for BrainKey.ai
BrainKey.ai manages sensitive neurological imaging data and patient history.
Gart Solutions implemented:
- Terraform-driven infrastructure
- Kubernetes-based orchestration
- HashiCorp Vault for key management
- Dynamic scaling via RabbitMQ
- ELK-based compliance visibility
Results:
- 99.9% uptime
- Successful HIPAA audit
- Significant cost reduction
- Full control over data residency and security
Where Gart Solutions Can Help
Gart Solutions supports healthcare organizations at every stage of cloud repatriation and compliance transformation—without compromising delivery speed or regulatory posture.
1. HIPAA-First Architecture & Risk Assessment
We evaluate your current cloud setup and:
- identify hidden compliance risks
- map HIPAA safeguards to real controls
- define what must stay in the cloud vs. what should move
Outcome: a clear, defensible repatriation strategy aligned with business priorities.
2. Compliance Wrapper Design & Implementation
Gart designs and deploys a full Compliance Wrapper around PostgreSQL, including:
- Infrastructure as Code (Terraform)
- Automated hardening (Ansible)
- Database-level auditing and logging
- Encryption and key ownership models
- SIEM integration with HIPAA mapping
Outcome: compliance that is auditable, repeatable, and provable.
3. Secure PostgreSQL Migration & Optimization
We handle:
- zero- or low-downtime database migration
- performance tuning for bare metal and NVMe
- HA and failover design
- backup, retention, and disaster recovery strategy
Outcome: higher performance, lower cost, and operational stability.
4. Audit-Ready Documentation & Evidence
Gart prepares:
- control mappings for HIPAA §164.312
- logging and monitoring evidence
- access and encryption documentation
- audit narratives auditors can follow
Outcome: faster audits, fewer findings, less stress on internal teams.
Conclusion: PostgreSQL HIPAA Compliance as a Signal of Infrastructure Maturity
For healthtech organizations in 2026, cloud repatriation is not a retreat—it is a declaration of maturity.
The evidence is clear:
- Hardened PostgreSQL can exceed RDS in security transparency
- Costs drop by up to 90%
- Performance becomes deterministic
- Compliance becomes auditable, not assumed
By building a Compliance Wrapper around dedicated infrastructure, organizations gain control over both their economics and their regulatory posture.
The security blanket was never the cloud.
The real security is understanding and owning your infrastructure.
See how we can help to overcome your challenges