If you've been tracking the AI space lately, you've probably heard "MCP" thrown around with increasing frequency. But before we dive into why it matters for your enterprise architecture, let's clear up a small naming collision that's been causing confusion.
"MCP Server" is actually an acronym that moonlights across three different tech worlds: the Mod Coder Pack (a Minecraft modding toolkit from a simpler time), the Master Control Program (Unisys ClearPath's legacy enterprise OS), and the one that actually deserves your attention right now — the Model Context Protocol.
If you're reading this in 2026, we're almost certainly talking about the last one. Let's get into it.
From Clever Chatbot to Actual Agent: What MCP Changes
Here's the core problem with enterprise AI adoption: the models are smart, but connecting them to your systems has been a mess. You'd end up with brittle API pipelines, one-off integrations, and an AI that could discuss your business eloquently but couldn't actually do anything in it.
The Model Context Protocol fixes this. Think of it as the USB-C port of the AI world — a universal, standardized interface that gives AI agents structured, secure access to three things:
Data sources — your files, databases, knowledge bases
Actionable tools — APIs, search engines, business logic
Defined workflows — step-by-step instructions for executing complex tasks
The result? An AI that doesn't just respond — it acts, decides, and delivers results inside your actual infrastructure.
The Architecture: Hosts, Clients, and Servers
MCP is built on a clean three-part model, and each component has a clearly defined role.
The MCP Server is the "shopkeeper." It advertises what's available — a GitHub repository, a database, a document store — and waits for an agent to ask for what it needs. It never oversteps its announced scope.
The MCP Client (your AI agent — Claude, Copilot, or any LLM) is the operator. It negotiates which tools it needs, requests tasks, and keeps different server connections isolated so a failure in one integration doesn't cascade through the system.
The Host is the mediator — the layer that manages connections, collects context, and critically, enforces user consent before the AI executes anything consequential. Think of it as the responsible gateway between intelligence and action.
This isn't just a clever design pattern. For enterprise environments — especially regulated industries like healthcare, fintech, or critical infrastructure — this separation of duties is essential for governance, auditing, and compliance.
At Gart Solutions, this kind of architectural thinking sits at the heart of how we approach Digital Transformation. Before connecting AI agents to your systems, you need a clean, well-governed integration layer. MCP is increasingly that layer.
Three Pillars: Tools, Resources, and Prompts
MCP organizes AI capabilities into three distinct categories, each with clear security boundaries.
Tools are where the action happens. Writing to a database, calling an API, triggering business logic, creating a pull request — these are tools. Each one has a defined schema, requires user consent before execution, and is auditable. This is the category that transforms AI from analyst to operator.
Resources are the knowledge base. Read-only, context-rich, and perfect for grounding AI responses in real, proprietary data — database schemas, documentation, runtime telemetry. The hard rule: resources inform, they don't act. This clear line between "read" and "write" is what makes enterprise risk teams comfortable.
Prompts are reusable workflow templates. Instead of hoping the AI figures out the right sequence of steps for "generate a quarterly performance report from live CRM data," you define that workflow once as a prompt and reuse it consistently. Think of them as guardrails that keep AI output reliable and repeatable at scale.
Real Enterprise Use Cases
DevOps and GitOps Automation
This is where MCP has had some of its most immediate, practical impact. The GitHub MCP Server allows AI agents to traverse repositories, manage issues, review pull requests, and trigger workflows — all through natural language. Combined with tools like Jira for ticketing and Docker Hub for container management, AI agents move from observing your dev pipeline to actively orchestrating it.
Our DevOps Services team works with organizations at exactly this intersection — building the CI/CD pipelines, automation frameworks, and governance structures that make AI-assisted GitOps safe to run at scale. MCP is the protocol that makes those connections possible without creating a security nightmare.
Observability-Driven Remediation
Here's a workflow that's quickly becoming a best practice: connect your observability platform (Dynatrace, Datadog, Prometheus) to an AI coding agent via MCP. Now your runtime telemetry isn't just dashboards — it's actionable intelligence.
When Dependabot flags a vulnerability, instead of a developer manually triaging severity, the AI can query production telemetry to determine actual exposure, then automatically remediate high-priority issues within defined boundaries. It's the kind of closed-loop automation that our SRE Services team helps build — where monitoring, incident response, and continuous improvement become a single integrated workflow rather than three separate processes.
Enterprise Data Access and RAG Pipelines
MCP standardizes how AI connects to modern data infrastructure. Vector database servers (Pinecone, Weaviate) let agents store and query semantic embeddings for intelligent search. Tools like Vectara MCP and Supabase MCP provide grounded, real-time access to company knowledge. Salesforce, Slack, Notion, Google Workspace — all increasingly exposing their capabilities through MCP servers.
This is critical for Cloud Computing architectures where AI needs to pull from multiple sources — on-premises databases, cloud-native services, SaaS platforms — without you building a custom connector for each one.
Strategic Implications for Enterprise Architects
Multi-Agent Orchestration
MCP isn't limited to a single agent talking to a single server. An AI agent can negotiate connections to multiple MCP servers simultaneously — one for internal infrastructure data, another for business context, a third for execution tools — all within a single orchestrated workflow. AWS Bedrock, Azure AI, and other enterprise AI platforms are already embracing this model.
Legacy System Integration
One of the most underappreciated benefits of MCP is how it bridges the gap between modern AI capabilities and legacy infrastructure. ERPs, SCADA systems, mainframe services — these don't need to be replaced to become MCP-accessible. They need to be wrapped. Our Infrastructure Management and Migration Services teams help organizations navigate exactly this challenge — preserving decades of business logic while making it available to next-generation AI workflows.
Security and Governance by Design
MCP builds security into the protocol rather than bolting it on afterward. Server isolation, host-mediated consent, the strict read/write boundary between resources and tools — these aren't optional features. They're the foundation. For organizations in healthcare, fintech, or other regulated environments, this matters enormously.
Our IT Audit Services include reviewing AI integration architectures for exactly these properties — ensuring that before your MCP-connected agents go to production, your security posture, compliance requirements, and audit trails are solid.
MCP Server Capability Reference
Building BlockFunctionSecurity ControlEnterprise ExampleToolsExecute actions with side effectsRequires explicit user consentAuto-merging PRs (GitHub), updating CRM records (Salesforce), sending alerts (Slack)ResourcesProvide read-only context for groundingRead-only access restrictionDatabase schemas (Supabase), documentation (Notion), runtime telemetry (Dynatrace)PromptsDefine reusable multi-step workflowsDeveloper/user-defined guardrailsGenerating sales reports from live data, summarizing incident timelines
The Bottom Line
The Model Context Protocol isn't just another integration spec. It's the emerging standard for how AI agents connect to enterprise systems — securely, auditably, and at scale.
For organizations investing in AI capabilities, the strategic question isn't "should we adopt MCP" but "how quickly can we build the infrastructure to support it." That means clean data access layers, governed tool boundaries, robust CI/CD pipelines, and infrastructure that can support stateful, multi-step agent workflows without sacrificing reliability or security.
That's the kind of work Gart does. Whether you're starting with an IT Audit to understand your current integration maturity, building out DevOps pipelines to support automated deployment workflows, or designing a cloud architecture that can host AI agents at scale — we help you build the foundation that makes agentic AI actually work in production.
Ready to explore what MCP-ready infrastructure looks like for your organization? Let's talk →
Gart Solutions helps businesses across healthcare, fintech, retail, and greentech achieve digital transformation through DevOps, cloud, SRE, and infrastructure services. Rated 4.9/5 on Clutch.

Healthcare organizations have quietly been sitting on a burning platform for years. The clinical world demands real-time data, AI-assisted decisions, and seamless cross-system communication. But underneath most hospitals and health plans, the foundational infrastructure hasn't meaningfully changed since the early 2000s — or in some cases, the 1990s.
In 2026, that contradiction has become a crisis. The global healthcare AI market is on track to reach $111 billion by 2030, yet the organizations expected to deploy these tools are shackled by monolithic EHR platforms, siloed care management systems, and mainframe databases that consume up to 75% of IT budgets just to keep the lights on. That leaves a mere 25 cents of every IT dollar for the digital transformation work that drives actual business outcomes.
Legacy system modernization for healthcare is no longer a forward-thinking ambition — it is a survival imperative. The organizations that master this transition will define the next era of care delivery. Those that don't risk a fate that is already visible: unsustainable operational costs, catastrophic data breaches, failed value-based care initiatives, and a workforce burning out under the weight of administrative systems designed for a different century.
This guide is for CIOs, CTOs, and healthcare IT leaders who need more than a high-level pitch — they need a technical and strategic framework they can act on.
The True Cost of Doing Nothing: A Financial Reckoning
Before mapping out a modernization path, it helps to quantify the cost of the alternative. The financial case for legacy system modernization in healthcare is no longer theoretical.
The $10.92 Million Breach
The average cost of a healthcare data breach in 2026 has climbed to $10.92 million — the highest of any industry, and nearly double the cross-sector average. Legacy systems are disproportionately responsible. Their inability to support modern encryption standards, zero-trust network architectures, or rapid patching cycles makes them the primary entry points for ransomware and data exfiltration campaigns.
The 2024 Change Healthcare cyberattack remains the defining case study: it affected 70% of US providers and payers, disrupting claim processing for weeks and causing cascading financial damage across the industry. The attack's blast radius was so wide precisely because legacy infrastructure lacked the isolation and fault-tolerance that modern architectures provide by design.
$8 Billion in Annual Operational Losses
Disconnected systems and manual workflows cost the US healthcare industry over $8 billion annually in communication delays and extended patient stays. These aren't theoretical losses. They show up in real time: a care coordinator who can't pull a patient's prior authorization history because the billing system doesn't talk to the EHR. A nurse who re-enters the same data into three separate platforms. A physician waiting for lab results that are sitting in a system with no real-time notification capability.
Claim Denial Rates That Are Bleeding Revenue
Nearly 90% of insurance claim denials are considered avoidable in 2026 — yet legacy revenue cycle management platforms continue to submit claims without the real-time analytics needed to flag errors before they reach the payer. For a mid-sized health system, recapturing even half of those denials can mean $5 million to $10 million in annual recovered revenue.
The IT Budget Trap
The 75-80% maintenance burden that legacy systems impose is self-reinforcing. Because so much capital is consumed by keeping old systems running, organizations can't invest in the modern tooling that would reduce that maintenance overhead. The result is a debt spiral that compounds with every passing year — and becomes harder to escape as the systems age further, vendors sunset support contracts, and specialized legacy developers become increasingly scarce.
Architectural Root Cause: Why Monoliths Fail Modern Healthcare
To understand why legacy system modernization for healthcare is so urgent, you need to understand what's fundamentally wrong with the underlying architecture.
Most legacy healthcare platforms — clinical, billing, scheduling, and care management systems alike — were built as monolithic applications: a single, tightly-coupled codebase where the user interface, business logic, and data layer are woven together inseparably. This architecture made sense in the era of on-premises servers and predictable, batch-driven workflows. It is profoundly ill-suited to the distributed, high-frequency data environment of modern healthcare.
The problem with monolithic systems isn't just performance. It's structural fragility. When a patient portal update goes wrong in a monolithic EHR, it doesn't just take the portal offline — it risks taking the entire clinical record system with it. Every component depends on every other component, which means the blast radius of any single failure expands to encompass the whole.
For high-throughput healthcare systems in 2026 — processing millions of daily events from labs, pharmacies, wearables, and telehealth platforms — this architectural model isn't just inefficient. It's clinically dangerous.
The Modern Alternative: Microservices, Containers, and Kubernetes
The architectural answer to the monolith problem is microservices: decomposing applications into small, independent services that each handle a specific business function and communicate with one another through standardized APIs. A Kubernetes-orchestrated microservices environment is now the operational gold standard for healthcare IT organizations undertaking legacy system modernization.
Why Kubernetes Is Mission-Critical for Healthcare
Kubernetes, the open-source container orchestration platform, offers healthcare organizations three capabilities that directly address the limitations of legacy infrastructure:
Horizontal scalability. A telehealth platform handling 500 simultaneous video consultations requires fundamentally different computational resources than it does at 3 AM on a Tuesday. Kubernetes automatically scales service instances up during peak hours and down during low-volume periods — optimizing cloud spend without sacrificing performance or availability.
Fault isolation and self-healing. When a specific microservice fails — say, the appointment scheduling module — Kubernetes automatically restarts it without cascading that failure to adjacent systems. The radiology viewer keeps working. The billing engine keeps processing. Clinical care continues. This is the exact opposite of what happens in a monolithic architecture.
Hybrid cloud integration. Healthcare data is governed by strict regulatory requirements that make a wholesale move to public cloud impractical for many organizations. Kubernetes enables a hybrid model: sensitive PHI can be retained in on-premises secure zones or private cloud environments, while computationally intensive AI workloads — imaging analysis, predictive modeling, NLP processing — are offloaded to AWS, Azure, or GCP.
What the ROI Actually Looks Like
Gart Solutions' real-world migrations from legacy EC2-based infrastructure to consolidated Kubernetes clusters have demonstrated a 45% reduction in overall infrastructure costs, while simultaneously increasing deployment frequency from four releases per year to multiple releases per week. That ratio — dramatically lower cost paired with dramatically higher delivery velocity — is the core value proposition of cloud-native architecture for healthcare.
The Seven-R Framework: A Decision Matrix for Every Application in Your Portfolio
Legacy system modernization for healthcare doesn't mean rebuilding everything from scratch. A systematic portfolio analysis using the Seven-R framework allows IT leadership to match the right modernization strategy to each application's risk profile, business value, and technical state.
Retain
Not every system needs to change. Applications that are stable, low-risk, and where modernization ROI is insufficient should be retained — but never left isolated. Best practice is to encapsulate retained systems behind API gateways, enabling them to surface data to modern dashboards and workflows without exposing their internal vulnerabilities or requiring costly refactoring.
Retire
Often the most overlooked cost-saving measure in enterprise healthcare IT. Portfolios in 2026 routinely contain redundant tools — a scheduling application acquired in an acquisition five years ago, a reporting tool that was replaced but never decommissioned. Retiring these systems simplifies the environment, reduces the attack surface, and eliminates ongoing licensing costs.
Rehost (Lift and Shift)
Moving an application to cloud infrastructure without changing its architecture. Rehosting offers the fastest exit from aging data centers and can accelerate OpEx optimization by converting capital expenditure to elastic cloud spend. However, it preserves underlying architectural flaws. This strategy is best suited to applications with a defined sunset date or those that are candidates for eventual replacement.
Replatform (Lift, Tinker, and Shift)
A more strategic evolution of the rehost approach. Rather than simply moving a legacy self-managed database to the cloud, replatforming replaces it with a managed cloud-native service — Azure SQL, Amazon RDS, or equivalent. The application's core architecture is preserved, but significant operational overhead is transferred to the cloud provider, improving scalability and reducing the maintenance burden on internal teams.
Refactor
Refactoring involves restructuring the application's internal code without changing its external behavior or interfaces. For core clinical systems, this is often necessary to achieve the performance and API-first design required for real-time diagnostics and AI-assisted workflows. Refactoring reduces technical debt incrementally and positions the application for future rearchitecting without requiring a full rebuild.
Rearchitect
The transition from monolithic to microservices architecture. This is the highest-complexity, highest-reward path in the Seven-R framework. In practice, Gart Solutions typically implements this using the Strangler Pattern: individual functionalities — patient scheduling, lab results interface, billing engine — are gradually extracted from the monolith and replaced with independent microservices. This approach eliminates the "big bang" deployment risk that has sunk many large-scale healthcare IT projects.
Rebuild
Reserved for systems that are genuinely beyond saving — applications so technically compromised that refactoring would cost more than a ground-up rebuild. Rebuilding from scratch using modern frameworks (Spring Boot, .NET Core) ensures the resulting application is fully optimized for cloud-native deployment and avoids inheriting the architectural constraints of the original system.
Replace (SaaS)
For administrative functions — revenue cycle management, human resources, supply chain logistics — replacing a legacy in-house system with a purpose-built SaaS solution is often the most efficient path. The internal maintenance burden is eliminated entirely, and the organization inherits the SaaS provider's ongoing development investment.
FHIR, Interoperability, and the Persistent Patient Graph
Legacy system modernization for healthcare doesn't just mean moving compute workloads to the cloud. It means transforming how clinical data is structured, shared, and acted upon across the continuum of care.
The interoperability crisis that defined healthcare IT for decades is finally being resolved in 2026 through the widespread adoption of FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). More than 90% of US hospitals have now adopted FHIR as their primary standard for clinical data exchange, up from less than 40% just three years ago. FHIR enables different EHR systems to communicate via modern, web-friendly RESTful APIs — the same architectural pattern that powers consumer internet applications.
The Longitudinal Patient Record
The practical consequence of FHIR adoption is the emergence of the Persistent Patient Graph, also called the Longitudinal Patient Record. Unlike legacy systems that stored data in episodic silos — one record for the inpatient stay, a separate one for the ambulatory visit, another for the pharmacy transaction — the Longitudinal Patient Record weaves together clinical notes, claims data, social determinants of health, genomic markers, and real-time wearable data into a single, continuously updated view of the patient.
This integrated view is not an academic ideal. It is the technical prerequisite for value-based care. Accurate risk adjustment, proactive care gap identification, and effective care coordination all depend on having a complete longitudinal picture of the patient — something that siloed legacy systems are structurally incapable of providing.
Solving the Semantic Interoperability Problem
Data transfer is necessary but not sufficient. The more fundamental challenge is semantic interoperability: ensuring that when one system sends a piece of clinical data to another, the receiving system understands it correctly. In practice, a single condition might be coded differently across three separate legacy systems. A medication name might appear in five different formulations depending on which formulary the prescribing system uses.
To address this, organizations undertaking legacy system modernization for healthcare are building ontology layers — invisible translation infrastructures that use standardized vocabularies (SNOMED CT for clinical terminology, RxNorm for medications, LOINC for lab results) to map concept meanings in real time as data moves between systems. This layer is what allows AI agents to safely interpret and act upon clinical data without requiring a clinician to manually reconcile conflicting terminologies.
AI Integration: From Experimental to Agentic
In 2026, healthcare AI has moved well beyond experimental chatbots and narrow diagnostic tools. The frontier is Agentic AI — systems that don't just generate text in response to prompts, but observe clinical and operational workflows, identify required actions, and execute them across multiple systems simultaneously.
What Agentic AI Actually Does in Healthcare
A concrete example: a patient is seen for a complex rheumatologic condition. Historically, the treating physician would need to manually draft a prior authorization request, pull relevant clinical notes, pre-fill insurance forms, and identify documentation gaps — a process that can take 45 minutes to two hours. An Agentic AI system can do all of this autonomously, in minutes, by accessing the relevant context from clinical notes and executing across the EHR, the billing system, and the payer portal simultaneously.
Early production deployments of agentic workflows are demonstrating 30% to 60% reductions in manual administrative work. Given that 57% of primary care practitioners reported sustained burnout in recent surveys — with administrative load as the primary driver — this isn't just an efficiency metric. It's a workforce retention and patient safety metric.
Ambient Clinical Intelligence: Giving Time Back to Clinicians
Ambient intelligence represents perhaps the most transformative near-term application of AI in clinical settings. Using natural language processing, ambient systems listen to patient-provider consultations and automatically generate clinical notes, suggest diagnostic codes, and identify care gaps — without requiring any additional input from the clinician beyond the conversation they were already having.
The documented time savings are significant: clinicians using ambient documentation technology save approximately 20% to 26% of their total documentation time. At a per-physician value of approximately $13,000 in additional revenue capacity annually, the ROI of ambient AI compounds quickly across a large employed physician group.
This capability is only available on modern, cloud-native infrastructure. Legacy systems — with their batch-processing architectures and limited API surface areas — cannot support the real-time, bidirectional data flows that ambient intelligence requires.
Predictive Analytics: From Reactive to Proactive
Predictive analytics has matured from a pilot project category into an operational discipline at leading healthcare organizations. The technical pipeline follows four stages: multi-source data integration, preprocessing and cleansing (which typically consumes 40% of total project time), model development, and clinical workflow integration.
The clinical outcomes are measurable. Organizations that have integrated predictive readmission models with social determinants of health data — food insecurity scores, housing stability metrics, transportation access — have achieved 50% reductions in preventable readmissions. The predictive accuracy improvement is dramatic: models using only clinical variables achieve approximately 68% accuracy in readmission prediction. Add SDOH data, and that figure rises to 84%.
For every 10% reduction in readmissions, a health system can save over $4 million annually in avoided Medicare penalties and operational costs. A typical readmission reduction implementation costing $890,000 generates an ROI of 472% over three years.
Cybersecurity and the Zero Trust Imperative
Legacy system modernization for healthcare and cybersecurity transformation are not separate workstreams — they are the same initiative. The traditional "castle and moat" security model, where a hardened perimeter was supposed to keep threats out, failed comprehensively in the era of cloud computing, remote work, and third-party vendor integrations.
The 2025 and 2026 HIPAA and HITECH regulatory updates have codified what security architects already knew: the perimeter is dead. The new requirements mandate technology asset inventories, comprehensive network mapping, multi-factor authentication, and — critically — the ability to demonstrate continuous monitoring and access governance across every system that touches PHI.
Zero Trust Architecture in Practice
Zero Trust operates on a single foundational principle: trust nothing, verify everything. Every access request — whether it originates from a clinician at a nursing station, a third-party vendor integration, or an internal microservice — is continuously verified, monitored, and governed. Identity becomes the new perimeter.
For healthcare organizations, the practical implementation of Zero Trust architecture involves several key components:
Encryption key management. Organizations must now manage their own encryption keys using tools like AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault, rather than relying on shared vendor infrastructure. This ensures that PHI remains protected even if the underlying cloud provider is compromised.
Immutable audit logs. Every interaction with protected health information must generate a timestamped, tamper-resistant audit record. In a modernized cloud-native environment, this can be automated at the infrastructure level.
Automated threat detection. AI-driven security systems that can identify and isolate ransomware or anomalous network behavior within seconds — not hours or days. This is the difference between an incident that is contained and one that affects 70% of the industry, as the Change Healthcare attack demonstrated.
DevSecOps: Security Baked In, Not Bolted On
Gart Solutions' approach to healthcare modernization integrates security practices directly into the CI/CD pipeline — a methodology called DevSecOps. Rather than treating security as a compliance checkpoint at the end of the development cycle, security controls are automated and enforced at every stage of the code delivery process.
This includes secret management using HashiCorp Vault to securely store and rotate API keys and database credentials, data masking to protect patient identities in non-production environments, and automated vulnerability scanning on every code commit. The result is a system where security posture improves with every release, rather than degrading as new features are added.
Infrastructure as Code: Compliance at Scale
One of the most underappreciated components of legacy system modernization for healthcare is Infrastructure as Code (IaC). Managing HIPAA compliance manually across a complex hybrid cloud environment — where configurations drift over time, team members make ad-hoc changes, and environments multiply — is operationally unsustainable and regulatory dangerous.
IaC, using tools like Terraform, defines the entire cloud environment — VPCs, subnets, security groups, access controls — in version-controlled scripts. This means:
The environment is compliant by design. Security policies are codified in the infrastructure definition, not applied after the fact.
Recovery is rapid and deterministic. If a server is compromised or fails, Terraform scripts can recreate the entire secure infrastructure in minutes — achieving the 99.99% clinical uptime that life-critical systems require, and reducing recovery time from days or weeks to minutes.
Audits become straightforward. Every infrastructure change is version-controlled with a complete history. HIPAA and ISO 27001 audits that once required weeks of manual documentation can be satisfied with automated reports generated from the IaC version history.
Gart Solutions' IaC implementations have demonstrated a 25% reduction in compute costs through automated shutdown of non-production assets, in addition to eliminating the configuration drift errors that create both performance degradation and security vulnerabilities over time.
Gart Solutions in Practice: Healthcare Case Studies
The outcomes described in this article aren't projections — they're results from production healthcare environments.
BrainKey.ai: Scaling Medical Imaging Infrastructure
BrainKey.ai operates a platform that analyzes MRI scans and genetic data, processing massive volumes of sensitive patient information under strict HIPAA compliance requirements. The challenge was combining that compliance posture with the elastic scalability required to handle unpredictable imaging workloads.
Gart Solutions implemented a secure network architecture using Kubernetes for container orchestration and HashiCorp Vault for secrets management. The introduction of RabbitMQ as a message queue enabled dynamic scaling: when the processing queue for new scan submissions exceeded defined thresholds, the system automatically provisioned additional compute resources. When volume dropped, those resources were released. The result was a platform that could handle demand spikes without over-provisioning — and without compromising the security controls required for a clinical-grade application.
MedWrite.ai: AI-Driven Discharge Documentation
MedWrite.ai sought to reduce the administrative burden on hospital clinicians by automating the generation of discharge letters using AI. The infrastructure challenge was building a compliant, highly available cloud environment that could support continuous software delivery without creating compliance gaps or clinical downtime.
Gart Solutions designed a cloud architecture with automated CI/CD pipelines that enforced security and compliance checks at every stage of the delivery process. The pipeline supported multiple weekly releases — a frequency that would have been operationally impossible on legacy infrastructure — while maintaining a security posture that satisfied HIPAA requirements. Clinicians gained access to progressively improved AI capabilities without service disruption.
National E-Health Platform: Cross-Institutional Data Consolidation
A national-scale project required consolidating medical histories and insurance data across a network of medical centers operating under both HIPAA and GDPR requirements. The complexity was substantial: multiple institutions, multiple data formats, multiple regulatory frameworks, and a need for rigorous data validation to prevent errors from propagating across the consolidated record.
Gart Solutions implemented infrastructure automation that standardized deployment processes across institutions and built automated data validation checks into every data ingestion pipeline. Release cycles were shortened significantly, and the reliability of cross-institutional data sharing improved measurably — creating the foundation for population health initiatives that had been impossible with the prior siloed architecture.
The Workforce Dimension: Modernization Requires Cultural Change
Technical modernization is a necessary but not sufficient condition for transformation. The "engagement crisis" in healthcare IT is real: over 40% of hospitals report Shadow AI, where clinical and administrative staff use unauthorized, consumer-grade AI tools because official enterprise systems are too slow, too limited, or too difficult to use.
Shadow AI is not primarily a security problem — it's a symptom of failed adoption. When the enterprise tools don't meet the needs of the people who are supposed to use them, those people find workarounds. Addressing this requires treating workforce enablement as a core component of the modernization roadmap, not an afterthought.
Role-Based Microlearning
Effective AI and systems training in healthcare has moved away from annual compliance lectures toward immersive, role-based microlearning designed around the realities of clinical and operational schedules. Nurses and physicians don't have blocks of uninterrupted training time. They have five-minute windows between patients. Training programs designed for those windows — short, contextually relevant, immediately applicable — achieve dramatically better retention than traditional formats.
Organizations that invest in structured AI literacy programs report an 82% skill retention rate and an average ROI of 380% on their training investment. Those numbers reflect not just reduced Shadow AI risk, but measurable gains in clinical efficiency, administrative throughput, and staff retention.
From Tool to Teammate
The cultural shift underlying successful legacy system modernization for healthcare is a reframing of what technology is. When nurses and physicians are actively involved in the rollout and evaluation of ambient listening tools, virtual nursing assistants, and AI-augmented documentation systems, they experience the technology as relieving burden — not adding it. That shift, from "technology as overhead" to "technology as a dynamic teammate," is the difference between adoption and resistance.
Eight in ten healthcare employers now cite digital toolsets as a critical factor in talent attraction and retention. In a labor market defined by persistent clinical staffing shortages, that matters.
The 2026–2030 Horizon: Ambulatory Empires and Genomic Integration
Legacy system modernization for healthcare is not a project with a finish line. It is the ongoing operational capability to evolve — and the landscape that capability must track is itself evolving rapidly.
The next five years will be defined by the accelerating fragmentation of care away from the acute hospital setting. Oncology infusion, complex wound care, and even selected surgical procedures are migrating to ambulatory surgical centers, specialty clinics, and home settings. This "Ambulatory Empire" model creates technical requirements that are simply impossible to meet with monolithic, hospital-centric legacy architecture.
Modern infrastructure must evolve to support this distributed care landscape through Virtual Command Centers — centralized monitoring hubs that maintain clinical oversight across patients in home, retail, and ambulatory settings simultaneously. These centers depend on real-time data flows from wearables and IoT devices, AI-driven alert prioritization, and the kind of low-latency, high-availability infrastructure that only cloud-native architectures can reliably provide.
Genomic integration represents the next frontier of predictive analytics: using AI to interpret genetic markers in real time, stratifying population risk, and moving toward genuinely personalized medicine at scale. Patient data volume in healthcare is growing at a rate of 1,834% CAGR when genomic and IoT streams are included. Legacy systems were not built for this volume, this velocity, or this variety of data. Modern cloud-native platforms, by contrast, are designed to scale with it.
Building Your Modernization Roadmap: Where to Start
For healthcare organizations beginning their legacy system modernization journey, the path forward involves five foundational steps:
Start with a portfolio assessment. Apply the Seven-R framework to your current application inventory. Identify the systems that are consuming the most maintenance budget, presenting the most significant security risk, and blocking the most valuable clinical or operational initiatives. This assessment establishes the prioritization logic for everything that follows.
Establish your data foundation. Before deploying AI or advanced analytics, ensure that your clinical data infrastructure supports FHIR-based interoperability and the ontology layers required for semantic consistency. AI tools are only as good as the data they operate on.
Modernize your security posture in parallel. Zero Trust architecture and DevSecOps practices are not separate workstreams — they should be implemented as core components of every modernization initiative, not retrofitted afterward.
Adopt Infrastructure as Code from day one. The compliance and operational benefits of IaC compound over time. Starting with IaC prevents the configuration drift and manual management overhead that will otherwise undermine modernization gains.
Invest in workforce enablement proportionally. Technical modernization without adoption is waste. Allocate training and change management resources at a scale commensurate with the technical investment.
Conclusion: The Cost of Standing Still Has Become Untenable
Legacy system modernization for healthcare has crossed a threshold. It is no longer a strategic option that forward-thinking organizations pursue for competitive advantage — it is the minimum viable response to an environment in which outdated infrastructure creates existential financial, operational, and clinical risk.
The organizations that lead this transformation will be defined not by the specific tools they adopt, but by the outcomes they achieve: lower readmission rates, recaptured revenue, protected patient trust, and a revitalized clinical workforce freed from the cognitive overhead of systems that were never designed for the world they're now asked to support.
At Gart Solutions, we have built our practice around making this transformation real — not just technically viable in theory, but operationally achievable in the complex, regulated, high-stakes environment of healthcare delivery. From Kubernetes migrations and CI/CD pipeline architecture to HIPAA-compliant cloud infrastructure and AI integration, we bring the engineering depth and healthcare domain expertise required to navigate this transition successfully.
The era of reinvention is not coming. It is already here.
Ready to assess your legacy infrastructure? Contact Gart Solutions to schedule a technical discovery session and portfolio modernization assessment.

Every enterprise running digital operations is carrying a hidden liability. It doesn't appear on balance sheets. It rarely surfaces in quarterly reviews. Yet it compounds quietly in server rooms, cloud environments, and configuration files — and by 2026, it is costing U.S. organizations an estimated $1.52 trillion every single year.
That liability is infrastructure debt — and it may be the most underestimated threat to your organization's ability to innovate, scale, and compete.
Unlike the day-to-day friction of software bugs or poor UX, infrastructure debt operates beneath the surface of your digital estate. It lives in outdated hardware, fragile network configurations, manually patched servers, and cloud environments that have drifted far from any documented standard. It grows silently between sprints, accumulates across cloud migrations, and reveals itself at the worst possible moments: when you're trying to scale an AI workload, when a critical system fails at 2 a.m., or when a security audit uncovers configuration gaps that have existed for years.
This guide is for the CTO who suspects their cloud environment has grown beyond control, the platform engineer frustrated by recurring incidents that trace back to the same aging components, and the IT leader who needs a language — and a framework — for communicating infrastructure risk to the board.
We will cover what infrastructure debt is, how it differs from other forms of technical debt, how to measure it rigorously, and — most importantly — how to build a sustainable strategy for managing it before it manages you.
What Is Infrastructure Debt? A Precise Definition
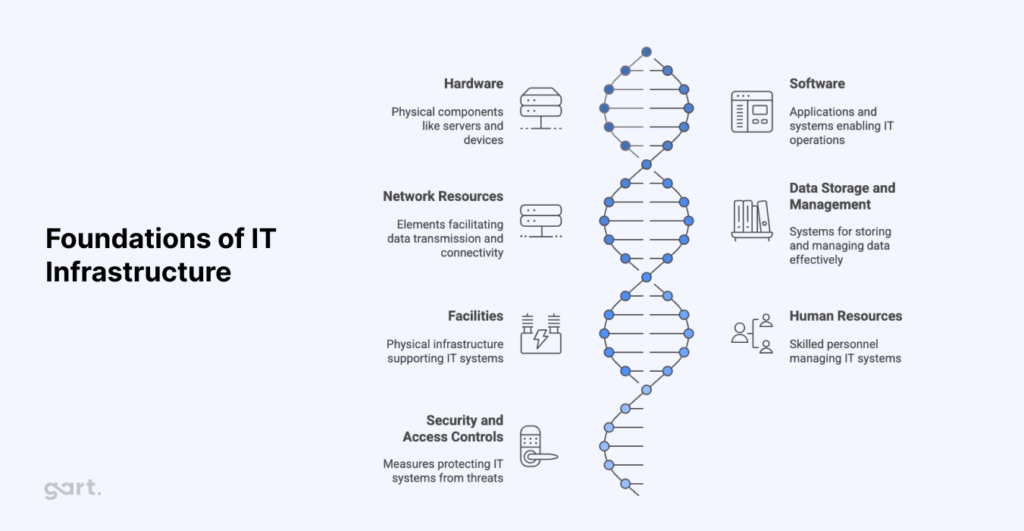
Infrastructure debt is a specific category within the broader landscape of technical debt — a term originally coined by software engineer Ward Cunningham to describe the rework costs that accumulate when speed is prioritized over quality. While technical debt as a concept typically conjures images of messy codebases and missing unit tests, infrastructure debt specifically targets the environmental layers that support software: physical and virtual servers, network topologies, storage systems, cloud configurations, and the automation pipelines that manage them.
Where code debt manifests as poor documentation or fragile logic inside a single application, infrastructure debt is systemic. It affects every service that runs on top of it. A single misconfigured Kubernetes cluster or an unpatched on-premises database server doesn't just create one problem — it creates a category of risk across every workload that depends on that environment.
At Gart Solutions, we define infrastructure debt as:
The cumulative cost — financial, operational, and strategic — of suboptimal decisions made during the design, deployment, and maintenance of the underlying systems that support software applications. These costs manifest as increased operational risk, reduced system reliability, higher maintenance overhead, and constrained organizational agility.
This definition is important because it frames infrastructure debt not as a purely technical concern but as a business risk with measurable financial consequences.
The Full Taxonomy of Digital Debt: Where Infrastructure Fits
To manage infrastructure debt effectively, it helps to understand how it relates to the other categories of liability that accumulate across modern digital organizations. Each type has a distinct domain, manifestation, and detection mechanism:
Category of DebtDomain of ImpactPrimary ManifestationDetection MechanismCode DebtApplication LayerFragile logic, poor maintainability, "code smells"Static analysis, peer reviewsInfrastructure DebtEnvironment LayerManual patches, outdated hardware, configuration driftInfrastructure audits, automated drift detectionArchitecture DebtSystemic LayerMonolithic silos, rigid integrations, scalability capsPortfolio analysis, architecture reviewsData DebtIntelligence LayerSchema mismatches, poor partitioning, replication lagsLatency monitoring, data quality auditsCultural DebtHuman LayerKnowledge silos, fear of failure, resistance to changeQualitative surveys, team dynamic observation
Infrastructure debt and architecture debt are frequently confused — and conflated — by engineering teams. The distinction matters operationally. Architecture debt arises from flawed structural decisions at the system level: fragile point-to-point integrations, duplicated platforms, monolithic designs that prevent horizontal scaling. Infrastructure debt is more immediate: it's the outdated AMI on your EC2 instance, the manually edited security group, the storage volume no one has touched in three years but everyone is afraid to delete.
Architecture debt is often invisible during standard code reviews or pull requests. It only reveals itself during critical transformation phases — such as a cloud migration or the scaling of an AI initiative — when the underlying inconsistencies prevent adoption of modern operational patterns.
How Infrastructure Debt Accumulates: The Root Causes
Understanding where infrastructure debt comes from is the first step toward preventing its accumulation. The genesis is rarely accidental — it is the predictable outcome of identifiable operational pressures.
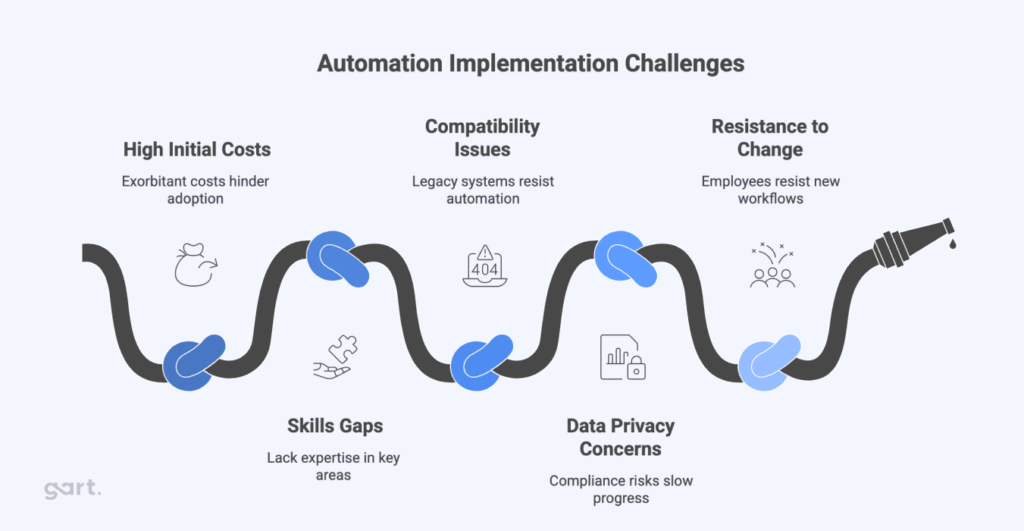
1. Time-to-Market Pressure: The Velocity-Quality Trade-off
The most pervasive driver of infrastructure debt is the tension between delivery speed and structural quality. When sprint goals demand a working data pipeline by Friday, the engineer who knows it won't scale to projected volumes in Q3 often has no choice but to ship it anyway. This is the "Velocity-Quality Trade-off" in its most common form: an organization intentionally borrows against the future to achieve short-term business objectives.
This is not inherently wrong. Taking on calculated debt to accelerate a market opportunity can be a rational strategic decision. The problem arises when the "repayment plan" never materializes — when the temporary solution becomes permanent infrastructure, and the team that built it has long since moved on.
2. The Skill and Knowledge Gap
As organizations adopt complex cloud-native technologies — Kubernetes, Terraform, service meshes, event-driven architectures — the expertise required to manage these systems often lags significantly behind their deployment. Inexperienced engineers may introduce infrastructure debt through poor Kafka broker configurations, misconfigured cloud security groups, or Terraform modules that lack the state management practices required for safe, collaborative use.
This gap is not a reflection of talent shortages alone. It is also a governance failure: organizations are deploying technology faster than they are training the people responsible for operating it.
3. Legacy System Inertia and the Brownfield Burden
Many enterprises are burdened by what practitioners call "brownfield" applications — systems that have passed through multiple development teams over decades. Each handover introduces inconsistencies in standards and design patterns, leading to fragmented, tightly coupled architectures that are extraordinarily difficult to modernize. Documentation debt — where critical system paths and API specifications are either missing or dangerously outdated — compounds this problem, causing new teams to reimplement existing functionality rather than reusing it.
The result is a digital environment where no one has a complete map, and where every infrastructure change carries an asymmetric risk: a small modification can trigger cascading failures in systems that were never properly documented.
4. "Dark Debt": The Underinvestment in Testing and Observability
Perhaps the most dangerous category of infrastructure debt is the kind that remains invisible until it isn't. Dark debt emerges from underinvestment in testing and observability infrastructure — the monitoring, tracing, and alerting systems that make the health of your environment legible. When these systems are absent or inadequate, debt hides in the complex interactions between system components, accumulating silently until a catastrophic failure forces it into view.
Dark debt is particularly common in fast-growing organizations that scaled rapidly and "bolted on" observability after the fact, or in enterprises where observability was deprioritized during cloud migrations in favor of raw lift-and-shift speed.
5. Cultural Debt: The Human Amplifier
Technical debt and cultural debt exist in a destructive feedback loop. A dysfunctional culture — characterized by unclear ownership, misaligned incentives, and a pervasive "fear of failure" — leads teams to avoid touching fragile infrastructure components. This avoidance allows debt to compound undisturbed. The resulting brittleness then reinforces team silos, as engineers become increasingly reluctant to take responsibility for systems they don't feel safe modifying.
Breaking this cycle requires more than technical solutions. It requires deliberate cultural intervention.
The Real Cost of Infrastructure Debt: By the Numbers
The financial case for addressing infrastructure debt has never been clearer — or more urgent.
The total annual cost of technical debt in the United States reached $2.41 trillion, with infrastructure debt accounting for $1.52 trillion of that figure.
This represents a near-doubling of these liabilities over the past decade, driven by the accelerating adoption of cloud-native technologies and the complexity they introduce.
Organizations managing below-average levels of technical debt demonstrate a revenue growth rate of 5.3%, significantly outperforming high-debt peers who struggle at 4.4% — a gap that compounds meaningfully over time.
Cloud waste alone — driven by unattached storage volumes, idle instances, and over-provisioned resources — can inflate cloud budgets by up to 30% annually.
Organizations that invest in remediation typically see a 300% ROI through reduced maintenance costs and increased developer throughput.
By 2026, 75% of technology decision-makers expect technical debt to rise to moderate or high severity, driven primarily by the demands of generative AI adoption.
These figures underscore a fundamental strategic reality: infrastructure debt is not a technology problem.
It is a business risk with a balance sheet.
How to Measure Infrastructure Debt: The Quantitative Framework
Moving from intuition to action requires rigorous measurement. Technical leaders who can quantify their infrastructure debt are far better positioned to prioritize remediation investments and communicate risk to executive stakeholders.
The Technical Debt Ratio (TDR)
The industry-standard formula for assessing the viability of remediation versus replacement is the Technical Debt Ratio:
TDR = (Remediation Cost ÷ Development Cost) × 100
A TDR below 5% is generally indicative of a healthy system.
Ratios exceeding 5% suggest escalating operational risk.
When TDR approaches 100%, the cost of fixing the system equals the cost of a complete rebuild — often making modernization the more cost-effective choice.
This formula provides a defensible, quantitative basis for the "fix vs. replace" conversation that infrastructure teams regularly face — and struggle to win — with finance and executive leadership.
The Seven Core Infrastructure Health Metrics
In 2025, DevOps and platform engineers focus on seven metrics to monitor structural decay and resource pressure in real time:
1. Saturation
Measures the pressure on compute resources: CPU, memory, thread pools. High saturation (consistently above 85% CPU) can lead to pod evictions and latency spikes, signaling that infrastructure is no longer appropriately sized for its workload.
2. Infrastructure Drift and Change Frequency
Tracks how often manual edits are made outside of the Infrastructure as Code (IaC) pipeline. Frequent drift is a direct measure of infrastructure debt accumulation — every manual change is an undocumented deviation from the desired state, increasing the risk of unexpected outages during routine deployments.
3. Latency Percentiles (P95 and P99)
Reveals performance bottlenecks that averages systematically hide. If your P99 latency is 10x your P50, you have significant infrastructure issues — potentially cache misses, database query delays, or network congestion — that aggregate metrics will never surface.
4. Cloud Waste Metrics
Monitors the cost and stability impact of "zombie" resources: unattached storage volumes, idle compute instances, oversized reserved capacity. These resources represent pure, recoverable infrastructure debt — paying for something that provides no value while adding management complexity.
5. Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) and Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)
Evaluates the effectiveness of the monitoring and incident response stack. High MTTR is often a direct consequence of infrastructure debt: brittle systems are harder to diagnose, and fragmented observability makes root cause analysis slow and uncertain.
6. Disk I/O and Storage Latency
Identifies "silent bottlenecks" where applications degrade due to exhausted IOPS, even when CPU usage appears normal. Storage performance issues are a classic symptom of infrastructure debt that has been deferred through repeated patching rather than architectural remediation.
7. Network Saturation and Retransmits
Monitors packet loss and congestion within Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) that lead to request timeouts. Network debt — the accumulation of undocumented routing rules, legacy security groups, and ad-hoc peering configurations — is among the most complex and dangerous forms of infrastructure debt to remediate.
DORA Metrics: The Organizational Diagnostic
Beyond infrastructure-specific metrics, the DORA (DevOps Research and Assessment) framework provides a powerful organizational diagnostic for infrastructure health:
DORA MetricHigh Performance (Elite)Low PerformanceStrategic ImplicationDeployment FrequencyMultiple times per dayOnce per month or lessHigh frequency reduces risk per releaseLead Time for ChangesLess than one hourMore than six monthsLong lead times indicate workflow bottlenecksChange Failure Rate0%–15%Above 45%High failure rates signal inadequate quality gatesMean Time to RecoveryLess than one hourMore than one weekFast recovery indicates system resilience
Organizations with high infrastructure debt consistently perform in the "low performance" tier across these metrics — particularly on Change Failure Rate and MTTR, which are most directly influenced by the quality and reliability of the underlying infrastructure.
Infrastructure as Code: The Primary Technical Remedy
The single most impactful technical strategy for preventing and remediating infrastructure debt is the adoption of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) — the practice of defining, versioning, and managing infrastructure through declarative or procedural code rather than manual configuration.
By treating infrastructure as versioned code, organizations can eliminate the "snowflake" configurations — unique, manually configured environments that cannot be reliably reproduced or audited — that define legacy environments and represent the densest concentrations of infrastructure debt.
Choosing the Right IaC Tool
IaC ToolPhilosophyLanguage SupportKey AdvantageTerraformDeclarativeHCLMassive ecosystem, mature state managementPulumiHybridPython, TypeScript, Go, C#General-purpose programming for complex logicAnsibleProceduralYAMLExcellence in configuration managementOpenTofuDeclarativeHCLOpen-source, community-driven Terraform alternativeAWS CloudFormationDeclarativeJSON, YAMLNative AWS integration and stack management
The choice of IaC tool is secondary to the discipline of using it consistently. A robust IaC strategy requires twelve operational best practices: automating the creation of IaC from existing cloud accounts, ensuring modularity through reusable templates, integrating policy-as-code guardrails, enforcing peer reviews before any infrastructure change reaches production, and making console-only changes a policy violation rather than a convenience.
The IaC Anti-Patterns That Create New Debt
IaC is not a silver bullet. Without discipline, it becomes a new source of infrastructure debt. The most common IaC anti-patterns include:
Hardcoded secrets embedded in configuration files, creating security debt that compounds with every commit
Copy-paste configurations that replicate errors across environments and make refactoring exponentially more complex
Console-only changes made during incidents that are never reflected in the IaC repository, creating drift from day one
Monolithic modules that bundle unrelated infrastructure components, making testing and rollback difficult
Missing remote state management, which allows multiple engineers to apply conflicting changes simultaneously
Policy as Code: Automating Compliance
A critical evolution of IaC practice is policy as code — the use of tools like Open Policy Agent (OPA) or Kyverno to automate the enforcement of security and compliance rules before infrastructure is provisioned. Policy as code can block unencrypted storage buckets, flag oversized instance types, and enforce tagging standards automatically, preventing entire categories of infrastructure debt from being introduced at the source.
Immutable Infrastructure: Replacing Instead of Patching
The most advanced IaC organizations have moved beyond configuration management to immutable infrastructure — an approach where components are replaced rather than patched in place. Every deployment produces a new, clean environment from a known, versioned artifact. This approach eliminates configuration drift by design, simplifies vulnerability management, and dramatically reduces the operational complexity that accumulates through repeated in-place patching.
GitOps: Making the Desired State Non-Negotiable
GitOps extends the principles of IaC by establishing Git as the single source of truth for the entire infrastructure state. In a GitOps model, every infrastructure change is a pull request. Every deployment is a reconciliation between the Git repository and the live environment. Every deviation from the desired state is automatically detected and remediated.
This model provides three capabilities that are directly relevant to infrastructure debt management:
1. Complete Audit Trail
Because every change is recorded in Git, organizations gain a complete, immutable history of their infrastructure state. This is invaluable for compliance audits, incident post-mortems, and the forensic analysis of debt accumulation patterns.
2. Automated Drift Remediation
GitOps controllers — ArgoCD, Flux, and similar tools — continuously reconcile the live state of infrastructure with the desired state defined in the repository. When drift is detected (as it inevitably will be, particularly after manual interventions during incidents), the controller can automatically revert the deviation and restore the known good state. This "self-healing" capability is essential for managing large-scale, multi-cluster environments where manual oversight is operationally impossible.
3. Security Through Pull Request Governance
By requiring peer reviews, automated policy checks, and branch protection rules before any change merges to the main branch, GitOps creates multiple opportunities to catch errors and security vulnerabilities before they reach production. Combined with secrets management platforms like HashiCorp Vault or Sealed Secrets, this model ensures that sensitive data is encrypted at rest and accessible only to authorized services during runtime.
Auditing Your Infrastructure: Where to Start
Before any remediation can begin, you need a complete and honest picture of what you have. A rigorous infrastructure audit is the foundation of effective debt management.
At Gart Solutions, our infrastructure audit process addresses four domains:
Asset Inventory and End-of-Life Assessment
A comprehensive catalog of all hardware and software assets, cross-referenced against vendor support lifecycles. End-of-life (EOL) equipment — operating systems, databases, network appliances, and cloud services past their supported maintenance windows — represents concentrated infrastructure debt because it receives no security patches and is typically excluded from vendor SLA commitments.
Network Topology Review
Evaluation of network architecture to identify single points of failure, undocumented routing rules, legacy security groups, and peering configurations that have accumulated over years of ad-hoc modification. Network topology debt is among the most dangerous to carry because network failures have the broadest blast radius of any infrastructure component.
Reliability and Resilience Assessment
Systematic testing of failover mechanisms, backup and recovery procedures, and disaster recovery capabilities. This assessment frequently surfaces "dark debt" — resilience assumptions that were documented but never tested, or that were valid at one point in the system's lifecycle but have since been invalidated by configuration changes.
Cloud Architecture Review
Validation that cloud configurations are optimized for scalability, security, and cost efficiency. This includes analysis of IAM policies, VPC configurations, storage lifecycle rules, instance sizing, and Reserved Instance coverage — all common sources of cloud-specific infrastructure debt.
Observability: Making Infrastructure Debt Visible in Real Time
Audits provide a point-in-time snapshot. Observability provides the continuous visibility required to detect infrastructure debt as it accumulates and to correlate infrastructure health with application performance and business outcomes.
Modern observability platforms connect logs, metrics, and traces into unified views that enable faster root cause analysis and more confident infrastructure changes. Leading infrastructure monitoring solutions in 2025 include Datadog, New Relic, and Grafana — each offering real-time dashboards, intelligent alerting, and root cause analysis capabilities that transform raw infrastructure data into actionable operational intelligence.
For data infrastructure specifically, data observability tools like Monte Carlo and SYNQ track "data downtime" — periods when data is inaccurate, missing, or inconsistent — using AI-powered anomaly detection to identify schema changes, volume discrepancies, and pipeline failures before they affect downstream consumers.
The key observability signals for infrastructure debt monitoring include:
Anomalous latency patterns that indicate degrading infrastructure components
Increasing error rates correlated with specific infrastructure changes or configurations
Rising resource saturation trends that signal approaching capacity limits
Drift detection alerts from GitOps controllers that indicate unauthorized manual changes
Cost anomalies that reveal zombie resources and inefficient provisioning patterns
Strategic Remediation: A Prioritization Framework
Remediating infrastructure debt is not a sprint — it is a sustained strategic program. The organizations that succeed treat it as liability management, not a one-time cleanup project.
The foundational principle of effective remediation is the 80/20 rule of technical debt: 20% of your infrastructure debt is causing 80% of your operational problems. Identifying and targeting that 20% — the highest-impact, highest-risk debt clusters — delivers disproportionate operational improvement and builds organizational momentum for deeper remediation work.
Four Proven Remediation Patterns
1. Tactical Reengineering
Upgrading systems and refactoring infrastructure "low-and-slow" — making incremental improvements that avoid downtime while delivering faster return on investment. This approach is best suited for systems with high operational dependency that cannot tolerate the disruption of a wholesale replacement.
2. Cloud-Native Refactoring
Adopting microservices, containerization, and serverless patterns to modularize functionality and isolate problematic infrastructure components. This approach addresses architecture debt and infrastructure debt simultaneously, replacing monolithic environments with loosely coupled services that can be upgraded, scaled, and replaced independently.
3. Lift-and-Shift to Modern Platforms
Transitioning away from brittle on-premises databases and aging infrastructure to managed cloud services that reduce operational overhead and eliminate entire categories of patching and maintenance debt. This approach delivers the fastest time-to-value for organizations with significant on-premises legacy debt.
4. Resource Optimization and Right-Sizing
Implementing automated right-sizing, storage lifecycle policies, and Reserved Instance planning to eliminate cloud waste and deliver immediate cost savings. This is often the fastest-returning remediation investment available and provides the budget justification for deeper, longer-cycle modernization work.
The Modernization Scorecard
For organizations with complex legacy estates, modernization scorecards provide a structured methodology for prioritizing remediation investment. By mapping debt density against business value for each system in the portfolio, enterprise architects can ensure that remediation efforts are aligned with the strategic roadmap — investing most heavily in modernizing the systems that are both highly indebted and strategically critical.
Organizational Enablement: Addressing Cultural Debt
No technical framework for managing infrastructure debt will succeed in an organization where the culture works against it. The most sophisticated GitOps workflow is useless if engineers are afraid to touch the infrastructure it manages. The most comprehensive monitoring platform is irrelevant if no one is empowered to act on what it reveals.
The Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE)
Establishing a Cloud Center of Excellence provides the multi-disciplinary governance required to scale modern infrastructure practices. A CCoE focuses on creating repeatable patterns, training engineering personnel, establishing architectural standards, and — critically — preventing the accumulation of new infrastructure debt through proactive governance rather than reactive cleanup.
Blame-Free Incident Culture
Fostering a "blame-free" culture during incident retrospectives encourages transparency and allows teams to identify the systemic root causes of failures rather than focusing on individual human error. This is essential for surfacing infrastructure debt that would otherwise remain hidden, as engineers in blame-heavy cultures routinely avoid reporting problems with systems they didn't create and can't easily fix.
Developer Experience as a Leading Indicator
Developer Experience (DX) is a powerful qualitative measure of infrastructure debt's organizational impact. When engineers spend more time fighting legacy systems than building new features — navigating brittle deployment pipelines, waiting for slow test environments, manually intervening in processes that should be automated — it manifests as friction, frustration, and ultimately burnout.
Research increasingly shows that top engineering talent actively avoids organizations with outdated technology stacks. Infrastructure debt is not just a technology problem — it is a talent retention problem and, consequently, a competitive disadvantage.
Emerging Frontiers: AI Debt and Multi-Cloud Complexity
The infrastructure debt challenge is not static. Two emerging trends are poised to significantly expand its scope and complexity.
AI and GenAI Infrastructure Debt
The rapid adoption of generative AI is introducing a new category of infrastructure debt: the accumulated cost of AI implementation shortcuts and the scaling challenges of compute-intensive AI workloads. AI places extreme demands on global infrastructure — data center power, GPU availability, networking bandwidth, and storage throughput — and organizations that scaled their AI initiatives without proportional infrastructure investment are now discovering significant structural debt in their AI platforms.
By 2025, 75% of technology decision-makers expect technical debt to rise to moderate or high severity, with AI adoption cited as a primary driver. The organizations that address this proactively — building AI infrastructure on well-governed, IaC-managed, observable foundations — will have a significant operational advantage as AI workloads continue to scale.
Multi-Cloud Complexity
While 89% of enterprises have embraced multi-cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize for specific workload requirements, this diversification increases infrastructure debt through fragmented governance and the need for specialized expertise across multiple cloud ecosystems. Each cloud provider introduces its own configuration syntax, security model, networking constructs, and operational tooling — and the gaps between them become repositories for undocumented, inconsistently managed infrastructure.
The multi-cloud networking market is projected to reach $13.14 billion by 2033, reflecting the scale of investment organizations will need to make in automation and observability capabilities that can span these distributed environments effectively.
ESG and the Carbon Cost of Infrastructure Debt
Aging, energy-inefficient data centers consume significant power and cooling resources, often falling well short of modern environmental standards. As ESG commitments move from aspirational to board-level priority, the carbon impact of legacy infrastructure is becoming a concrete driver for modernization. Organizations carrying significant on-premises infrastructure debt are increasingly discovering that their environmental compliance obligations provide an additional, non-technical justification for cloud migration and data center consolidation programs.
The Gart Solutions Approach: from Assessment to Resilience
At Gart Solutions, we approach infrastructure debt management as a strategic advisory engagement — not a one-time fix. Our framework combines the quantitative rigor of infrastructure audits and health metrics with the operational expertise to translate findings into prioritized, actionable remediation roadmaps.
Our engagements typically follow four phases:
Phase 1: Discovery and Baseline
Comprehensive infrastructure audit covering asset inventory, network topology, cloud architecture, and reliability posture. We establish baseline metrics — TDR, DORA performance tier, drift frequency, cloud waste — that provide the quantitative foundation for prioritization decisions.
Phase 2: Debt Mapping and Business Impact Analysis
Using modernization scorecard methodology, we map debt density against business value across the infrastructure portfolio. This produces a prioritized debt register that connects technical findings to business risk, enabling executive-level prioritization conversations grounded in operational reality.
Phase 3: Remediation Architecture
Development of a phased modernization roadmap aligned with the organization's strategic priorities, budget cycles, and risk tolerance. This includes IaC migration planning, GitOps implementation, observability platform selection, and cloud optimization strategies.
Phase 4: Continuous Governance
Establishment of the governance structures, tooling, and cultural practices required to prevent infrastructure debt from reaccumulating: IaC standards, policy-as-code guardrails, drift detection automation, regular audit cadences, and CCoE enablement.
Conclusion: Infrastructure Debt Is a Strategic Choice
Infrastructure debt is inevitable. Every organization operating at speed will accumulate some degree of structural compromise in its digital estate. The question is never whether you have infrastructure debt — it's whether you are managing it deliberately or letting it manage you.
The organizations that will lead their industries through the next wave of digital transformation — AI adoption, multi-cloud optimization, global scaling — are the ones that treat infrastructure debt as a strategic liability: auditing it regularly, measuring it rigorously, prioritizing its remediation through the 80/20 rule, and building the cultural and governance foundations that prevent its uncontrolled accumulation.
The technical tools exist. GitOps, IaC, policy as code, observability platforms, and cloud-native architectures have matured to the point where any organization can deploy them effectively with the right guidance. The harder work — and the more valuable work — is building the operational discipline and organizational culture that makes these tools effective over time.
In 2026 and beyond, a healthy infrastructure debt ratio will be the defining characteristic of elite technology organizations. It will determine who can move fast without breaking things, who can adopt AI at scale, and who can attract and retain the engineering talent necessary to compete.
The debt is already on your books. The question is what you do about it.
Interested in understanding your organization's infrastructure debt position? Contact the Gart Solutions team to schedule an Infrastructure Audit — the first step toward a resilient, high-performance digital foundation.